CIC CBIC Certified Infection Control Exam Free Practice Exam Questions (2025 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CBIC CIC CBIC Certified Infection Control Exam certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2025, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
A patient has a draining sinus at the site of a left total hip arthroplasty. A culture from the sinus tract reveals four organisms. Which of the following specimens is optimal for identifying the eliologic agent?
Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC)-associated bloodstream infections (BSIs) have been increasing over the past four months. Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to have contributed to the increase?
Which of the following represents a class II surgical wound?
What should an infection preventionist prioritize when designing education programs?
An infection preventionist reviewing patient records in an outpatient hemodialysis center notes an increase in localized infections at catheter access sites. Which of the following strategies reduces the risk of infection in this population?
Which of the following is an example of an outcome measure?
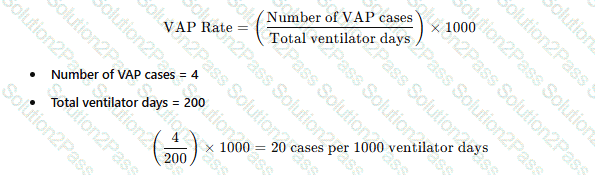
There are four cases of ventilator-associated pneumonia in a surgical intensive care unit with a total of 200 ventilator days and a census of 12 patients. Which of the following BEST expresses how this should be reported?
During an outbreak of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), the infection preventionist should FIRST:
Assume the mean age of onset for patients with tuberculosis (TB) is 62 years, with one standard deviation of 5 years, and the age of onset follows a normal distribution. What is the percentage of patients expected to have the age of onset ranging from 57 to 67 years?
A 36-year-old female presents to the Emergency Department with a petechial rash, meningitis, and cardiac arrest. During the resuscitation, a phlebotomist sustained a needlestick injury. The next day, blood cultures reveal Neisseria meningitidis. The exposure management for the phlebotomist is:
Which of the following represents the most effective strategy for preventing Clostridioides difficile transmission in a healthcare facility?
 A white paper with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A white paper with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.