L4M7 CIPS Whole Life Asset Management Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIPS L4M7 Whole Life Asset Management certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
When purchasing a capital asset, an organisation should analyse the costs and benefits that the asset may bring. Which of the following factors are considered in cost-benefit analysis? Select TWO that apply.
When deciding on the storage facilities and locations, an organisation needs to assess the current situation comprehensively and forecast the future demands. Quantitative analysis is the best method for these activities. Is this statement true?
XYZ Ltd is a retailer in the US. Their customers' demand for Thanksgiving and Christmas decora-tions usually rises in the end of the year. This irregular demand results in more required storage space for finished goods during peak seasons. Which of the following are possible solutions for dealing with required additional space?
1. Maximising aisle width
2. Keeping high buffer stock throughout the year
3. Maximising flexibility in warehouse layout
4. Installing mezzanine floor
A procurement manager has agreed a contract for the acquisition of a piece of capital equipment and has negotiated a staged payment contract of 30% with order, 30% on delivery, and the remaining 40% on acceptance testing. Was this the right thing to do?
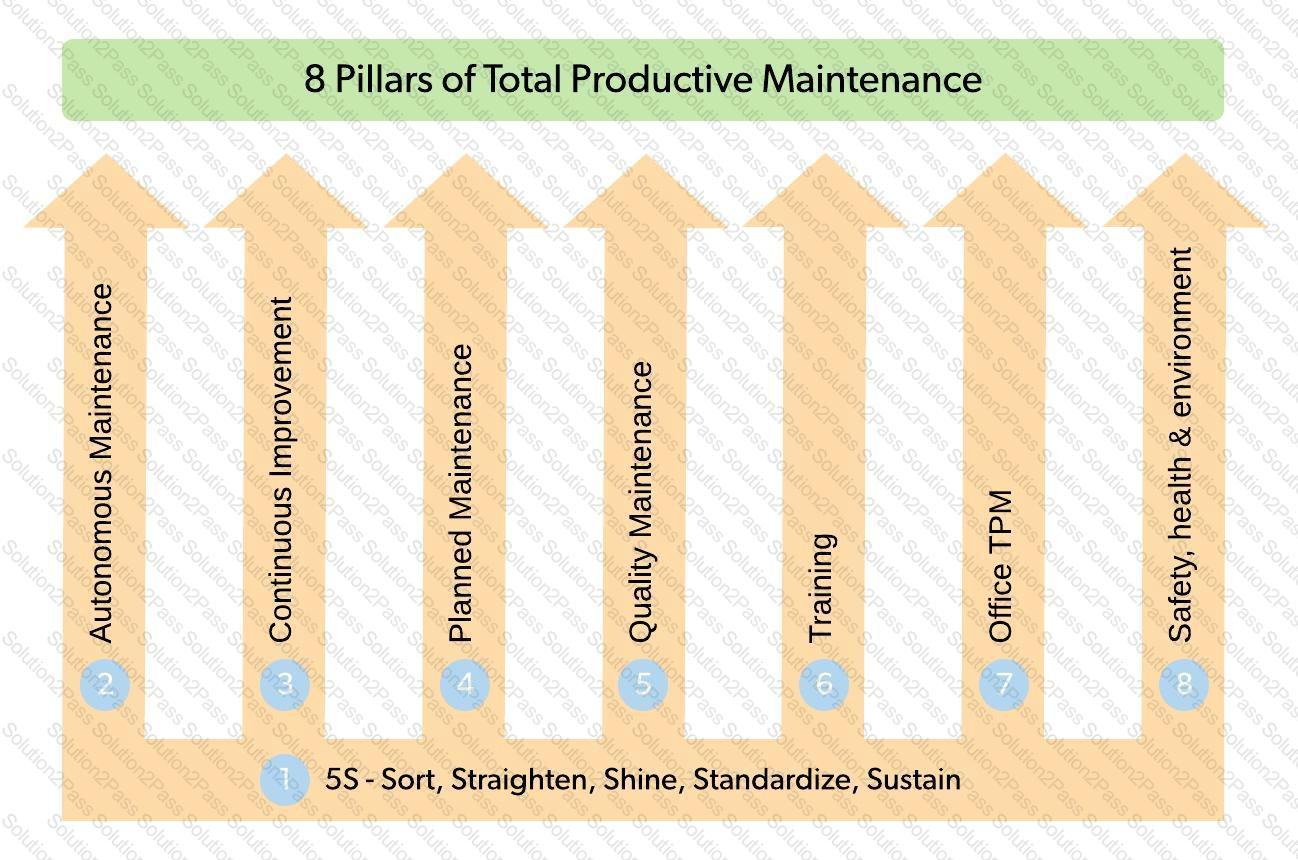
Which of the following are the key elements of total productive maintenance?
