1D0-541 CIW v5 Database Design Specialist Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIW 1D0-541 CIW v5 Database Design Specialist certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which subset of Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to create and name database entities?
Consider the following DBDL description of an entity: Teachers (teach_num: variable length character string length 10 NOT NULL teach_name: variable length character string length 10 NOT NULL) Primary Key: teach_num which integrity constraint is satisfied?
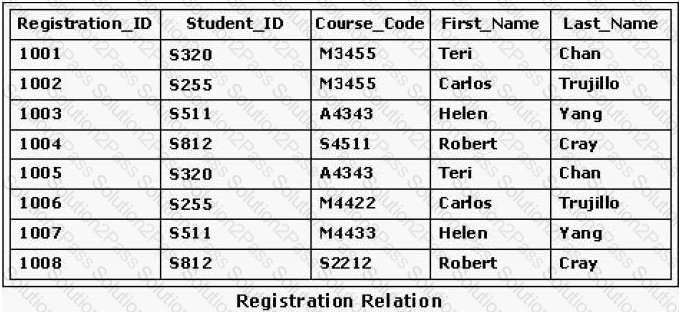
What is the highest normal form of the relation(s) shown in the exhibit?
Which of the following best describes the two-tier database architecture?
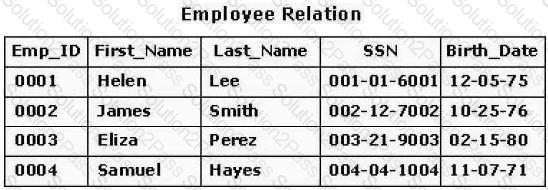
Consider the table for an employee database shown in the exhibit. What is the cardinality of the table?
Which process is used to prevent the current database operation from reading or writing a data item while that data item is being accessed by another operation?
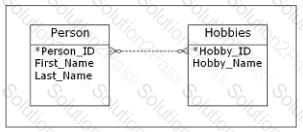
Consider the entity-relationship (ER) diagram shown in the exhibit. Which type of relationship between the two entities is shown?
Consider the Information Engineering diagram in the exhibit showing a conceptual data model of the relations BUILDING and RESIDENT. What is the next step in refining the data model?

Which database architecture is best suited to implementation in the World Wide Web environment?
Consider the Stu_Act and Act_Fee tables shown in the exhibit. Which relational algebraic operation would yield the Activity Relation table in the exhibit?
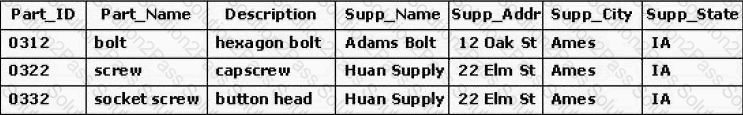
Your enterprise is creating a relation (shown in the exhibit) that tracks parts and suppliers. Which situation would occur if new supplier information were entered in the relation before any information about specific parts?
Consider the relation shown in the exhibit. Which of the following SQL statements would properly add information for a new employee?
Which of the following ACID properties requires that a transaction be executed in its entirety or not all?
With regard to databases, what is normalization?
Consider the Information Engineering diagram shown in the exhibit. Building_ID, R_ID, Room_Count and Room_Num are integer numbers, whereas Bldg_Name, Location and Res_Name are all represented by variable-length strings with a maximum of 20 characters.
Which SQL statement best implements the RESIDENT relation shown in this diagram?
