5V0-41.20 VMware SD-WAN Troubleshoot Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your VMware 5V0-41.20 VMware SD-WAN Troubleshoot certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Scenario 3:
After completing the branch activation activities for all required branches, the network administrator attempts to test connectivity between the various branches and between the hubs and branches. The administrator notices a lack of connectivity despite being certain that configurations have been complete. The administrator also observed that several users are reporting intermittent connectivity to some of the applications they are accessing. Other users are reporting no access to these applications. Other users at some of the branches claim they cannot get to certain public resources. The administrator wants to ensure that all sites can talk to each other and all resources are accessible.
Exhibit.
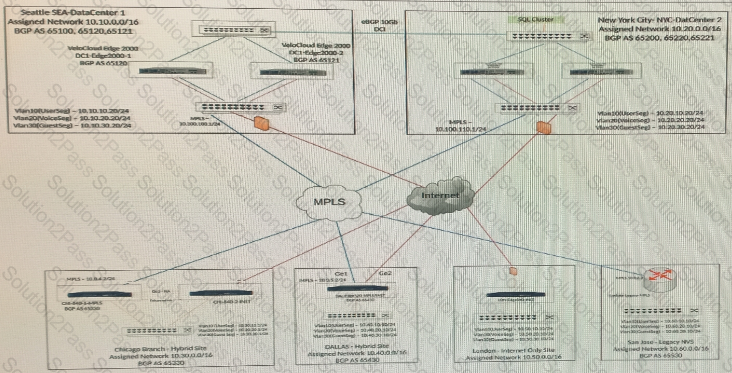
The network administrator determines that dynamic routes to SD-WAN sites are missing at the San Jose branch router. The network administrator decides to look into the configurations of hub Edges. All SD-WAN branch sites must use a hub to communicate with the San Jose site. Best practices have been implemented at these SD-WAN sites.
Where should the administrator check first to verify if the configuration is correct?
Scenario 2:
After completing the branch activation activities for all required branches, the network administrator attempts to test connectivity between the various branches and between the hubs and branches. The administrator notices a lack of connectivity despite being certain that configurations have been complete. The administrator also observed that several users are reporting intermittent connectivity to some of the applications they are accessing. Other users are reporting no access to these applications. Other users at some of the branches claim they cannot get to certain public resources. The administrator wants to ensure that all sites can talk to each other and all resources are accessible.
Exhibit.
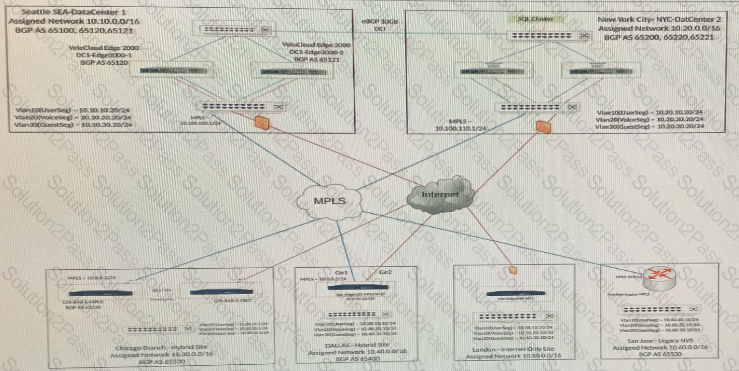
When checking connectivity from the San Jose branch, all users report that they can reach certain resources at the main data center. They are unable to reach locations elsewhere. The network administrator investigates and first looks at the Overlay Flow Control (OFC) Table.
What should the network administrator look for next to determine what the issue might be?
Scenario 3:
After resolving numerous connectivity issues throughout the various branch sites, connectivity between applications and users is finally present. The network administrator is informed that during certain tests, applications are not performing as they are expected to. Users report that call quality has not fully improved and that some of their calls either drop or have poor voice quality where the conversation is breaking up. Other users are noticing that file transfers are slower than expect. A group of users from a few sites have reported slowness in accessing internal and external applications.
Users at multiple branches complain that a highly performant SQL Database cluster residing at the New York Data Center is not responding to database queries or inserts as expected. It is affecting the order management site. A network administrator investigates and finds that traffic from the branches are going through Seattle to reach the SQL Cluster in New York. The design for this SD-WAN network does not call for routing security.
The SQL Cluster is reachable through either Data Center, but for performance reasons, must flow through the New York DC. The network administrator has verified that the routes are not present in the OFC and the BGP neighborship is down in Network Services.
Refer to the Exhibit(s).
Exhibit.
