4A0-112 Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your Nokia 4A0-112 Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
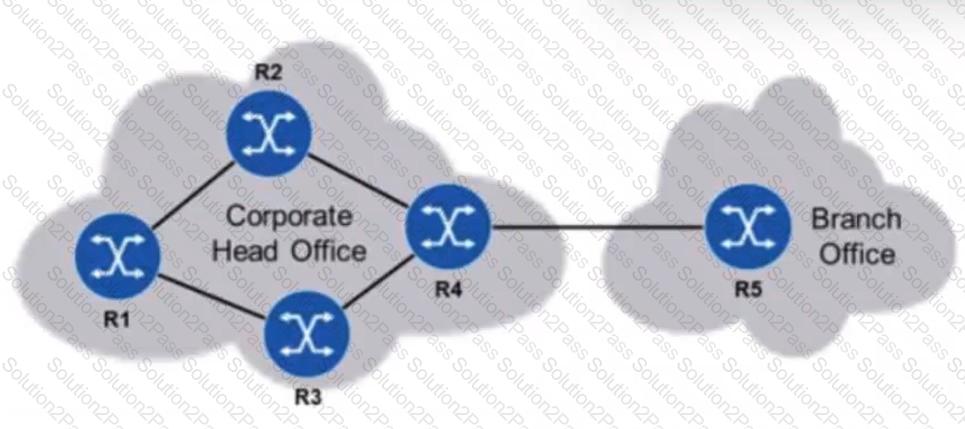
Static routing is to be used in a network between a corporate head office and a branch office. The head office has many connected subnetworks, whereas the branch office has one subnetwork and a single connection to the head office. Which of the following is the most likely configuration on the head office and branch office routers?
Which of the following definitions best describes route redistribution?
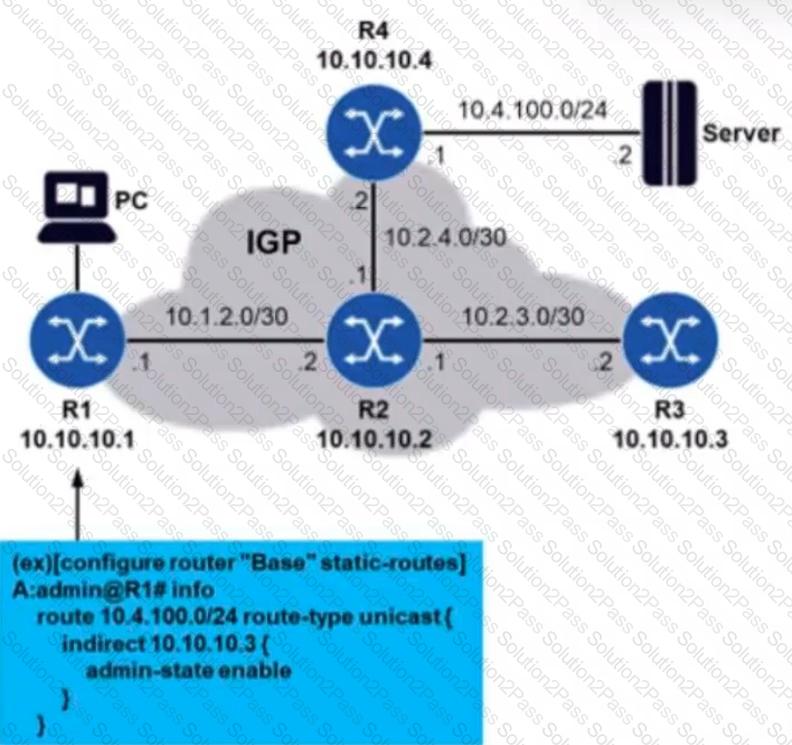
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other’s system IP addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails. What may be the problem in this case?
When a router performs the SPF calculation, which router is used as the root of the shortest path tree?