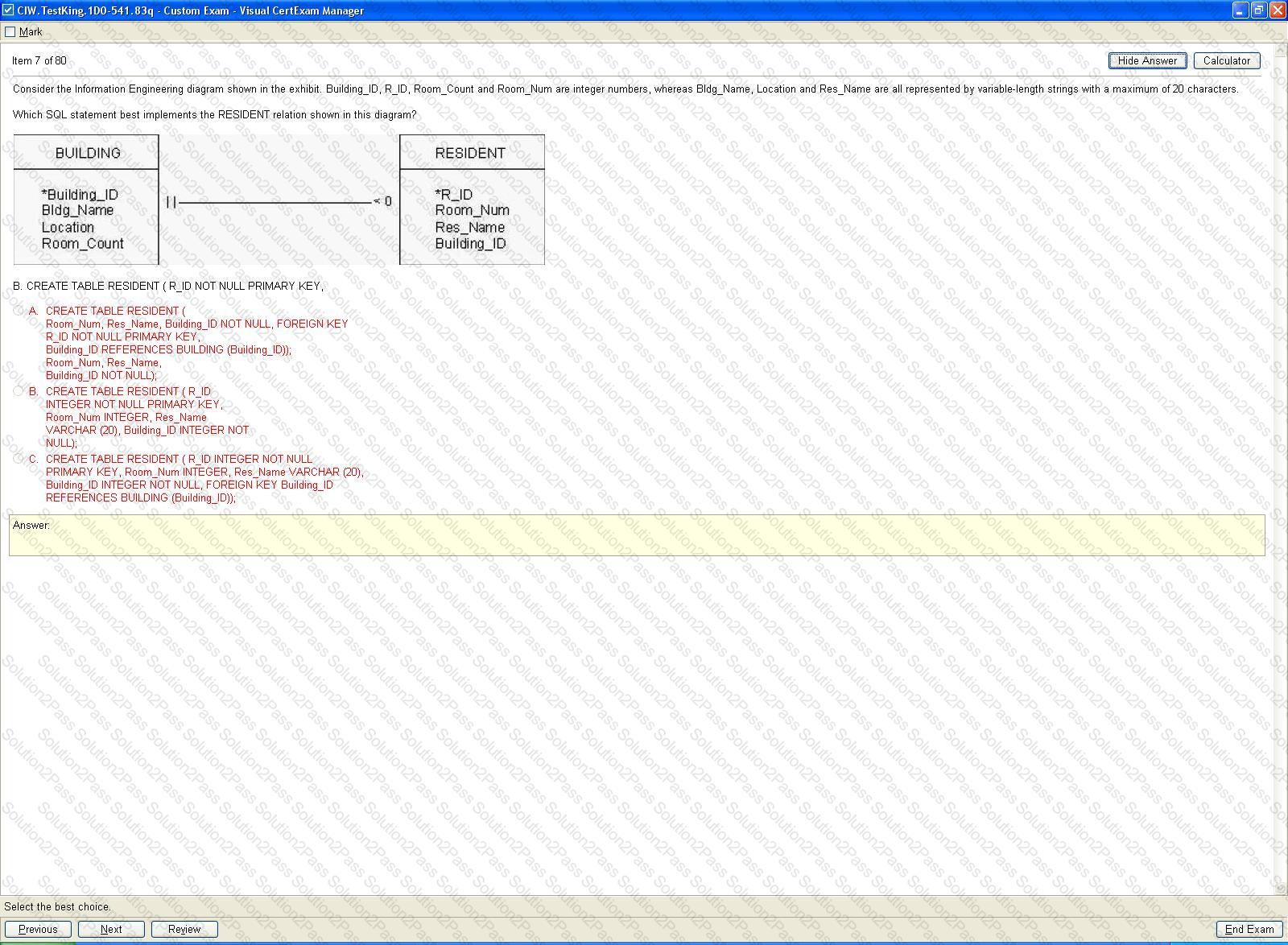
Consider the symbols shown in the exhibit. Which of the following correctly identifies these symbols when used in an entity-relationship (ER) diagram?
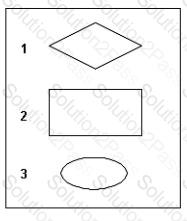
Consider the Information Engineering diagram in the exhibit showing the relations BUILDING and RESIDENT. What is the relationship between BUILDING and RESIDENT?