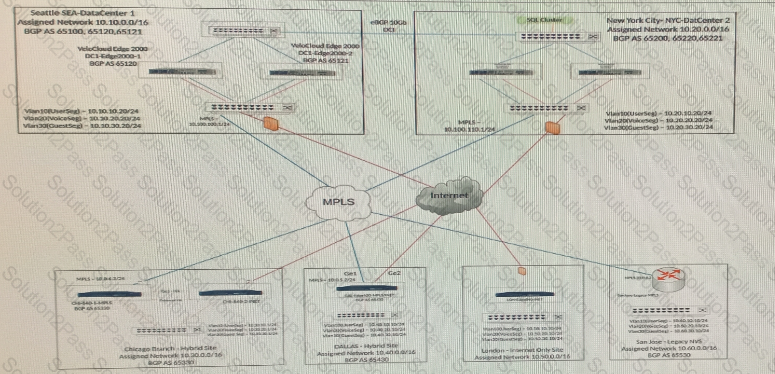
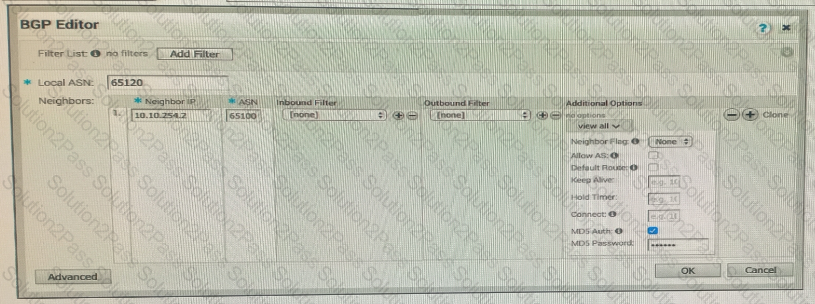
What should the administrator verify?
Scenario 2:
After completing the branch activation activities for all required branches, the network administrator attempts to test connectivity between the various branches and between the hubs and branches. The administrator notices a lack of connectivity despite being certain that configurations have been complete. The administrator also observed that several users are reporting intermittent connectivity to some of the applications they are accessing. Other users are reporting no access to these applications. Other users at some of the branches claim they cannot get to certain public resources. The administrator wants to ensure that all sites can talk to each other and all resources are accessible.
Exhibit.
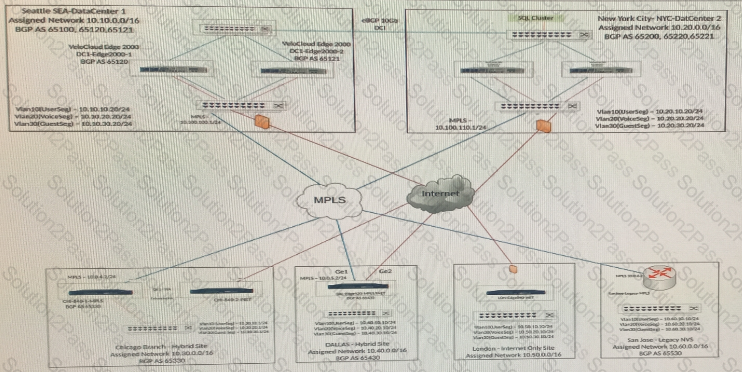
Several reports have come in from branch locations indicating customers cannot reach applications being served by the hub location. The hub location has a single LAN-side port from which it should be learning dynamic routes for the subnets serving the applications.
How should the technician verify if the ports on the Edge are up and working?
Scenario 2:
After completing the branch activation activities for all required branches, the network administrator attempts to test connectivity between the various branches and between the hubs and branches. The administrator notices a lack of connectivity despite being certain that configurations have been complete. The administrator also observed that several users are reporting intermittent connectivity to some of the applications they are accessing. Other users are reporting no access to these applications. Other users at some of the branches claim they cannot get to certain public resources. The administrator wants to ensure that all sites can talk to each other and all resources are accessible.
Exhibit.
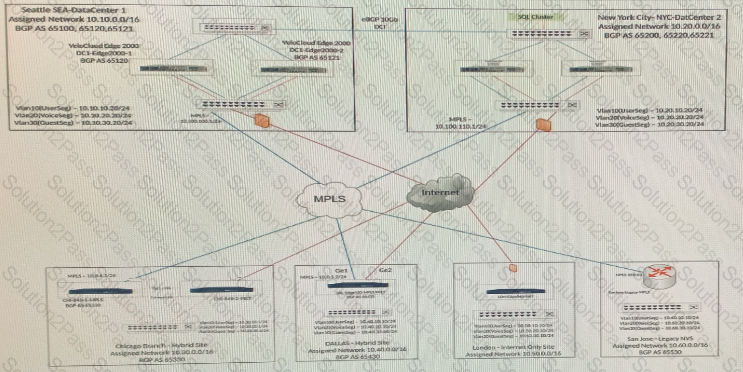
A network administrator decides to deploy a local Checkpoint VNF appliance on the Edge in London to cut back on unnecessary traffic towards the NY Hub location. While attempting to deploy the VNF, the process keeps failing.
