1z0-071 Oracle Database 12c SQL Free Practice Exam Questions (2025 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your Oracle 1z0-071 Oracle Database 12c SQL certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2025, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which two tasks require subqueries?
Which three are true aboutprivileges and roles?
Examine the description of the EMPLOYEES table:

Which statement will fail?
Examine the command to create the BOOKS table.
SQL> create table books(book id CHAR(6) PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR2(100) NOT NULL,
publisher_id VARCHAR2(4),
author_id VARCHAR2 (50));
The BOOK ID value 101 does not exist in the table.
Examine the SQL statement.
insert into books (book id title, author_id values
(‘101’,’LEARNING SQL’,’Tim Jones’)
Examine the description of the EMPLOYEES table:

Which two queries return rows for employees whose manager works in a different department?
Which two are true about virtual columns?
Which four statements are true about constraints on Oracle tables?
Which two statements are true about a full outer join?
Examine the description of the sales table.
The sales table has 55,000 rows.
Examine this statements:
Which two statements are true?
Examine the description of the PRODUCT_ DETAILS table:

Which two statements are true?
Which is true about the & and && prefixes with substitution variables?
You execute this command:
TRUNCATE TABLE dept;
Which two are true?
Examine this data in the EMPLOYERS table:
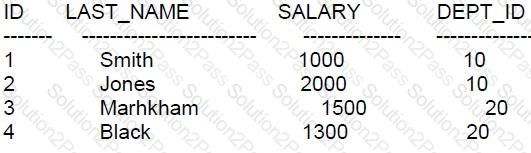
Which statement will execute successfully?
Which three actions can you perform on an existing table containing date?
Which three privileges can be restricted to a subset of columns in a table?
You need to allow user ANDREW to:
1. Modify the TITLE and ADDRESS columns of your CUSTOMERS table.
2. GRANT tha permission to other users.
Which statement will do this?
Which three statements are true about GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLES?
Which two are true about granting privilege on objects?
Examine the data in the EMP table:
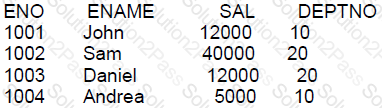
You execute this query:
SELECT deptno AS "Department", AVG(sal) AS AverageSalary, MAX(sal) AS "Max Salary"
FROM emp
WHERE sal >= 12000
GROUP BY "Department "
ORDER BY AverageSalary;
Why does an error occur?
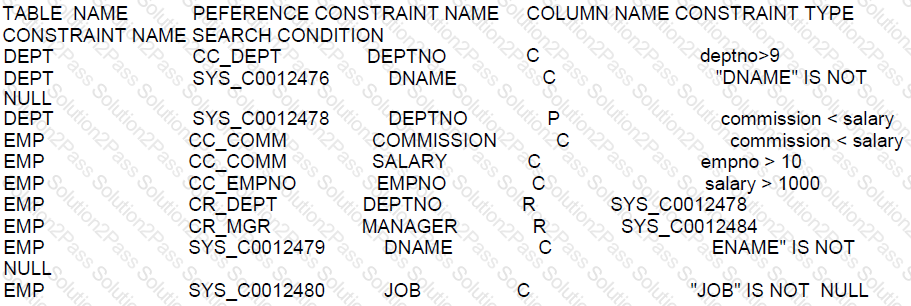
Which three statements are true?
