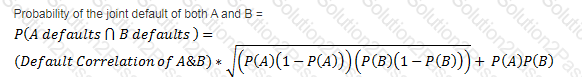8008 PRMIA PRM Certification - Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks, Operational Risk, Credit Risk, Counterparty Risk, Market Risk, ALM, FTP - 2015 Edition Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PRMIA 8008 PRM Certification - Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks, Operational Risk, Credit Risk, Counterparty Risk, Market Risk, ALM, FTP - 2015 Edition certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Regulatory arbitrage refers to:
Which of the following introduces model error when basing VaR on a normal distribution with a static mean and standard deviation?
What is the risk horizon period used for credit risk as generally used for economic capital calculations and as required by regulation?
The probability of default of a security during the first year after issuance is 3%, that during the second and third years is 4%, and during the fourth year is 5%. What is the probability that it would not have defaulted at the end of four years from now?
A corporate bond has a cumulative probability of default equal to 20% in the first year, and 45% in the second year. What is the monthly marginal probability of default for the bond in the second year, conditional on there being no default in the first year?
There are two bonds in a portfolio, each with a market value of $50m. The probability of default of the two bonds are 0.03 and 0.08 respectively, over a one year horizon. If the probability of the two bonds defaulting simultaneously is 1.4%, what is the default correlation between the two?
Which of the following are considered asset based credit enhancements?
I. Collateral
II. Credit default swaps
III. Close out netting arrangements
IV. Cash reserves
Which of the following assumptions underlie the 'square root of time' rule used for computing VaR estimates over different time horizons?
I. the portfolio is static from day to day
II. asset returns are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.)
III. volatility is constant over time
IV. no serial correlation in the forward projection of volatility
V. negative serial correlations exist in the time series of returns
VI. returns data display volatility clustering
As opposed to traditional accounting based measures, risk adjusted performance measures use which of the following approaches to measure performance:
The Altman credit risk score considers:
There are two bonds in a portfolio, each with a market value of $50m. The probability of default of the two bonds over a one year horizon are 0.03 and 0.08 respectively. If the default correlation is zero, what is the one year expected loss on this portfolio?
Which of the following formulae describes CVA (Credit Valuation Adjustment)? All acronyms have their usual meanings (LGD=Loss Given Default, ENE=Expected Negative Exposure, EE=Expected Exposure, PD=Probability of Default, EPE=Expected Positive Exposure, PFE=Potential Future Exposure)
Under the internal ratings based approach for risk weighted assets, for which of the following parameters must each institution make internal estimates (as opposed to relying upon values determined by a national supervisor):
When modeling severity of operational risk losses using extreme value theory (EVT), practitioners often use which of the following distributions to model loss severity:
I. The 'Peaks-over-threshold' (POT) model
II. Generalized Pareto distributions
III. Lognormal mixtures
IV. Generalized hyperbolic distributions
A corporate bond maturing in 1 year yields 8.5% per year, while a similar treasury bond yields 4%. What is the probability of default for the corporate bond assuming the recovery rate is zero?
When modeling operational risk using separate distributions for loss frequency and loss severity, which of the following is true?
Which of the following statements is correct in relation to liquidity risk management?
I. Pricing for products that do not impact the balance sheet need not reflect the cost of maintaining liquidity
II. Time horizons for liquidity risk management are impacted by both regulatory requirements and the speed at which new sources of liquidity can be tapped
III. Collateral management is an important aspect of liquidity risk management
IV. The maturity period of various instruments in the capital structure has a significant impact on liquidity needs
If a borrower has a default probability of 12% over one year, what is the probability of default over a month?
The 10-day VaR of a diversified portfolio is $100m. What is the 20-day VaR of the same portfolio assuming the market shows a trend and the autocorrelation between consecutive periods is 0.2?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Pre-settlement risk is the risk that one of the parties to a contract might default prior to the maturity date or expiry of the contract.
II. Pre-settlement risk can be partly mitigated by providing for early settlement in the agreements between the counterparties.
III. The current exposure from an OTC derivatives contract is equivalent to its current replacement value.
IV. Loan equivalent exposures are calculated even for exposures that are not loans as a practical matter for calculating credit risk exposure.