1z0-071 Oracle Database 12c SQL Free Practice Exam Questions (2025 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your Oracle 1z0-071 Oracle Database 12c SQL certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2025, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which three statements are true about a self join?
which three statements are true regarding single row subqueries?
Which two statements are true about substitution variables?
Which two true about a sql statement using SET operations such as UNION?
Examine the description of the PRODUCT_ STATUS table:

The STATUS column contains the values IN STOCK or OUT OF STocK for each row.
Which two queries will execute successfully?
Examine this SQL statement:

Which two are true?
You create a table by using this command:
CREATE TABLE rate_list (rate NUMBER(6,2));
Which two are true about executing statements?
Which three statements are true about Structured Query Language (SQL)?
Examine these statements which execute successfully:
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT = ‘DD-MON-YYYY HH24 MI: SS’
ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ ZONE = ‘-5:00’;
SELECT DBTIMEZONE, SYSDATE FROM DUAL
Examine the result:

If LOCALTIMESTAMP was selected at the same time what would it return?
Examine the description of the EMPLOYEES table:

Which two queries return the highest salary in the table?
You execute these commands:
SQL> DEFINE hiredate = ’01-APR -2011’;
SQL> SELECT employee_id, first_name, salary FROM employees WHERE hire date > &hiredate AND manager_id >&mgr_id;
For which substitution variables will you be prompted?
You execute this command:
ALTER TABLE employees SET UNUSED (department_id);
Which two are true?
Examine the description of the PRODUCT_STATUS table:

The STATUS column contains the values 'IN STOCK' or 'OUT OF STOCK' for each row
Which two queries will execute successfully?
Examine the description of the CUSTOMERS table:

You need to display last names and credit limits of all customers whose last name starts with A or B In lower or upper case, and whose credit limit is below 1000.
Examine this partial query:
SELECT cust_last_nare, cust_credit_limit FROM customers
Which two WHERE conditions give the required result?
Examine the data in the EMPLOYEES table:

Which statement will compute the total annual compensation for each employee?
Which two statements are true about Oracle synonyms?
Which two statements are true regarding non equijoins?
Which two queries execute successfully?
Which two are true about creating tables in an Oracle database?
Examine this partial statement:
SELECT ename, sal,comm FROM emp
Now examine this output:
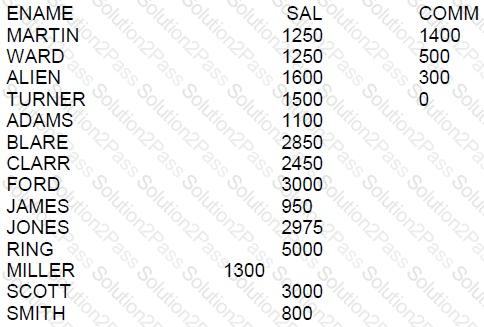
WHICH ORDER BY clause will generate the displayed output?
