BA2 CIMA Fundamentals of management accounting Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA BA2 Fundamentals of management accounting certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
The accounting treatment for overheads over absorbed is to:
C Ltd produces a chemical in a single process. Information for this process last month is as follows:
(a) Opening work in progress - 10000 kg valued at £10000 for direct material and £7500 for conversion costs.
(b) Materials input - 25000 kg at £1.10 per kg.
(c) Conversion costs - £17000
(d) Output during the month - 23000 kg.
(e) There were 7500 units of closing work in progress which was complete as to materials and 30% complete as to conversion.
(f) Normal loss for the month was 10% of input and all losses have a scrap value of 80p per kg.
What was the average cost per kg of finished output during the month?
Each finished carton of product P contains 15 litres of liquid L. During the production process there is an unavoidable loss of 20% of the liquid input. The standard price of liquid L is $2 per litre.
The standard ingredient cost for liquid L shown on the standard cost card for one carton of product P will be
In an integrated cost and financial accounting system, the accounting entries for the payment of net wages to indirect production workers would be:
PQR Manufacturing Ltd. has £3,000,000 of fixed costs for the forthcoming period. The company produces a single product 'X', which has a selling price of £75 per unit and total cost of £50.
75% of the total cost represents variable costs.
What are the break-even units?
A budget that is continuously updated by adding a further accounting period when the earliest period has expired is known as:
Refer to the Exhibit.

A company operates a batch costing system.
Production overhead costs are absorbed into the cost of batches using a direct labour hour rate. Other overhead costs are absorbed at a rate of 20% of total production cost. The company adds a mark-up of 10% to total cost in order to derive its selling prices.
Budgeted production overheads for the period are $44,000 and the budgeted level of activity is 8,800 direct labour hours.
The following data are available for batch number 309:
The required selling price per unit (to two decimal places) is:
Which of the following best describes a step cost?
Refer to the Exhibit.
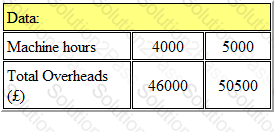
PJ Ltd has forecast that the relationship between total overheads and machine hours will be as follows:
If the budget is to be based on 4,000 machine hours, the variable overhead absorption rate will be:
*per machine hour.
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
An overtime premium may be defined as:
In order to provide information that is suitable for control purposes, the budget must be:
Refer to the exhibit.

T operates a process costing system. Data is available for Process A for the month of July.
Inputs for the month:
Normal losses are 15% of input and can be sold for $6 per kg. Actual output was 2,600 kg. There is no opening or closing work in progress for the period.
What is the value of the output from the process in the month?
Refer to the exhibit.
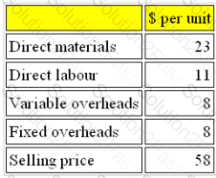
SL manufactures a single product, the cost and selling price of which are given below:
Fixed overheads per unit are based on a budgeted production volume of 25,000 units.
Budgeted sales are assumed to be 25,000 units.
If all costs increase by 5% but selling price remains the same, by how much must sales change from the budgeted volume to achieve the same budgeted profit?
Refer to the Exhibit.
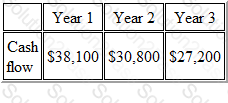
The following forecast cash flows relate to a proposed investment in new delivery vehicles at a total cost of $75,000.
The internal rate of return (IRR) of the proposed investment is (to two decimal places)
Refer to the Exhibit.
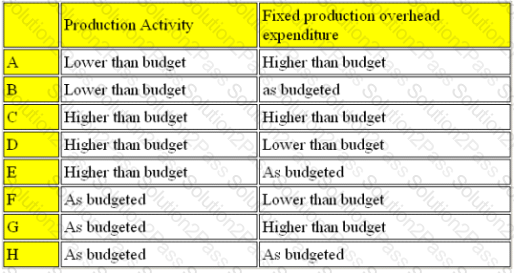
A company operates an absorption costing system. The management accounts show that fixed production overheads were over-absorbed in the period.
Which FOUR combinations could possibly have resulted in this situation?
In the process account, the accounting treatment of the value of the abnormal gain is:
Which of the following categories of costs is the most relevant for decision making?
Refer to the exhibit.
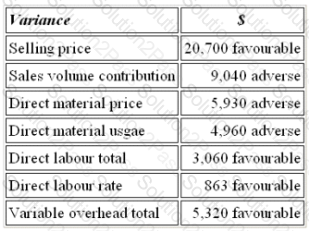
The budgeted contribution for last month was $53,600. The variances reported were as follows:
The actual contribution for last month was:
In a manufacturing company which produces a range of products, the cost of factory rent and rates would be classified as A.
A company wishes to achieve a 20% return on the capital of $937,500 invested in the company. Total costs for the next period are budgeted to be $1,250,000.
The standard cost for product P is $11 per unit.
In order to achieve the required return on investment the selling price per unit of product P must be:
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