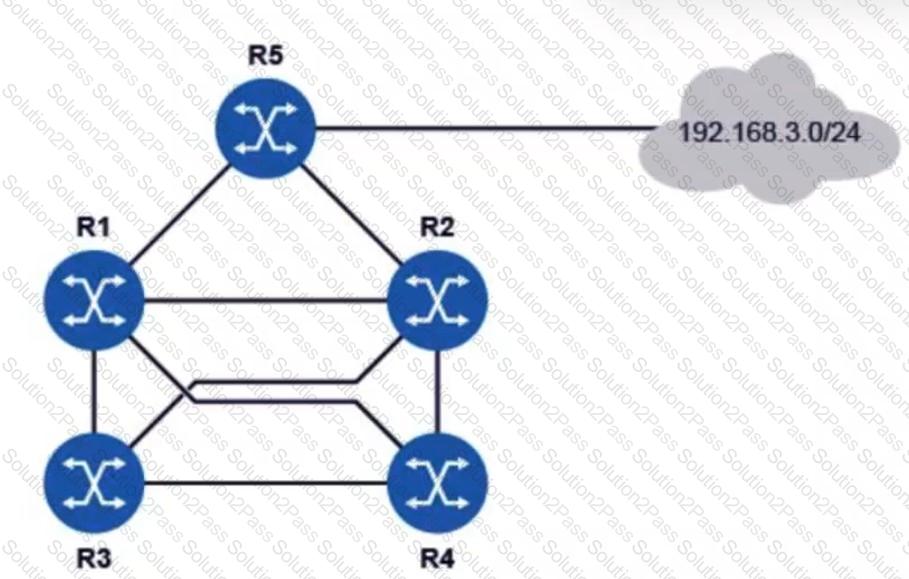
All routers in the diagram are running an interior gateway protocol (IGP) and have been configured with an ECMP value of 4. Router R5 advertises the prefix 192.168.3.0/24 using the IGP. Assuming all links have the same cost, how many entries for prefix 192.168.3.0/24 will be in router R3’s routing table?
Which of the following statements about the IP forwarding process on a router is TRUE?
A series of actions are triggered on a router as a result of enabling both loopfree-alternate for a link-state routing protocol and ip-fast-reroute. Which of the following is NOT one of those actions?
Two IS-IS neighboring routers are trying to establish an adjacency, but the interface has been configured as broadcast on one of them and as point-to-point on the other. Why is the adjacency not established?
Which of the following statements regarding the databases used by a link-state routing protocol in a single-are routing domain is FALSE?
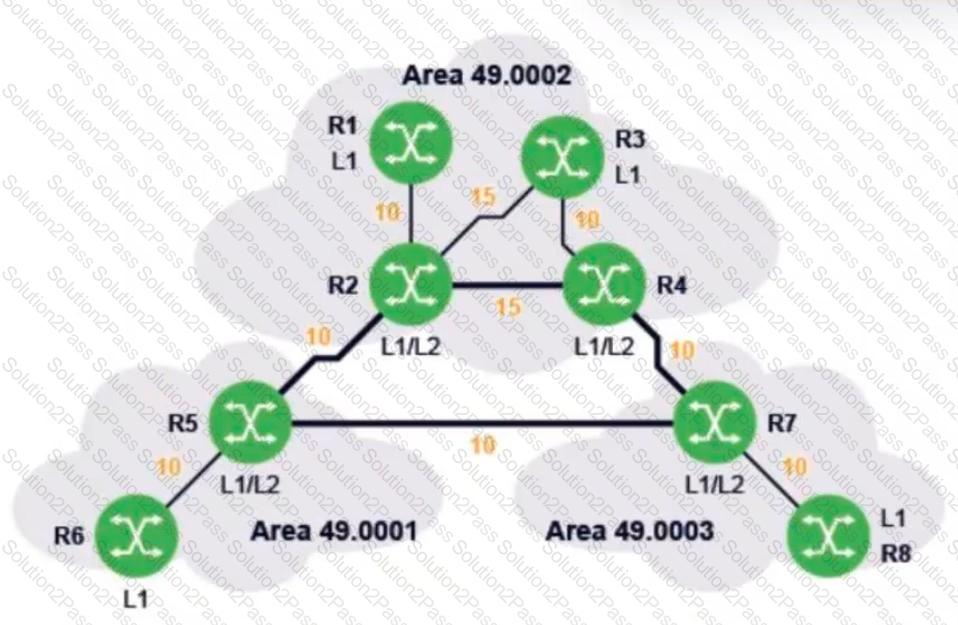
In the diagram, all routers are using IS-IS as their routing protocol. The number next to each link is its metric value.
What path will traffic follow from router R6 to router R3, and from router R3 to router R6?
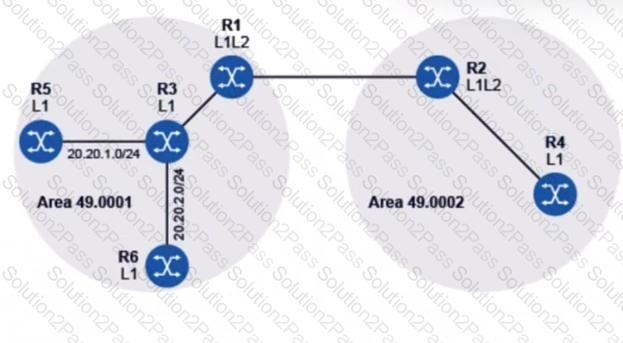
In the IS-IS network shown, router R1 has been configured to summarize subnetworks 20.20.1.0/24 and 20.20.2.0/24 as 20.20.0.0/16. Which routers’ routing tables will be reduced, compared to their routing tables before the summarization?
An IS-IS router receives a CSNP that references an older LSP than the one in its local database. What action is taken?
