CISSP ISC Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your ISC CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when developing a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)?
The dynamic reconfiguration of systems
The cost of downtime
A recovery strategy for all business processes
A containment strategy
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
According to the CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide1, the most important consideration when developing a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) is to have a recovery strategy for all business processes. A DRP is a document that defines the procedures and actions to be taken in the event of a disaster that disrupts the normal operations of an organization. A recovery strategy is a plan that specifies how the organization will restore the critical business processes and functions, as well as the supporting resources, such as data, systems, personnel, and facilities, within the predefined recovery objectives and time frames. A recovery strategy should cover all business processes, not just the IT-related ones, as they may have interdependencies and impacts on each other. A recovery strategy should also be aligned with the business continuity plan (BCP), which is a document that defines the procedures and actions to be taken to ensure the continuity of the essential business operations during and after a disaster. The dynamic reconfiguration of systems is not the most important consideration when developing a DRP, although it may be a useful technique to enhance the resilience and availability of the systems. The dynamic reconfiguration of systems is the ability to change the configuration and functionality of the systems without interrupting their operations, such as adding, removing, or replacing components, modules, or services. The dynamic reconfiguration of systems may help to reduce the downtime and recovery time of the systems, but it does not address the recovery of the business processes and functions. The cost of downtime is not the most important consideration when developing a DRP, although it may be a factor that influences the recovery objectives and priorities. The cost of downtime is the amount of money that the organization loses or spends due to the disruption of its normal operations, such as loss of revenue, productivity, reputation, or customers, as well as the expenses for recovery, restoration, or compensation. The cost of downtime may help to justify the investment and budget for the DRP, but it does not address the recovery of the business processes and functions. A containment strategy is not the most important consideration when developing a DRP, although it may be a part of the incident response plan (IRP), which is a document that defines the procedures and actions to be taken to detect, analyze, contain, eradicate, and recover from a security incident. A containment strategy is a plan that specifies how the organization will isolate and control the incident, such as disconnecting the affected systems, blocking the malicious traffic, or changing the passwords. A containment strategy may help to prevent or limit the damage and spread of the incident, but it does not address the recovery of the business processes and functions. References: 1
How should an organization determine the priority of its remediation efforts after a vulnerability assessment has been conducted?
Use an impact-based approach.
Use a risk-based approach.
Use a criticality-based approach.
Use a threat-based approach.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
According to the CISSP For Dummies4, the best way to determine the priority of the remediation efforts after a vulnerability assessment has been conducted is to use a risk-based approach. A vulnerability assessment is the process of identifying and measuring the weaknesses and exposures in a system, network, or application, that may be exploited by threats and cause harm to the organization or its assets. A risk-based approach is a method that prioritizes the remediation efforts based on the level of risk associated with each vulnerability, which is calculated by considering the impact and likelihood of the threat exploiting the vulnerability. A risk-based approach helps to allocate the resources and efforts to the most critical and urgent vulnerabilities, and to reduce the overall risk to an acceptable level. Using an impact-based approach is not the best way to determine the priority of the remediation efforts, as it only considers the potential consequences of the threat exploiting the vulnerability, but not the probability of the occurrence. An impact-based approach may overestimate or underestimate the risk level of some vulnerabilities, and may not reflect the true urgency and severity of the vulnerabilities. Using a criticality-based approach is not the best way to determine the priority of the remediation efforts, as it only considers the importance or value of the asset or system that is affected by the vulnerability, but not the threat or the vulnerability itself. A criticality-based approach may overestimate or underestimate the risk level of some vulnerabilities, and may not reflect the true urgency and severity of the vulnerabilities. Using a threat-based approach is not the best way to determine the priority of the remediation efforts, as it only considers the characteristics and capabilities of the threat that may exploit the vulnerability, but not the vulnerability or the impact itself. A threat-based approach may overestimate or underestimate the risk level of some vulnerabilities, and may not reflect the true urgency and severity of the vulnerabilities. References: 4
Order the below steps to create an effective vulnerability management process.
The Answer Is:
In the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories is a critical part of
systems integration.
risk management.
quality assurance.
change management.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide1, the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories is change management. SDLC is a structured process that is used to design, develop, and test good-quality software. SDLC consists of several phases or stages that cover the entire life cycle of the software, from the initial idea or concept to the final deployment or maintenance of the software. SDLC aims to deliver high-quality, maintainable software that meets the user’s requirements and fits within the budget and schedule of the project. Change management is the process of controlling or managing the changes or modifications that are made to the software or the system during the SDLC, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the policies, procedures, or tools of the project. Change management helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the software or the system, as well as the quality or the performance of the software or the system, by preventing or minimizing the risks or the impacts of the changes or modifications that may affect or impair the software or the system, such as the errors, defects, or vulnerabilities of the software or the system. Maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories is a critical part of change management, as it provides or supports a reliable or consistent source or basis to identify or track the hardware and software components or elements that are involved or included in the software or the system, as well as the changes or modifications that are made to the hardware and software components or elements during the SDLC, such as the name, description, version, status, or value of the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system. Maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the software or the system, as well as the quality or the performance of the software or the system, by enabling or facilitating the monitoring, evaluation, or improvement of the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the reporting, auditing, or optimization of the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system. Systems integration is not the SDLC phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of change management. Systems integration is the process of combining or integrating the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the interfaces, protocols, or standards of the project. Systems integration helps to ensure the functionality or the interoperability of the software or the system, as well as the compatibility or the consistency of the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system, by ensuring or verifying that the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system work or operate together or with other systems or networks, as intended or expected by the user or the client of the software or the system. Systems integration may be a benefit or a consequence of change management, as change management may provide or support a framework or a guideline to perform or conduct the systems integration, by controlling or managing the changes or modifications that are made to the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system, as well as by maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories of the software or the system. However, systems integration is not the SDLC phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories, as it is not the main or the most important objective or purpose of systems integration, which is to combine or integrate the hardware and software components or elements of the software or the system. Risk management is not the SDLC phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of change management. Risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and treating the risks or the uncertainties that may affect or impair the software or the system, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the policies, procedures, or tools of the project. Risk management helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the software or the system, as well as the quality or the performance of the software or the system, by preventing or minimizing the impact or the consequence of the risks or the uncertainties that may harm or damage the software or the system, such as the threats, attacks, or incidents of the software or the system. Risk management may be a benefit or a consequence of change management, as change management may provide or support a framework or a guideline to perform or conduct the risk management, by controlling or managing the changes or modifications that are made to the software or the system, as well as by maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories of the software or the system. However, risk management is not the SDLC phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories, as it is not the main or the most important objective or purpose of risk management, which is to identify, analyze, evaluate, and treat the risks or the uncertainties of the software or the system. Quality assurance is not the SDLC phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of change management. Quality assurance is the process of ensuring or verifying the quality or the performance of the software or the system, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the standards, criteria, or metrics of the project. Quality assurance helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the software or the system, as well as the quality or the performance of the software or the system, by preventing or detecting the errors, defects, or vulnerabilities of the software or the system, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the testing, validation, or verification of the software or the system. Quality assurance may be a benefit or a consequence of change management, as change management may provide or support a framework or a guideline to perform or conduct the quality assurance, by controlling or managing the changes or modifications that are made to the software or the system, as well as by maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories of the software or the system. However, quality assurance is not the SDLC phase that requires maintaining accurate hardware and software inventories, as it is not the main or the most important objective or purpose of quality assurance, which is to ensure or verify the quality or the performance of the software or the system.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) restricts access according to
data classification labeling.
