8006 PRMIA Exam I: Finance Theory Financial Instruments Financial Markets - 2015 Edition Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PRMIA 8006 Exam I: Finance Theory Financial Instruments Financial Markets - 2015 Edition certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
The zero rates for 1, 2 and 3 years respectively are 2%, 2.5% and 3% compounded annually. What is the value of an FRA to a bank which will pay 4% on a principal of $10m in year 3?
If the zero coupon spot rate for 3 years is 5% and the same rate for 2 years is 4%, what is the forward rate from year 2 to year 3?
An asset manager is of the view that interest rates are currently high and can only decline over the coming 5 years. He has a choice of investing in the following four instruments, each of which matures in 5 years. Given his perspective, what would be the most suitable investment for the asset manager? Assume a flat yield curve.
Identify the underlying asset in a treasury note futures contract?
Determine the enterprise value of a firm whose expected operating free cash flows are $100 each year and are growing with GDP at 2.5%. Assume its weighted average cost of capital is 7.5% annually.
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
Which of the following best describes a shout option
A trader comes in to work and finds the following prices in relation to a stock: $100 spot, $10 for a call expiring in one year with a strike price of $100, and $10 for a put with the same expiry and strike. Interest rates are at 5% per year, and the stock does not pay any dividends. What should the trader do?
Which of the following is not a relevant consideration for a trader desirous of delta hedging his or her options portfolio?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. An interest rate swap is equivalent to the swap counterparties placing deposits with each other, one carrying a fixed rate of interest and the other a floating rate
II. The parties to a currency swap exchange principals
III. The risky leg in an IRS is the floating rate leg
IV. Swaps do not carry counterparty risks
Where futures are being used to hedge a commodities position, which of the following formulae should be used to determine the number of futures contracts to buy (or sell)?
Basis risk between spot and futures prices for stock indices is caused by changes in:
I. The risk free rate, or the funding cost for the futures
II. Expected dividend yield
III. Volatility of the underlying stock index
An investor has a bullish outlook on the market. Which of the following option strategies would suit him?
I. Risk reversal
II. Collar
III. Bull spread
IV. Butterfly spread
Two portfolios with identical Sharpe ratios will have
A stock that pays no dividends is trading at $100 spot or $104 as a three month forward. The interest rate you can borrow at is 6% per annum. US treasury yields are 4% per annum. What should you do to profit in the situation?
Which of the following statements is true:
I. On-the-run bonds are priced higher than off-the-run bonds from the same issuer even if they have the same duration.
II. The difference in pricing of on-the-run and off-the-run bonds reflects the differences in their liquidity
III. Strips carry a coupon generally equal to that of similar on-the-run bonds
IV. A low bid-ask spread indicates lower liquidity
Suppose the S&P is trading at a level of 1000. Using continuously compounded rates, calculate the futures price for a contract expiring in three months, assuming expected dividends to be 2% and the interest rate for futures funding to be 5% (both rates expressed as continuously compounded rates)
The relationship between covariance and correlation for two assets x and y is expressed by which of the following equations (where covarx,y is the covariance between x and y, σx and σy are the respective standard deviations and ρx,y is the correlation between x and y):
A)
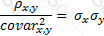
B)
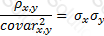
C)
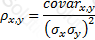
D)
None of the above
Which of the following assumptions underlie the 'square root of time' rule used for computing volatility estimates over different time horizons?
I. asset returns are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.)
II. volatility is constant over time
III. no serial correlation in the forward projection of volatility
IV. negative serial correlations exist in the time series of returns
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
What is the current conversion premium for a convertible bond where $100 in market value of the bond is convertible into two shares and the current share price is $50?
Profits and losses on futures contracts are:
