HPE6-A70 HP Aruba Certified Mobility Associate Exam Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your HP HPE6-A70 Aruba Certified Mobility Associate Exam certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution with a WLAN that assigns users to VLANs 10–19. The company wants the Aruba solution to act at Layer 3 to route wireless user traffic.
What must network administrators configure to permit the solution to forward traffic correctly?
Which feature is unique to 802.11ac Wave 2 access points?
An Aruba solution has a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security. How are encryption keys dynamically managed for the wireless users?
Which APs operate in an autonomous or standalone mode?
A WLAN in an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution enforces Enterprise-WPA2 security and uses the tunnel forwarding mode. The company has an external RADIUS server.
Which device exchanges RADIUS packets with the RADIUS server?
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM). The MM will manage 50 Mobility Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 680 APs, and 10 Virtual Mobility Controllers (VMCs) that will control a total of 160 APs.
How many MM licenses does the company require?
A company has a Mobility Master (MM)-based solution. A network administrator wants to monitor data transfer speed ranges of all currently connected clients.
Which dashboard page in the MM interface should the administrator visit?
A company currently uses 802.11ac Wave 1 as a wireless solution. They want to upgrade to 802.11ac Wave2.
Which new feature will now be available with this upgrade?
A company deploys an Aruba wireless solution for the first time. In which deployment is clustering supported?
A network administrator examines a list of 2.4GHz clients with low performance in the Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. Which property for a client should pose a concern as a potential performance issue?
What is required for a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security?
A company deploys a wireless network in a typical office environment with many surfaces where the signal can bounce. Which 802.11 technology uses the characteristics of this environment to increase wireless speeds?
Refer to the exhibit.
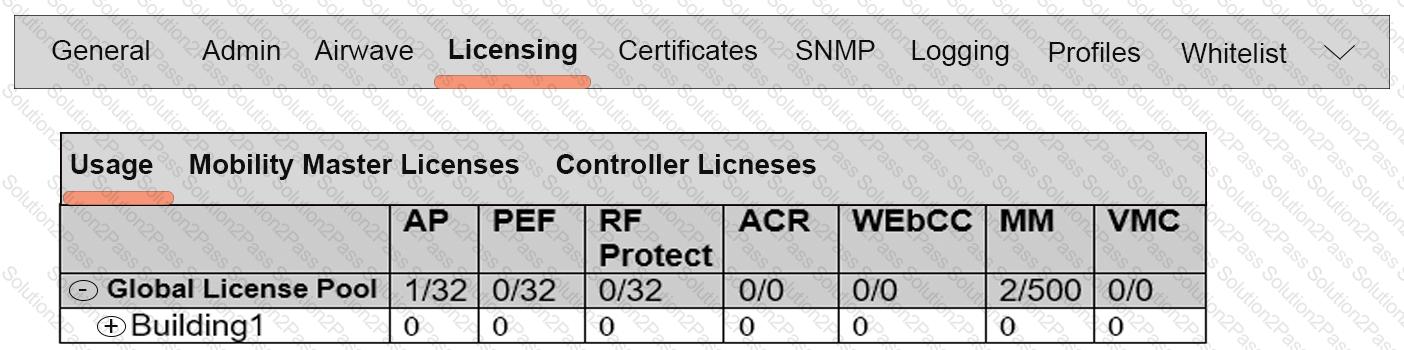
Based on the exhibit, what is the maximum number of APs that this Mobility Master (MM) solution can support?
Refer to the exhibit.
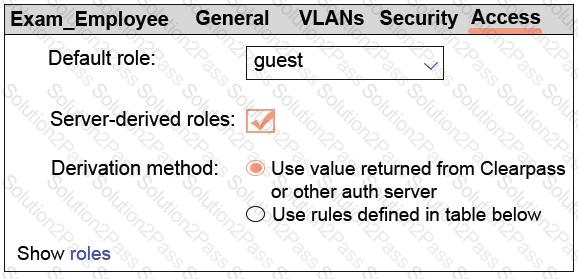
A network administrator sets up the Exam_Employees WLAN on an Aruba solution with a default role of guest, as shown in the exhibit. To which users does the guest role apply?
What is a requirement for the Dashboard > Traffic Analysis window on the Aruba Mobility Master (MM) to show data?
What is a role fulfilled by an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1
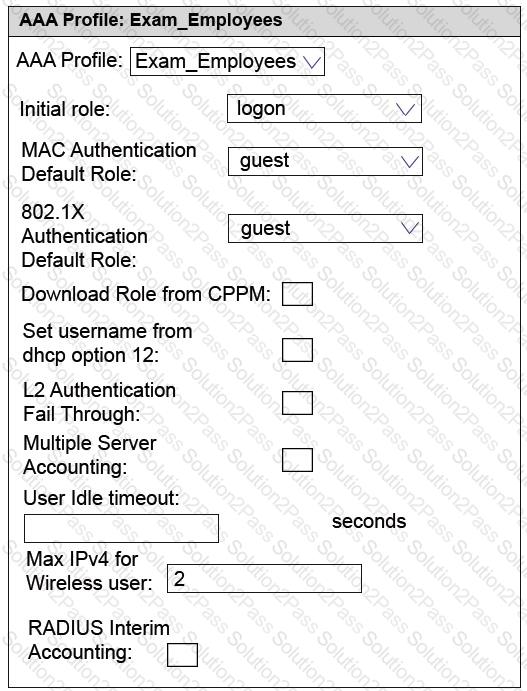
Exhibit 2

An Aruba solution supports a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security. Exhibit 1 shows the AAA policy for the WLAN. Users are supposed to be assigned to different roles after authentication. Network administrators test a connection with the employee user account. Exhibit 2 shows the status for the client after this test.
What is a possible reason for the issue shown in Exhibit 2?
A company has an Aruba solution. The company wants to support a guest WLAN with the internal captive portal, but the company also wants to develop their own custom portal pages.
What correctly describes the level of customization that the internal captive portal supports?
Refer to the exhibit.
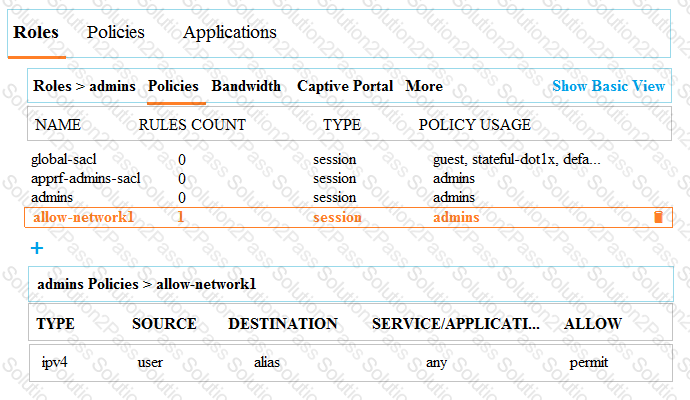
The alias in the rule shown in the exhibit is network 10.1.1.0/24.
A wireless client is assigned IP address 10.1.2.10/24 and the “admins” role. The wireless client at 10.1.2.10 attempts to initiate a Web session with a server at 10.1.1.2. A wired client at 10.1.1.3 attempts to initiate an SSH session with the wireless client at 10.1.2.10.
How does the Aruba firewall handle these attempts?