page views within an application.
authorizations granted to the user.
management accreditation.
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) restricts access according to authorizations granted to the user. DAC is a type of access control that allows the owner or creator of a resource to decide who can access it and what level of access they can have. DAC uses access control lists (ACLs) to assign permissions to resources, and users can pass or change their permissions to other users
What is the BEST way to encrypt web application communications?
Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA-1)
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code (CBC-MAC)
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
TLS is the successor to SSL and is considered to be the best option for encrypting web application communications. It provides secure communication between web browsers and servers, ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and authentication. References: ISC2 CISSP
Which of the following is the MOST important output from a mobile application threat modeling exercise according to Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)?
Application interface entry and endpoints
The likelihood and impact of a vulnerability
Countermeasures and mitigations for vulnerabilities
A data flow diagram for the application and attack surface analysis
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
The most important output from a mobile application threat modeling exercise according to OWASP is a data flow diagram for the application and attack surface analysis. A data flow diagram is a graphical representation of the data flows and processes within the application, as well as the external entities and boundaries that interact with the application. An attack surface analysis is a systematic evaluation of the potential vulnerabilities and threats that can affect the application, based on the data flow diagram and other sources of information. These two outputs can help identify and prioritize the security risks and requirements for the mobile application, as well as the countermeasures and mitigations for the vulnerabilities.
A. Application interface entry and endpoints is not the most important output from a mobile application threat modeling exercise according to OWASP, but rather one of the components or elements of the data flow diagram. Application interface entry and endpoints are the points where the data enters or exits the application, such as user inputs, network connections, or API calls. These points can be the sources or targets of attacks, and they need to be properly secured and validated.
B. The likelihood and impact of a vulnerability is not the most important output from a mobile application threat modeling exercise according to OWASP, but rather one of the factors or criteria for the risk assessment of the vulnerabilities. The likelihood and impact of a vulnerability are the measures of the probability and severity of the vulnerability being exploited, respectively. These measures can help determine the level of risk and the priority of the mitigation for the vulnerability.
C. Countermeasures and mitigations for vulnerabilities is not the most important output from a mobile application threat modeling exercise according to OWASP, but rather one of the outcomes or objectives of the threat modeling exercise. Countermeasures and mitigations for vulnerabilities are the actions or controls that can prevent, reduce, or eliminate the vulnerabilities or their consequences. These actions or controls can be implemented at different stages of the mobile application development life cycle, such as design, coding, testing, or deployment.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, page 487; [Official
Which of the following is the BEST method to assess the effectiveness of an organization's vulnerability management program?
Review automated patch deployment reports
Periodic third party vulnerability assessment
Automated vulnerability scanning
Perform vulnerability scan by security team
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
A third-party vulnerability assessment provides an unbiased evaluation of the organization’s security posture, identifying existing vulnerabilities and offering recommendations for mitigation. It is more comprehensive and objective compared to internal reviews or automated scans. References: CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests, Chapter 5, page 137
Which of the following are Systems Engineering Life Cycle (SELC) Technical Processes?
Concept, Development, Production, Utilization, Support, Retirement
Stakeholder Requirements Definition, Architectural Design, Implementation, Verification, Operation
Acquisition, Measurement, Configuration Management, Production, Operation, Support
Concept, Requirements, Design, Implementation, Production, Maintenance, Support, Disposal
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
The Systems Engineering Life Cycle (SELC) Technical Processes are the activities that transform stakeholder needs into a system solution. They include the following five processes: Stakeholder Requirements Definition, Architectural Design, Implementation, Verification, and Operation.
References:
Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 8, p. 489.
CISSP practice exam questions and answers, Question 11.
Which of the following approaches is the MOST effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives?
Delete every file on each drive.
Destroy the partition table for each drive using the command line.
Degauss each drive individually.
Perform multiple passes on each drive using approved formatting methods.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests3, the most effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives is to perform multiple passes on each drive using approved formatting methods. This means that the data on the hard drives should be overwritten with random or meaningless patterns several times, using software tools or commands that follow the standards and guidelines for secure data erasure. This can ensure that the data on the hard drives is irrecoverable and unreadable, even by using advanced forensic techniques or tools. Deleting every file on each drive is not an effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives, as it does not actually erase the data, but only removes the pointers or references to the data. The data can still be recovered and read by using undelete or recovery tools, or by accessing the slack or unallocated space on the drive. Destroying the partition table for each drive using the command line is not an effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives, as it does not actually erase the data, but only removes the information about how the drive is divided into logical sections. The data can still be recovered and read by using partition recovery tools, or by accessing the raw data on the drive. Degaussing each drive individually is not an effective way to dispose of data on multiple hard drives, as it may not work on modern hard drives that use perpendicular recording technology. Degaussing is a process that uses a strong magnetic field to erase the data on magnetic media, such as tapes or disks. However, modern hard drives have higher coercivity, which means they require a stronger magnetic field to be erased, and degaussing may not be able to generate such a field. Degaussing may also damage the hard drive components and render them unusable. References: 3
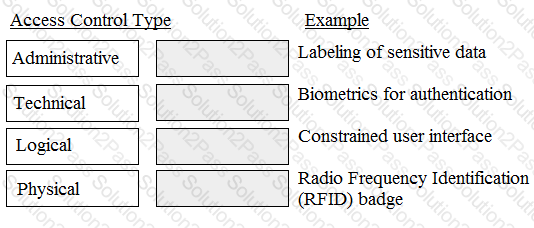
Match the access control type to the example of the control type.
Drag each access control type net to its corresponding example.
The Answer Is:
Explanation:
The following is a possible answer for the drag and drop question:

According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide1, access control is the process of granting or denying access to resources, data, or information, based on the identity, role, or credentials of the subject or the entity, as well as the security policies and rules of the system or the network. Access control can be classified into four types, which are:
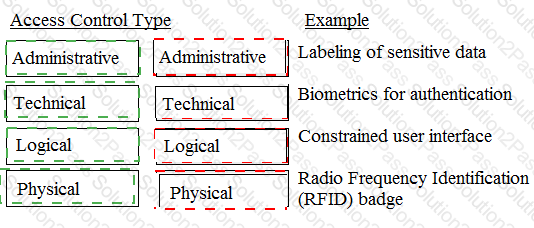
Administrative: Access control that is implemented through the policies, procedures, and processes that govern the management and monitoring of the access control system, such as the identification, authentication, authorization, and accountability of the subjects and the entities, as well as the classification, labeling, and handling of the resources, data, or information. An example of administrative access control is labeling of sensitive data, which is the process of applying security attributes or tags to the data that indicate the classification, sensitivity, or clearance of the data, such as top secret, secret, or confidential. Labeling of sensitive data helps to identify and distinguish the data based on their security attributes, as well as to inform and instruct the users or handlers of the data about the proper and secure handling and disposal of them.
Technical: Access control that is implemented through the hardware, software, or firmware components or mechanisms that enforce and execute the access control policies and rules, such as the encryption, decryption, hashing, or digital signature of the data, or the biometrics, tokens, or certificates of the subjects or the entities. An example of technical access control is biometrics for authentication, which is the process of verifying and confirming the identity of the subject or the entity based on their physical or behavioral characteristics, such as the fingerprint, iris, voice, or signature of the subject or the entity. Biometrics for authentication helps to ensure the authenticity and uniqueness of the subject or the entity, as it uses the characteristics that are inherent and distinctive to the subject or the entity, and that are difficult to forge, copy, or share.
Logical: Access control that is implemented through the software or application components or mechanisms that restrict and regulate the access or use of the resources, data, or information, based on the logic, function, or operation of the system or the network, such as the passwords, usernames, roles, or permissions of the subjects or the entities, or the firewalls, routers, or switches of the system or the network. An example of logical access control is constrained user interface, which is the process of limiting or hiding the features or functions of the system or the network that are not relevant or authorized for the subject or the entity, such as the menus, buttons, or commands of the system or the network. Constrained user interface helps to reduce the complexity and confusion of the system or the network, as well as to prevent or minimize the errors or problems that may occur from the misuse or abuse of the system or the network.
Physical: Access control that is implemented through the physical or tangible components or mechanisms that prevent or deter the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the resources, data, or information, such as the locks, keys, doors, or windows of the premises or the facilities, or the badges, cards, or tags of the subjects or the entities. An example of physical access control is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) badge, which is a device or a material that emits or responds to radio waves, and that contains or stores the identification or the information of the subject or the entity, such as the name, number, or photo of the subject or the entity. RFID badge helps to identify and locate the subject or the entity, as well as to grant or deny the access or entry to the premises or the facilities.
Which of the following describes the BEST configuration management practice?
After installing a new system, the configuration files are copied to a separate back-up system and hashed to detect tampering.
After installing a new system, the configuration files are copied to an air-gapped system and hashed to detect tampering.
The firewall rules are backed up to an air-gapped system.
A baseline configuration is created and maintained for all relevant systems.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
The best configuration management practice is to create and maintain a baseline configuration for all relevant systems. A baseline configuration is a documented and approved set of specifications and settings for a system or component that serves as a standard for comparison and evaluation. A baseline configuration can help ensure the consistency, security, and performance of the system or component, as well as facilitate the identification and resolution of any deviations or issues. A baseline configuration should be updated and reviewed regularly to reflect the changes and improvements made to the system or component12 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 7: Security Operations, p. 456; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 7: Security Operations, p. 869.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to perform regular vulnerability scanning of an organization network?
Provide vulnerability reports to management.
Validate vulnerability remediation activities.
Prevent attackers from discovering vulnerabilities.
Remediate known vulnerabilities.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
According to the CISSP Official (ISC)2 Practice Tests, the primary reason to perform regular vulnerability scanning of an organization network is to remediate known vulnerabilities. A vulnerability scanning is the process of identifying and measuring the weaknesses and exposures in a system, network, or application, that may be exploited by threats and cause harm to the organization or its assets. A vulnerability scanning can be performed by using various tools, techniques, or methods, such as automated scanners, manual tests, or penetration tests. The primary reason to perform regular vulnerability scanning of an organization network is to remediate known vulnerabilities, which means to fix, mitigate, or eliminate the vulnerabilities that are discovered or reported by the vulnerability scanning. Remediation of known vulnerabilities helps to improve the security posture and effectiveness of the system, network, or application, as well as to reduce the overall risk to an acceptable level. Providing vulnerability reports to management is not the primary reason to perform regular vulnerability scanning of an organization network, although it may be a benefit or outcome of it. Vulnerability reports are the documents that provide the evidence and analysis of the vulnerability scanning, such as the scope, objectives, methods, results, and recommendations of the vulnerability scanning. Vulnerability reports help to communicate and document the findings and issues of the vulnerability scanning, as well as to support the decision making and planning for the remediation of the vulnerabilities. Validating vulnerability remediation activities is not the primary reason to perform regular vulnerability scanning of an organization network, although it may be a part or step of it. Validating vulnerability remediation activities is the process of verifying and testing the effectiveness and completeness of the remediation actions that are taken to address the vulnerabilities, such as patching, updating, configuring, or replacing the system, network, or application components. Validating vulnerability remediation activities helps to ensure that the vulnerabilities are properly and successfully remediated, and that no new or residual vulnerabilities are introduced or left behind. Preventing attackers from discovering vulnerabilities is not the primary reason to perform regular vulnerability scanning of an organization network, although it may be a benefit or outcome of it. Preventing attackers from discovering vulnerabilities is the process of hiding or obscuring the vulnerabilities from the potential attackers, by using various techniques or methods, such as encryption, obfuscation, or deception. Preventing attackers from discovering vulnerabilities helps to reduce the likelihood and opportunity of the attackers to exploit the vulnerabilities, but it does not address the root cause or the impact of the vulnerabilities.
Which of the following entities is ultimately accountable for data remanence vulnerabilities with data replicated by a cloud service provider?
Data owner
Data steward
Data custodian
Data processor
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
The entity that is ultimately accountable for data remanence vulnerabilities with data replicated by a cloud service provider is the data owner. A data owner is a person or an entity that has the authority or the responsibility for the data or the information within an organization, and that determines or defines the classification, the usage, the protection, or the retention of the data or the information. A data owner has the obligation to ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization, as the data owner is ultimately accountable or liable for the security or the quality of the data or the information, regardless of who processes or handles the data or the information. A data owner can ensure that a third party provider is capable of processing and handling data in a secure manner and meeting the standards set by the organization, by performing the tasks or the functions such as conducting due diligence, establishing service level agreements, defining security requirements, monitoring performance, or auditing compliance. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 2, page 61; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 2, page 67
Which of the following media sanitization techniques is MOST likely to be effective for an organization using public cloud services?
Low-level formatting
Secure-grade overwrite erasure
Cryptographic erasure
Drive degaussing
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
Media sanitization is the process of rendering the data on a storage device inaccessible or unrecoverable by a given level of effort. For an organization using public cloud services, the most effective media sanitization technique is cryptographic erasure, which involves encrypting the data on the device with a strong key and then deleting the key, making the data unreadable. Cryptographic erasure is suitable for cloud environments because it does not require physical access to the device, it can be performed remotely and quickly, and it does not affect the performance or lifespan of the device. Low-level formatting, secure-grade overwrite erasure, and drive degaussing are media sanitization techniques that require physical access to the device, which may not be possible or feasible for cloud users. Additionally, these techniques may not be compatible with some cloud storage technologies, such as solid-state drives (SSDs) or flash memory, and they may reduce the performance or lifespan of the device.
When building a data classification scheme, which of the following is the PRIMARY concern?
Purpose
Cost effectiveness
Availability
Authenticity
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
A data classification scheme is a framework that defines the categories and levels of data sensitivity, as well as the policies and procedures for handling them. The primary concern when building a data classification scheme is the purpose of the data, i.e., why it is collected, processed, stored, and shared, and what are the risks and benefits associated with it. The purpose of the data determines its value, impact, and protection requirements.
Cost effectiveness (B) is a secondary concern that affects the implementation and maintenance of a data classification scheme, but it is not the primary driver for creating one. Availability © and authenticity (D) are two aspects of data security that depend on the data classification scheme, but they are not the main factors for designing one. Therefore, B, C, and D are incorrect answers.
The implementation of which features of an identity management system reduces costs and administration overhead while improving audit and accountability?
Two-factor authentication
Single Sign-On (SSO)
User self-service
A metadirectory
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
The feature of an identity management system that reduces costs and administration overhead while improving audit and accountability is user self-service. Identity management system is a system that manages the identity and the access of the users or the devices within an organization or a network, by performing the functions or the processes related to the identity and the access lifecycle, such as identification, authentication, authorization, and accountability. User self-service is a feature of an identity management system that allows the users or the devices to perform some of the tasks or the functions related to their identity and access management, such as creating, updating, or deleting their accounts, passwords, or profiles, or requesting, approving, or revoking their access rights or privileges, without requiring the intervention or the assistance of the administrators or the operators. User self-service can reduce the costs and the administration overhead for the organization, as it can decrease the workload and the dependency of the administrators or the operators, and it can increase the efficiency and the productivity of the users or the devices. User self-service can also improve the audit and the accountability for the organization, as it can provide more transparency and traceability of the identity and the access management activities, and it can enhance the compliance and the security of the identity and the access management policies and standards.
A. Two-factor authentication is not a feature of an identity management system that reduces costs and administration overhead while improving audit and accountability, but rather a feature of an identity management system that enhances the security and the reliability of the identity and the access management. Two-factor authentication is a feature of an identity management system that verifies the identity and the legitimacy of the users or the devices by requiring two or more factors or methods of authentication, such as something the user knows (e.g., password, PIN, or security question), something the user has (e.g., token, card, or smartphone), or something the user is (e.g., fingerprint, face, or voice). Two-factor authentication can enhance the security and the reliability of the identity and the access management, as it can prevent or reduce the risk of unauthorized or inappropriate access or login, by adding an extra layer of protection and verification for the users or the devices.
B. Single sign-on (SSO) is not a feature of an identity management system that reduces costs and administration overhead while improving audit and accountability, but rather a feature of an identity management system that improves the usability and the convenience of the identity and the access management. SSO is a feature of an identity management system that allows the users or the devices to access multiple or different applications, systems, or networks, by using a single or a common set of credentials, such as a username and a password, or a token and a PIN, without requiring to authenticate or to login separately or repeatedly for each application, system, or network. SSO can improve the usability and the convenience of the identity and the access management, as it can simplify and streamline the access and the login process for the users or the devices, and it can reduce the complexity and the redundancy of the credentials.
D. A metadirectory is not a feature of an identity management system that reduces costs and administration overhead while improving audit and accountability, but rather a feature of an identity management system that enables the integration and the synchronization of the identity and the access management. A metadirectory is a feature of an identity management system that stores and manages the identity and the access information of the users or the devices from multiple or different sources, such as directories, databases, or applications, and provides a unified and consistent view and access of the identity and the access information for the users or the devices. A metadirectory can enable the integration and the synchronization of the identity and the access management, as it can support the interoperability and the compatibility of the identity and the access information across different platforms, systems, or networks, and it can ensure the accuracy and the currency of the identity and the access information.
When evaluating third-party applications, which of the following is the GREATEST responsibility of Information Security?
Accept the risk on behalf of the organization.
Report findings to the business to determine security gaps.
Quantify the risk to the business for product selection.
