L4M5 CIPS Commercial Negotiation Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIPS L4M5 Commercial Negotiation certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Different types of relationships impact negotiations. Which source of leverage would most support the buyer?
A supplier can produce a product for $160. The supplier sells the product to their client for $240, making a profit before tax of $80 on the transaction.
What is the mark-up profit percentage earned by the supplier on this transaction?
Which of the following should be done when undertaking a reflection activity on negotiation? Select TWO that apply.
In which of the following persuasion methods, the influencer uses logics and objective reasons to persuade the others to buy into influencer's ideas?
Which characteristics are likely to feature in a partnership relationship in purchasing?
Close collaboration between supplier and buyer
Focus is on price and delivery only
Sharing of information
One-off commercial transactions
When planning a negotiation for sourcing internationally, which of the following divergent positions, and therefore potential conflict areas, should be prepared for? Select TWO that apply:
A supplier can produce a product for $160. The supplier sells the product to their client for $240, making a profit before tax of $80 on the transaction. What is the mark-up profit percentage earned by the supplier on this transaction?
Which of the following two are recognized strategies to achieve a win-lose outcome?
Making the other party lower its resistance point
Making the other party think this settlement is the best it can achieve
Employ empathy to gain mutual understanding
Using compromise and creativity tactics
The only procurement risk inherent in a distributive negotiation approach is the potential loss in the outcome. Is this statement TRUE?
Jayden works as a procurement manager for a large IT organisation. They are currently in their third round of negotiations with an increasingly frustrated software solutions provider. Ben is representing the supplier. Jayden has made eye contact in the latestmeeting to confirm his understanding of each of Ben's points. What communication technique is Jayden demonstrating?
Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI) is a Japan-based tyre manufacturer. In order to increase production, SRI is sourcing rubber from Southeast Asian firms. Which of the following micro factors are most likely to shift the balance of power to supplier? Select TWO that apply
According French and Raven's base model, which of the following are sources of personal power that can be used in commercial negotiation? Select THREE that apply.
Procurement gets involved in negotiating purchase requisitions only when there is a value analysis to ensure that only value-adding aspects are included. Is this statement true?
What are the potential sources of conflict between buyer and supplier? Select TWO.
Buying organisation may increase its leverage with suppliers by concentrating spend. Which of the following are most likely to be forms of supplier spend consolidation? Select THREE that apply.
If the price of a good is above the equilibrium price, which of the following will happen?
XYZ Ltd decides to go to market for a cleaning contract to service a number of offices. It knows that it will get a price which may, or may not, be better than the one it is currently paying. To gain leverage in the marketplace, the organisation decides to add other related services to the scope, such as gardening, security and maintenance, which increase the value of the contract. This is an example of which forms of spend consolidation?
Information generated through Purchase Price Cost Analysis can be useful to the purchaser, by helping to identify which of the following costs relating to the supplier? Select the THREE that apply.
In which of the following scenarios could you adopt a distributive-based negotiation approach?
A procurement manager is considering negotiating variable pricing for a contract duration of 12 months. Would this be the right thing to do?
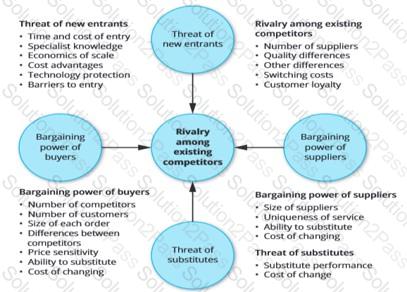 Diagram Description automatically generated
Diagram Description automatically generated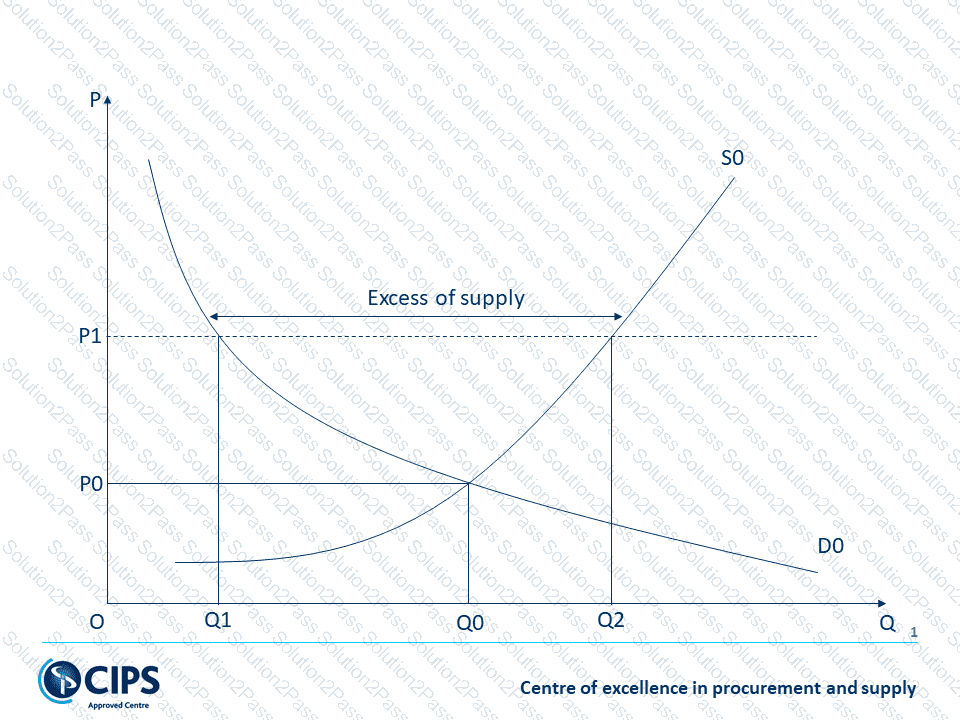 Chart, line chart Description automatically generated
Chart, line chart Description automatically generated