BA2 CIMA Fundamentals of management accounting Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA BA2 Fundamentals of management accounting certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which THREE of the following costs would normally be classified as semi-variable?
The direct labour efficiency variance is:
Refer to the exhibit.

The following extracts are taken from a company’s budgetary planning papers, showing the budgeted costs to be incurred at two activity levels:
Direct material is a wholly variable cost.
Direct labour is a semi-variable cost.
Production overhead is a step cost, with a single step at an output of 450 units.
The total budget cost allowance for an output of 480 units is:
LC produces a household detergent in a single process. Information for this process for last month is as follows:
(a) Materials input - 11,000 Litres at £2.00 per litre.
(b) Conversion costs - £23,000
(c) Output during the month - 8,000 litres.
(d) There were 2,000 units of closing work in progress which was complete as to materials and 35% complete as to conversion.
(e) Normal loss for the month was 5% of input and all losses have a scrap value of 50p per litre.
(f) There was no opening work in progress.
The value of closing work in progress at the end of the month is closest to:
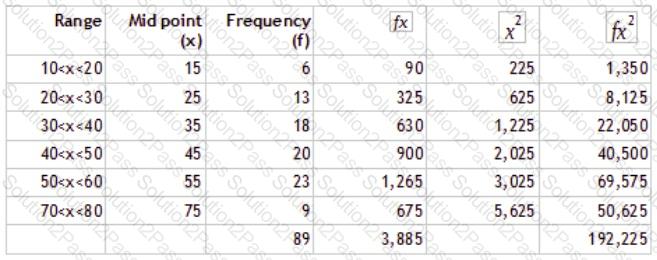
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the figures given in the table?
JB has fixed costs of $120,000 per annum. It manufactures a single product which it sells for $12 per unit. It has a profit/volume ratio of 60%.
JB’s break-even point is
When making a decision, for a cost or revenue to be classified as "relevant" it must be:
(a) Incremental
(b) Notional
(c) Cash
(d) Future
During the first financial period of this year a company posted profit of £340,000. However, their overheads were over absorbed by £20,000 in this period. As a result they tried to update their absorption rate for the current
period and as such they ended up under absorbing their overheads by £12,000.
They have also reported a sales volume increase of 550 when comparing this period to last.
You have been given the following information on unit cost/prices:
Selling price = £95 per unit
Variable production cost per unit = £15
Variable selling cost per unit = £18
Fixed overhead per unit = £8
They have asked you to reconcile their profit between periods.
Based on the information you have been given, what is their profit for the current period?
The value of the capital invested in producing and selling product F is $600,000. A return on investment of 14% is required from all products.
Budgeted production and sales of product F for next period are 25,000 units and the standard cost per unit is $33.
In order to achieve the required return on investment the selling price per unit of product F must be
The standard labour hours for all products manufactured by a company include an allowance for idle time. Idle time is budgeted to be 5% of total hours worked. Each unit of product G requires an input of 9.5 active labour hours. The labour rate is $12 per hour.
The standard labour cost shown on the standard cost card for one unit of product G will be
How does Beyond budgeting help to resolve the weaknesses of traditional budgeting? (Select ALL that apply.)
A flat letting company analyses its costs by individual property. Which of the following costs would be considered an indirect cost of the property?
In a manufacturing company which produces a range of products, the cost of a royalty payment made to the product designer would be classified as A.
Refer to the exhibit.
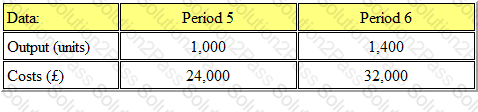
The output and costs for two periods were as follows:
Fixed costs will remain constant, but during Period 7, the variable cost per unit will increase by 25%. The output for Period 7 will be 1,600 units.
The budgeted total cost for period 7 will be:
Refer to the exhibit.
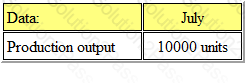
RX Ltd expects to have limited machine time for July, which will result in the following production levels:
It is anticipated that there will be 1,500 units of opening inventory and the company wishes to hold a minimum of 500 units of closing inventory at the end of July.
How many units will be available for sale during July?
If a company has a limiting factor, profit will be maximized by:
Refer to the exhibit.
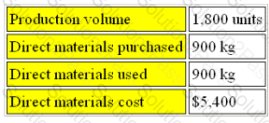
The budget for WP for the month of September contained the following data:
During the month the actual number of units produced was 1,860. The management accounts showed a direct material price variance of $1,200F and direct material usage variance of $180A. The direct materials purchased were 1,200 kg.
The actual quantity of material used in the month was