Approve the application that best meets security requirements.
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
According to the CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide1, the greatest responsibility of Information Security when evaluating third-party applications is to quantify the risk to the business for product selection. This means that Information Security should assess the potential impact and likelihood of threats and vulnerabilities associated with the applications, and communicate the results to the business stakeholders who are responsible for making the final decision. Information Security should not accept the risk on behalf of the organization, report findings to the business without providing risk analysis, or approve the application that best meets security requirements without considering the business needs and objectives.
What balance MUST be considered when web application developers determine how informative application error messages should be constructed?
Risk versus benefit
Availability versus auditability
Confidentiality versus integrity
Performance versus user satisfaction
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
According to the CXL blog2, the balance that must be considered when web application developers determine how informative application error messages should be constructed is risk versus benefit. Application error messages are the messages that are displayed or communicated to the users when an error or a problem occurs in the web application, such as a login failure, a form validation error, or a server error. Application error messages are important for the user experience and the conversion rate, as they help the users to understand and resolve the error or the problem, as well as to continue or complete their tasks or goals on the web application. However, application error messages also pose some risks or challenges for the web application developers, as they may reveal or expose some sensitive or confidential information about the web application, such as the system architecture, the database structure, or the security vulnerabilities, which may be exploited or attacked by the malicious users or hackers. Therefore, web application developers need to consider the balance between the risk and the benefit when determining how informative application error messages should be constructed. The risk is the potential or possibility of harm or damage to the web application, the data, or the users, as a result of the application error messages, such as the loss of privacy, integrity, or availability. The benefit is the value or advantage of the application error messages for the web application, the data, or the users, such as the improvement of usability, functionality, or security. Web application developers need to weigh the risk and the benefit of the application error messages, and decide how much and what kind of information to include or exclude in the application error messages, as well as how to present or format the information in the application error messages, in order to achieve the optimal balance between the risk and the benefit. Availability versus auditability is not the balance that must be considered when web application developers determine how informative application error messages should be constructed, as it is not related to the information or the presentation of the application error messages, but to the performance or the monitoring of the web application. Availability is the property that ensures that the web application, the data, or the users are accessible or usable when needed or desired, and are protected from unauthorized or unintended denial or disruption. Auditability is the property that ensures that the web application, the data, or the users are traceable or accountable for their actions or events, and are supported by the logging or recording mechanisms. Availability and auditability are both important for the web application, the data, and the users, but they are not the balance that must be considered when determining how informative application error messages should be constructed, as they do not affect or influence the information or the presentation of the application error messages. Confidentiality versus integrity is not the balance that must be considered when web application developers determine how informative application error messages should be constructed, as it is not related to the information or the presentation of the application error messages, but to the protection or the quality of the data. Confidentiality is the property that ensures that the data is only accessible or disclosed to the authorized parties, and is protected from unauthorized or unintended access or disclosure. Integrity is the property that ensures that the data is accurate, complete, and consistent, and is protected from unauthorized or unintended modification or corruption. Confidentiality and integrity are both important for the data, but they are not the balance that must be considered when determining how informative application error messages should be constructed, as they do not affect or influence the information or the presentation of the application error messages. Performance versus user satisfaction is not the balance that must be considered when web application developers determine how informative application error messages should be constructed, as it is not related to the information or the presentation of the application error messages, but to the efficiency or the effectiveness of the web application. Performance is the measure or indicator of how well the web application performs its functions or services, such as the speed, reliability, or scalability of the web application. User satisfaction is the measure or indicator of how satisfied the users are with the web application, its functions or services, or its user experience, such as the usability, functionality, or security of the web application. Performance and user satisfaction are both important for the web application, but they are not the balance that must be considered when determining how informative application error messages should be constructed, as they do not affect or influence the information or the presentation of the application error messages. References: 2
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation?
To verify that only employees have access to the facility.
To identify present hazards requiring remediation.
To monitor staff movement throughout the facility.
To provide a safe environment for employees.
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
According to the CISSP CBK Official Study Guide, the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation is to provide a safe environment for employees. Physical security personnel are the human or the personnel components or elements of the physical security system or the network, which is the system or the network that prevents or deters the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the resources, data, or information, such as the locks, keys, doors, or windows of the premises or the facilities, or the badges, cards, or tags of the subjects or the entities. Physical security personnel may perform various functions or tasks, such as the guarding, patrolling, or monitoring of the premises or the facilities, or the verifying, identifying, or authenticating of the subjects or the entities. Employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation helps to provide a safe environment for employees, as it enhances or supplements the security or the protection of the premises or the facilities, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the premises or the facilities, by adding or applying an additional layer or level of security or protection, as well as a human or a personal touch or factor, to the physical security system or the network. Providing a safe environment for employees helps to ensure the safety or the well-being of the employees, as well as the productivity or the performance of the employees, as it reduces or eliminates the risks or the threats that may harm or damage the employees, such as the theft, vandalism, or violence of the employees. To verify that only employees have access to the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. Verifying that only employees have access to the facility is the process of checking or confirming that the subjects or the entities that enter or access the facility are the employees or the authorized users or clients of the facility, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the card access, the biometrics, or the physical security personnel of the facility. Verifying that only employees have access to the facility helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, as it prevents or limits the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the facility, which may lead to the attacks or threats that may harm or damage the facility, such as the theft, vandalism, or violence of the facility. Verifying that only employees have access to the facility may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as physical security personnel may perform the function or the task of verifying, identifying, or authenticating the subjects or the entities that enter or access the facility, by using or applying the card access, the biometrics, or other methods or mechanisms of the facility. However, verifying that only employees have access to the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as it is not the main or the most important reason or objective for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. To identify present hazards requiring remediation is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. Identifying present hazards requiring remediation is the process of detecting or discovering the existing or the current hazards or dangers that may affect or impair the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, such as the fire, flood, or earthquake of the facility, as well as the actions or the measures that are needed or required to fix or resolve the hazards or dangers, such as the evacuation, recovery, or contingency of the facility. Identifying present hazards requiring remediation helps to ensure the safety or the well-being of the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, as it reduces or eliminates the impact or the consequence of the hazards or dangers that may harm or damage the facility, such as the fire, flood, or earthquake of the facility. Identifying present hazards requiring remediation may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as physical security personnel may perform the function or the task of detecting or discovering the existing or the current hazards or dangers that may affect or impair the facility, as well as the actions or the measures that are needed or required to fix or resolve the hazards or dangers, by using or applying the appropriate tools or techniques, such as the sensors, alarms, or cameras of the facility. However, identifying present hazards requiring remediation is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as it is not the main or the most important reason or objective for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. To monitor staff movement throughout the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, although it may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility is the process of observing or tracking the activities or the behaviors of the staff or the employees that work or operate in the facility, such as the entry, exit, or location of the staff or the employees, by using or applying the appropriate methods or mechanisms, such as the card access, the biometrics, or the physical security personnel of the facility. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility helps to ensure the security or the integrity of the facility, as well as the resources, data, or information that are contained or stored in the facility, as it prevents or limits the unauthorized or unintended access or entry to the facility, which may lead to the attacks or threats that may harm or damage the facility, such as the theft, vandalism, or violence of the facility. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility may also help to ensure the productivity or the performance of the staff or the employees, as it prevents or limits the misuse or abuse of the facility, such as the idle, waste, or fraud of the facility. Monitoring staff movement throughout the facility may be a benefit or a consequence of employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as physical security personnel may perform the function or the task of observing or tracking the activities or the behaviors of the staff or the employees that work or operate in the facility, by using or applying the card access, the biometrics, or other methods or mechanisms of the facility. However, monitoring staff movement throughout the facility is not the primary reason for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation, as it is not the main or the most important reason or objective for employing physical security personnel at entry points in facilities where card access is in operation.