Where can the administrator check to see more detail?
Scenario 1:
A network administrator is tasked with enabling SO-WAN at three branch locations. A topology has been provided for reference. For each site, the administrator is having issues bringing edges online, as another administrator has gone ahead and created a configuration ahead of time. The organization has several branch sites. One is an Internet-only site and two are Hybrid locations with both internet and MPLS. The last location is MPLS only. There are hub data center locations in this environment as well. Please refer to the topology.
After the network administrator has determined the problem with the Edge not being able to access the Internet, the administrator receives another error stating that the SD-WAN Orchestrator is still not reachable.
The VCO's address is Amer-vcoOl.velocloud.net.
Refer to the Exhibit(s).
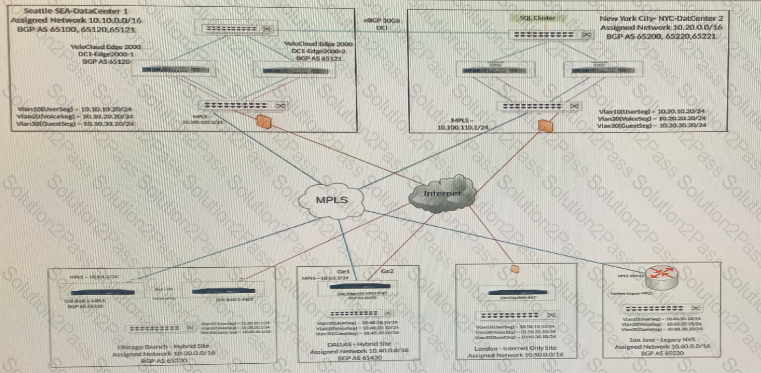
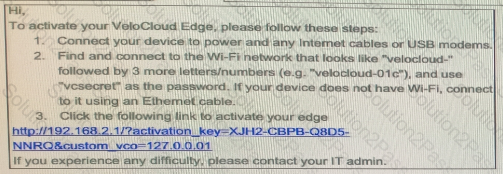
What might be disallowing the Edge to communicate with the Orchestrator?
Scenario 3:
After resolving numerous connectivity issues throughout the various branch sites, connectivity between applications and users is finally present. The network administrator is informed that during certain tests, applications are not performing as they are expected lo. Users report that call quality has not fully improved and that some of their calls either drop or have poor voice quality where the conversation is breaking up. Other users are noticing that file transfers are slower than expect. A group of users from a few sites have reported slowness in accessing internal and external applications.
Exhibit.
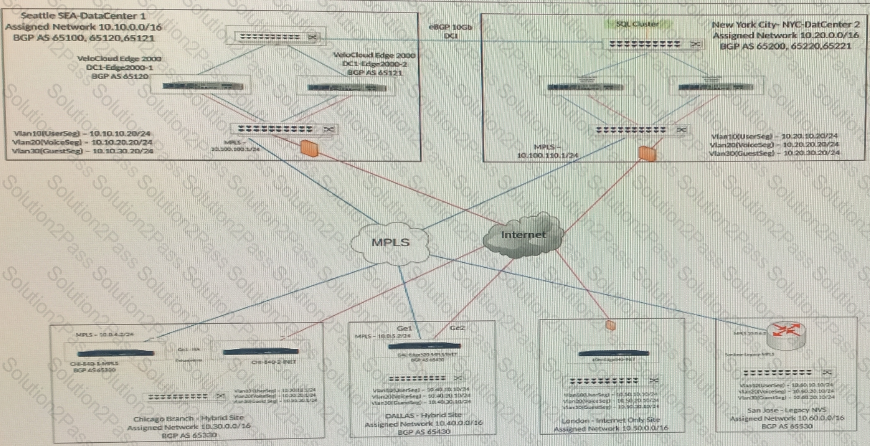
Users are complaining that web pages to certain web sites are very slow to load and at times unresponsive. The network administrator has verified that the traffic is going correctly out the underlay.
What should the administrator check next?
