L4M5 CIPS Commercial Negotiation Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIPS L4M5 Commercial Negotiation certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which of the following types of questions should be used most often in the proposing phase?
Which of the following are types of questions that are useful in opening and testing phases of a negotiation? Select the TWO that apply.
Which of the following are most likely to be sources of conflict that can emerge from the process of commercial negotiations? Select TWO that apply.
A garden furniture supplier who is currently in negotiations for a high-value contract has offered the procurement manager a visit to their site. The supplier suggests that during this visit, they can undertake the contract negotiation. What would be an appropriate response from the procurement manager?
Maria, an NHS buyer, needs cost savings due to budget cuts. She plans to achieve savings with a collaborative supplier. Which negotiation approach should she use?
For a commercial negotiation to be effective, the organisation has to identify resources required for negotiation. Which one of the following could help?
When considering a new supply source for a product, a procurement professional reviews supplier quotations before negotiation. Which of the following is a direct cost in the supplier’s quotation?
Which of the following is considered a weakness of a ‘dealer’ style negotiator?
Which of the following are microeconomic factors? Select THREE that apply.
Which type of negotiation strategy should be adopted when the relationship is important and both parties want to help each other achieve their goals?
Sally is negotiating with an oversea supplier on the price and payment period. Her company and the supplying organisation are equal in bargaining power. The supplier says that they are investing in new facilities and machinery so the payment period should not be longer than 30 days. Sally knows that her company often pays the suppliers after 45 days from the delivery, but at the moment the company has positive cash flow and it is able to pay immediately. Which of the following should be Sally's concession plan?
A purchasing organisation is discussing its approach to an upcoming negotiation with a key supplier over a contract for critical new services. They have decided they want to find a Win/Win (integrative) solution. Which TWO of the following would be appropriate in this scenario?
In what circumstances is the bargaining power of suppliers likely to be high, in relation to buyer power? Select the THREE that apply:
Which of the following is an objective of proposing phase?
The procurement manager of a private healthcare provider is running an IT project. Who would be the stakeholders?
General public
Pharmaceutical suppliers
Senior Management
Software support developers
Which of the following is an advantage of a fixed-price agreement?
Commercial negotiations on prices cover a range of aspects including pricing arrangements. A buyer may negotiate for a 'fixed price agreement'. Why is a fixed price agreement advantageous to the buyer?
A procurement professional is dissatisfied with how a recent negotiation was concluded. What could they do to improve their negotiation approach?
Seek feedback from the supplier on their recent performance
Prepare for all negotiations with a WIN/LOSE (distributive) approach
Involve lots of people in future negotiations
Undertake reflective practice after each negotiation
Which of the following are tactics of distributive bargaining?
Withholding information that may open up common ground
Coercing the other party to accept your position
Finding common ground between parties
Being open about all your common needs
Why is the use of power important for integrative commercial negotiations?
Moving negotiations forward when they get stuck on certain issues
Maximising the share of value gains for the negotiator's side
Coercion of the other party into a submissive agreement
Breaking through negotiation barriers related to attitude
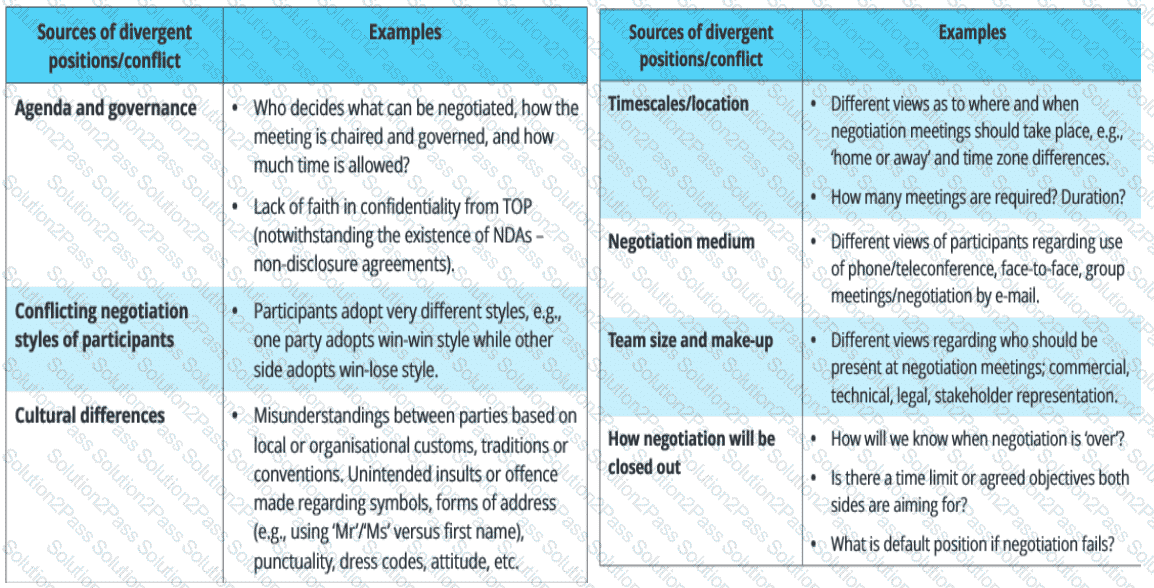 Table Description automatically generated
Table Description automatically generated