1. Reactive maintenance
2. Quality maintenance
3. Deferred maintenance
4. Autonomous maintenance
Extra units that are held in inventory to reduce the risks of stock-out are called...?
MRP system is the most suitable IT system to manage which type of items?
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is fast emerging as a major commercial technology. Like every new technology, it has advantages and disadvantages. An advantage of using RFID is that …
A light bulb supplier's catalogue shows a list of different products and product codes. Here is an example: 5WBC201, 5WBC202, 5WBC203. This supplier is using which of the following product coding structures?
A manufacturer is making a plan for strategic safety stock. To do so, they must analyse the proba-bility of a stock out occurring and the cost impacts if it does. Which of the following are typical costs the manufacturer may incur in 'out of stock' event? Select TWO that apply.
Which of the following factors should be considered in the choice of a warehouse location?
The type of barcoding that is used
The impact of local authority bylaws and regulations
The number of forklifts to be used
The nature of the items to be stored
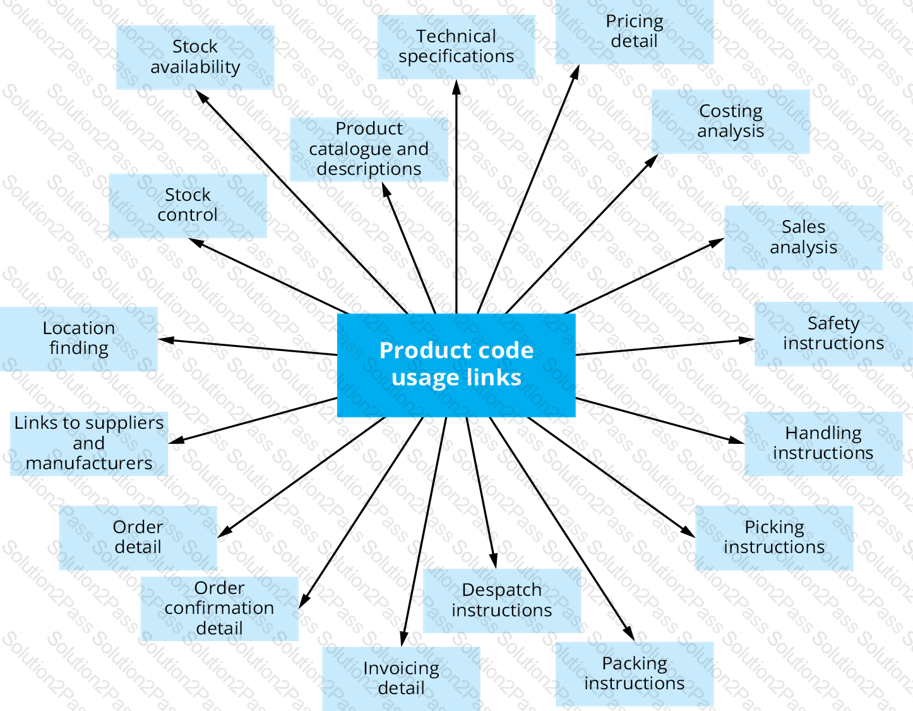
Which of the following are features of product codes?
1. Product codes link to products' characteristics
2. A product code must comply with international standards
3. Many internal processes use the product codes as facilitators
4. There are no duplicate product codes
Which ONE of the following correctly differentiates between obsolescent and redundant stock?
"Open stock plus purchases minus closing stock" is the formula of which of the following?
Buffer stock is a level of stock which ...
A construction organisation requires specialist equipment for digging deep foundations. Which of the following circumstances would result in the hire of equipment rather than leasing it?
When designing the layout of a warehouse or stores area, one of the factors to consider is the width of the aisles between the racking. Which of the following is a main consideration when calculating the aisle width?
Which of the following correctly describes the triple bottom line?
A meaning of 'decommissioning a piece of equipment' is to...
Which of the following are examples of subjective methods of forecasting? Select TWO that apply.
Trend line analysis
Moving averages
Market research
Expert opinion
Seasonal variations