Scenario 3:
After resolving numerous connectivity issues throughout the various branch sites, connectivity between applications and users is finally present. The network administrator is informed that during certain tests, applications are not performing as they are expected to. Users report that call quality has not fully improved and that some of their calls either drop or have poor voice quality where the conversation is breaking up. Other users are noticing that file transfers are slower than expect. A group of users from a few sites have reported slowness in accessing internal and external applications.
Exhibit.
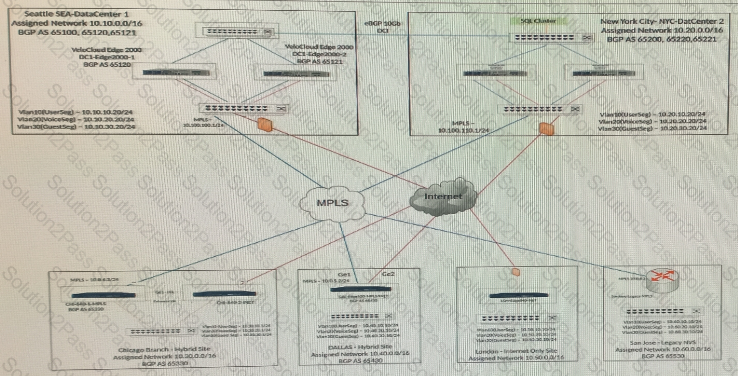
Users at a remote office are complaining about poor performance with certain applications. The network administrator has already configured Business Policies based on these requirements.
What is the sequence of parameters that the administrator can check to troubleshoot this problem? (Choose two.)
Scenario 2:
After completing the branch activation activities for all required branches, the administrator attempts to test connectivity between the various branches and between the hubs and branches- The administrator notices a lack of connectivity despite being certain that configurations have been complete. The administrator also observed that several users are reporting intermittent connectivity to some of the applications they are accessing. Other users are reporting no access to these applications. Other users at some of the branches claim they cannot get to certain public resources. The administrator wants to ensure that all sites can talk to each other and all resources are accessible.
Exhibit.
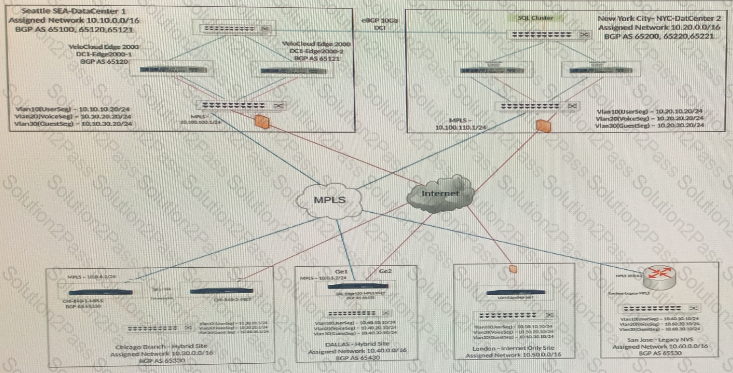
The tunnel from the Dallas site to the Seattle hub is not coming up.
What are two things that should be checked to determine the issue? (Choose two.)
Scenario:1
A network administrator is tasked with enabling SD-WAN at three branch locations, A topology has been provided for reference. For each site, the administrator is having issues bringing edges online, as another administrator has gone ahead and created a configuration ahead of time. The organization has several branch sites. One is an Internet-only site and two are Hybrid locations with both internet and MPLS. The last location is MPLS only. There are hub data center in this environment as well. Please refer to the topology.
Exhibit.
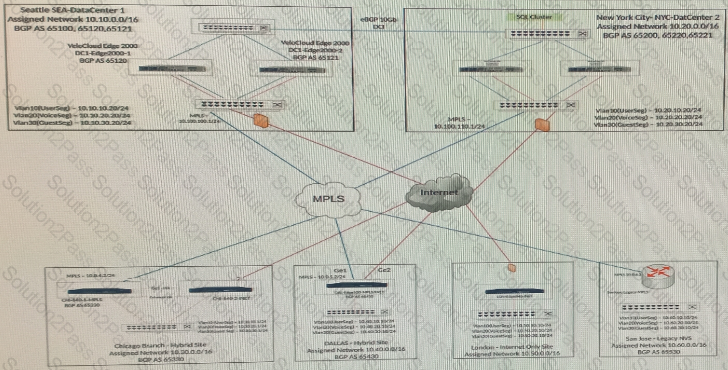
One of the Edges at the Chicago site is unable to activate. The Edge has a red LED. What is the next troubleshooting step?