A security professional has been asked to evaluate the options for the location of a new data center within a multifloor building. Concerns for the data center include emanations and physical access controls.
Which of the following is the BEST location?
On the top floor
In the basement
In the core of the building
In an exterior room with windows
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
The best location for a new data center within a multifloor building is in the core of the building. This location can minimize the emanations and enhance the physical access controls. Emanations are the electromagnetic signals or radiation that are emitted by electronic devices, such as computers, servers, or network equipment. Emanations can be intercepted or captured by attackers to obtain sensitive or confidential information. Physical access controls are the measures that prevent or restrict unauthorized or malicious access to physical assets, such as data centers, servers, or network devices. Physical access controls can include locks, doors, gates, fences, guards, cameras, alarms, etc. The core of the building is the central part of the building that is usually surrounded by other rooms or walls. This location can reduce the emanations by creating a shielding effect and increasing the distance from the potential attackers. The core of the building can also improve the physical access controls by limiting the entry points and visibility of the data center12 References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 3: Security Engineering, p. 133; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Domain 3: Security Engineering, p. 295.
The MAIN reason an organization conducts a security authorization process is to
force the organization to make conscious risk decisions.
assure the effectiveness of security controls.
assure the correct security organization exists.
force the organization to enlist management support.
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
The main reason an organization conducts a security authorization process is to force the organization to make conscious risk decisions. A security authorization process is a process that evaluates and approves the security of an information system or a product before it is deployed or used. A security authorization process involves three steps: security categorization, security assessment, and security authorization. Security categorization is the step of determining the impact level of the information system or product on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information and assets. Security assessment is the step of testing and verifying the security controls and measures implemented on the information system or product. Security authorization is the step of granting or denying the permission to operate or use the information system or product based on the security assessment results and the risk acceptance criteria. The security authorization process forces the organization to make conscious risk decisions, as it requires the organization to identify, analyze, and evaluate the risks associated with the information system or product, and to decide whether to accept, reject, mitigate, or transfer the risks. The other options are not the main reasons, but rather the benefits or outcomes of a security authorization process. Assuring the effectiveness of security controls is a benefit of a security authorization process, as it provides an objective and independent evaluation of the security controls and measures. Assuring the correct security organization exists is an outcome of a security authorization process, as it establishes the roles and responsibilities of the security personnel and stakeholders. Forcing the organization to enlist management support is an outcome of a security authorization process, as it involves the management in the risk decision making and approval process. References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 8, p. 419; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 3, p. 150.
Which of the following BEST avoids data reminisce disclosure for cloud hosted resources?
Strong encryption and deletion of the keys after data is deleted.
Strong encryption and deletion of the virtual host after data is deleted.
Software based encryption with two factor authentication.
Hardware based encryption on dedicated physical servers.
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
The best way to avoid data reminisce disclosure for cloud hosted resources is to use strong encryption and delete the virtual host after data is deleted. Data reminisce is the residual data that remains on the storage media after the data is deleted or overwritten. Data reminisce can pose a risk of data leakage or unauthorized access if the storage media is reused, recycled, or disposed of without proper sanitization. By using strong encryption, the data is protected from unauthorized decryption even if the data reminisce is recovered. By deleting the virtual host, the data is removed from the cloud provider’s infrastructure and the storage media is released from the allocation pool.
A. Strong encryption and deletion of the keys after data is deleted is not the best way to avoid data reminisce disclosure for cloud hosted resources, because it does not ensure that the data is completely erased from the storage media. Deleting the keys only prevents the data from being decrypted, but the data reminisce may still be recoverable by forensic tools or techniques.
C. Software based encryption with two factor authentication is not the best way to avoid data reminisce disclosure for cloud hosted resources, because it does not address the issue of data deletion or sanitization. Software based encryption relies on the operating system or the application to encrypt and decrypt the data, which may leave traces of the data or the keys in the memory or the cache. Two factor authentication only enhances the access control to the data, but it does not prevent the data reminisce from being exposed if the storage media is compromised.
D. Hardware based encryption on dedicated physical servers is not the best way to avoid data reminisce disclosure for cloud hosted resources, because it is not applicable to the cloud computing model. Hardware based encryption relies on the storage device or the controller to encrypt and decrypt the data, which may offer better performance and security than software based encryption. However, dedicated physical servers are not compatible with the cloud paradigm of shared, scalable, and elastic resources.
References: CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Eighth Edition, Chapter 5, page 282; Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, Fifth Edition, Chapter 5, page 247
Which of the following is the MOST important goal of information asset valuation?