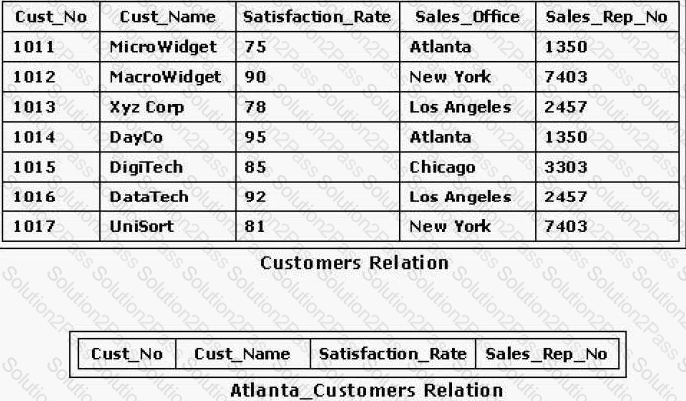
Consider the relations shown in the exhibit. Which of the following SQL statements would enter data from the Customers relation into the Atlanta_Customers relation?
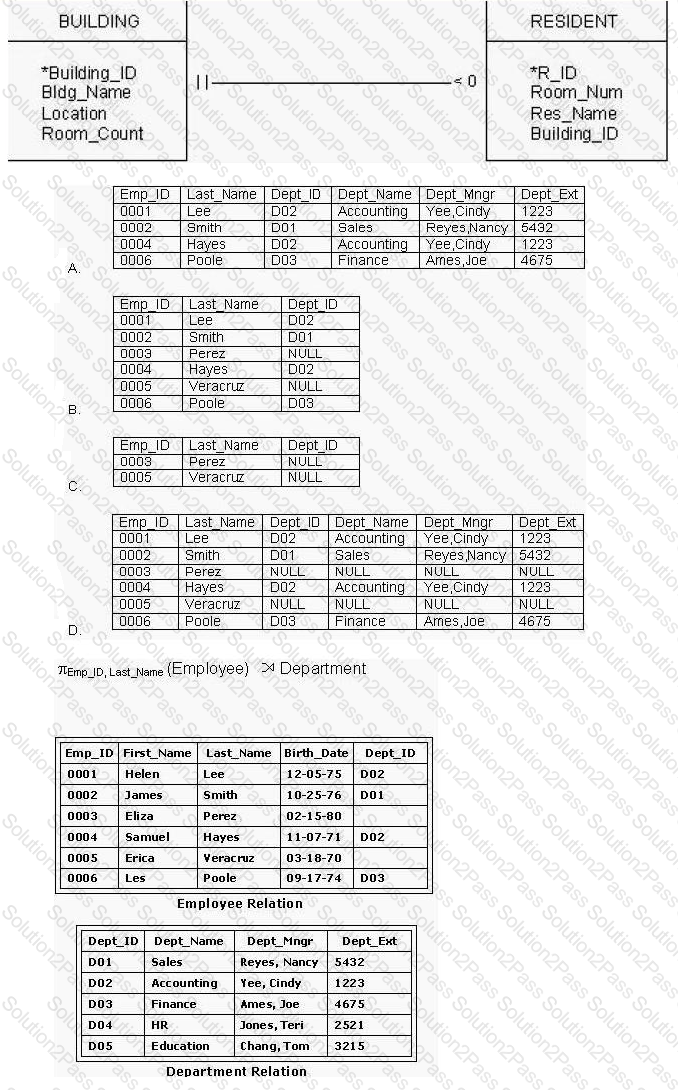
The creation of intermediate entities occurs during the logical database design phase for an enterprise. It is used to resolve which types of relationships?
Consider the following relation definition:
STUDENT(
Student_Number: integer NOT NULL
Name: variable length character string length 20 NOT NULL)
Primary Key Student_Number
HOUSING(
Housing_ID: integer NOT NULL
Student_Number: integer NOT NULL
Building: variable length character string length 25 NOT NULL)
Primary Key Housing_ID
Foreign Key Student_Number References
STUDENT(Student_Number)
ON DELETE NO CHECK
ON UPDATE
Which integrity constraint is violated in this relation definition?