Developing a consistent and uniform method of controlling access on information assets
Developing appropriate access control policies and guidelines
Assigning a financial value to an organization’s information assets
Determining the appropriate level of protection
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
According to the CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide2, the most important goal of information asset valuation is to assign a financial value to an organization’s information assets. Information asset valuation is the process of estimating the worth or importance of the information assets that an organization owns, creates, uses, or maintains, such as data, documents, records, or intellectual property. Information asset valuation helps the organization to measure the impact and return of its information assets, as well as to determine the appropriate level of protection, investment, and management for them. Information asset valuation also helps the organization to comply with the legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations that may require the disclosure or reporting of the value of its information assets. Developing a consistent and uniform method of controlling access on information assets is not the most important goal of information asset valuation, although it may be a benefit or outcome of it. Controlling access on information assets is the process of granting or denying the rights and permissions to access, use, modify, or disclose the information assets, based on the identity, role, or need of the users or processes. Controlling access on information assets helps the organization to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of its information assets, as well as to enforce the security policies and standards for them. Developing appropriate access control policies and guidelines is not the most important goal of information asset valuation, although it may be a benefit or outcome of it. Access control policies and guidelines are the documents that define the rules, principles, and procedures for controlling access on information assets, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders involved. Access control policies and guidelines help the organization to establish and communicate the expectations and requirements for controlling access on information assets, as well as to monitor and audit the compliance and effectiveness of the access control mechanisms. Determining the appropriate level of protection is not the most important goal of information asset valuation, although it may be a benefit or outcome of it. The level of protection is the degree or extent of the security measures and controls that are applied to the information assets, to prevent or mitigate the potential threats and risks that may affect them. The level of protection should be proportional to the value and sensitivity of the information assets, as well as the impact and likelihood of the threats and risks. References: 2
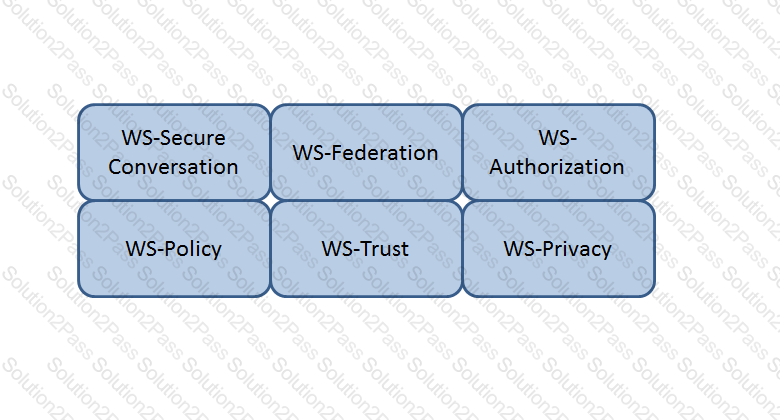
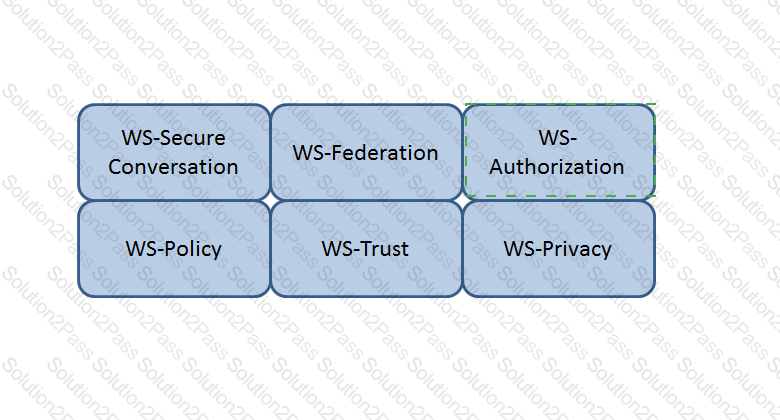
Which Web Services Security (WS-Security) specification handles the management of security tokens and the underlying policies for granting access? Click on the correct specification in the image below.
The Answer Is:
Explanation:
WS-Authorization
Which technique can be used to make an encryption scheme more resistant to a known plaintext attack?
Hashing the data before encryption
Hashing the data after encryption
Compressing the data after encryption
Compressing the data before encryption
The Answer Is:
DExplanation:
Compressing the data before encryption is a technique that can be used to make an encryption scheme more resistant to a known plaintext attack. A known plaintext attack is a type of cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to some pairs of plaintext and ciphertext encrypted with the same key, and tries to recover the key or decrypt other ciphertexts. A known plaintext attack can exploit the statistical properties or patterns of the plaintext or the ciphertext to reduce the search space or guess the key. Compressing the data before encryption can reduce the redundancy and increase the entropy of the plaintext, making it harder for the attacker to find any correlations or similarities between the plaintext and the ciphertext. Compressing the data before encryption can also reduce the size of the plaintext, making it more difficult for the attacker to obtain enough plaintext-ciphertext pairs for a successful attack.
The other options are not techniques that can be used to make an encryption scheme more resistant to a known plaintext attack, but rather techniques that can introduce other security issues or inefficiencies. Hashing the data before encryption is not a useful technique, as hashing is a one-way function that cannot be reversed, and the encrypted hash cannot be decrypted to recover the original data. Hashing the data after encryption is also not a useful technique, as hashing does not add any security to the encryption, and the hash can be easily computed by anyone who has access to the ciphertext. Compressing the data after encryption is not a recommended technique, as compression algorithms usually work better on uncompressed data, and compressing the ciphertext can introduce errors or vulnerabilities that can compromise the encryption.
Which security service is served by the process of encryption plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting cipher text with the sender’s public key?
Confidentiality
Integrity
Identification
Availability
The Answer Is:
CExplanation:
The security service that is served by the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key is identification. Identification is the process of verifying the identity of a person or entity that claims to be who or what it is. Identification can be achieved by using public key cryptography and digital signatures, which are based on the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key. This process works as follows:
The sender has a pair of public and private keys, and the public key is shared with the receiver in advance.
The sender encrypts the plaintext message with its private key, which produces a ciphertext that is also a digital signature of the message.
The sender sends the ciphertext to the receiver, along with the plaintext message or a hash of the message.
The receiver decrypts the ciphertext with the sender’s public key, which produces the same plaintext message or hash of the message.
The receiver compares the decrypted message or hash with the original message or hash, and verifies the identity of the sender if they match.
The process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key serves identification because it ensures that only the sender can produce a valid ciphertext that can be decrypted by the receiver, and that the receiver can verify the sender’s identity by using the sender’s public key. This process also provides non-repudiation, which means that the sender cannot deny sending the message or the receiver cannot deny receiving the message, as the ciphertext serves as a proof of origin and delivery.
The other options are not the security services that are served by the process of encrypting plaintext with the sender’s private key and decrypting ciphertext with the sender’s public key. Confidentiality is the process of ensuring that the message is only readable by the intended parties, and it is achieved by encrypting plaintext with the receiver’s public key and decrypting ciphertext with the receiver’s private key. Integrity is the process of ensuring that the message is not modified or corrupted during transmission, and it is achieved by using hash functions and message authentication codes. Availability is the process of ensuring that the message is accessible and usable by the authorized parties, and it is achieved by using redundancy, backup, and recovery mechanisms.
Which of the following mobile code security models relies only on trust?
Code signing
Class authentication
Sandboxing
Type safety
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
Code signing is the mobile code security model that relies only on trust. Mobile code is a type of software that can be transferred from one system to another and executed without installation or compilation. Mobile code can be used for various purposes, such as web applications, applets, scripts, macros, etc. Mobile code can also pose various security risks, such as malicious code, unauthorized access, data leakage, etc. Mobile code security models are the techniques that are used to protect the systems and users from the threats of mobile code. Code signing is a mobile code security model that relies only on trust, which means that the security of the mobile code depends on the reputation and credibility of the code provider. Code signing works as follows:
The code provider has a pair of public and private keys, and obtains a digital certificate from a trusted third party, such as a certificate authority (CA), that binds the public key to the identity of the code provider.
The code provider signs the mobile code with its private key and attaches the digital certificate to the mobile code.
The code consumer receives the mobile code and verifies the signature and the certificate with the public key of the code provider and the CA, respectively.
The code consumer decides whether to trust and execute the mobile code based on the identity and reputation of the code provider.
Code signing relies only on trust because it does not enforce any security restrictions or controls on the mobile code, but rather leaves the decision to the code consumer. Code signing also does not guarantee the quality or functionality of the mobile code, but rather the authenticity and integrity of the code provider. Code signing can be effective if the code consumer knows and trusts the code provider, and if the code provider follows the security standards and best practices. However, code signing can also be ineffective if the code consumer is unaware or careless of the code provider, or if the code provider is compromised or malicious.
The other options are not mobile code security models that rely only on trust, but rather on other techniques that limit or isolate the mobile code. Class authentication is a mobile code security model that verifies the permissions and capabilities of the mobile code based on its class or type, and allows or denies the execution of the mobile code accordingly. Sandboxing is a mobile code security model that executes the mobile code in a separate and restricted environment, and prevents the mobile code from accessing or affecting the system resources or data. Type safety is a mobile code security model that checks the validity and consistency of the mobile code, and prevents the mobile code from performing illegal or unsafe operations.
Which component of the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) specification contains the data required to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities identified automated vulnerability assessments?
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
Asset Reporting Format (ARF)
Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL)
The Answer Is:
BExplanation:
The component of the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP) specification that contains the data required to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities identified by automated vulnerability assessments is the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). CVSS is a framework that provides a standardized and objective way to measure and communicate the characteristics and impacts of vulnerabilities. CVSS consists of three metric groups: base, temporal, and environmental. The base metric group captures the intrinsic and fundamental properties of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across user environments. The temporal metric group captures the characteristics of a vulnerability that change over time, such as the availability and effectiveness of exploits, patches, and workarounds. The environmental metric group captures the characteristics of a vulnerability that are relevant and unique to a user’s environment, such as the configuration and importance of the affected system. Each metric group has a set of metrics that are assigned values based on the vulnerability’s attributes. The values are then combined using a formula to produce a numerical score that ranges from 0 to 10, where 0 means no impact and 10 means critical impact. The score can also be translated into a qualitative rating that ranges from none to low, medium, high, and critical. CVSS provides a consistent and comprehensive way to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities and prioritize their remediation.
The other options are not components of the SCAP specification that contain the data required to estimate the severity of vulnerabilities identified by automated vulnerability assessments, but rather components that serve other purposes. Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a component that provides a standardized and unique identifier and description for each publicly known vulnerability. CVE facilitates the sharing and comparison of vulnerability information across different sources and tools. Asset Reporting Format (ARF) is a component that provides a standardized and extensible format for expressing the information about the assets and their characteristics, such as configuration, vulnerabilities, and compliance. ARF enables the aggregation and correlation of asset information from different sources and tools. Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL) is a component that provides a standardized and expressive language for defining and testing the state of a system for the presence of vulnerabilities, configuration issues, patches, and other aspects. OVAL enables the automation and interoperability of vulnerability assessment and management.
Who in the organization is accountable for classification of data information assets?
Data owner
Data architect
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
Chief Information Officer (CIO)
The Answer Is:
AExplanation:
The person in the organization who is accountable for the classification of data information assets is the data owner. The data owner is the person or entity that has the authority and responsibility for the creation, collection, processing, and disposal of a set of data. The data owner is also responsible for defining the purpose, value, and classification of the data, as well as the security requirements and controls for the data. The data owner should be able to determine the impact of the data on the mission of the organization, which means assessing the potential consequences of losing, compromising, or disclosing the data. The impact of the data on the mission of the organization is one of the main criteria for data classification, which helps to establish the appropriate level of protection and handling for the data. The data owner should also ensure that the data is properly labeled, stored, accessed, shared, and destroyed according to the data classification policy and procedures.
The other options are not the persons in the organization who are accountable for the classification of data information assets, but rather persons who have other roles or functions related to data management. The data architect is the person or entity that designs and models the structure, format, and relationships of the data, as well as the data standards, specifications, and lifecycle. The data architect supports the data owner by providing technical guidance and expertise on the data architecture and quality. The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is the person or entity that oversees the security strategy, policies, and programs of the organization, as well as the security performance and incidents. The CISO supports the data owner by providing security leadership and governance, as well as ensuring the compliance and alignment of the data security with the organizational objectives and regulations. The Chief Information Officer (CIO) is the person or entity that manages the information technology (IT) resources and services of the organization, as well as the IT strategy and innovation. The CIO supports the data owner by providing IT management and direction, as well as ensuring the availability, reliability, and scalability of the IT infrastructure and applications.
