8008 PRMIA PRM Certification - Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks, Operational Risk, Credit Risk, Counterparty Risk, Market Risk, ALM, FTP - 2015 Edition Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PRMIA 8008 PRM Certification - Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks, Operational Risk, Credit Risk, Counterparty Risk, Market Risk, ALM, FTP - 2015 Edition certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
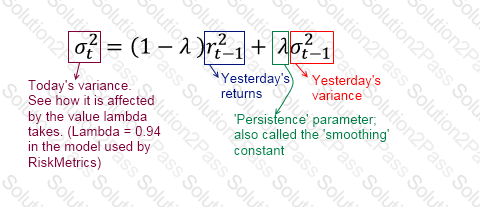
A stock's volatility under EWMA is estimated at 3.5% on a day its price is $10. The next day, the price moves to $11. What is the EWMA estimate of the volatility the next day? Assume the persistence parameter λ = 0.93.
The returns for a stock have a monthly volatilty of 5%. Calculate the volatility of the stock over a two month period, assuming returns between months have an autocorrelation of 0.3.
Which of the following statements are true in relation to Principal Component Analysis (PCA) as applied to a system of term structures?
I. The factor weights on the first principal component will show whether there is common trend in the system
II. The factors to be applied to principal components are obtained from eigenvectors of the correlation matrix
III. PCA is a standard method for reducing dimensionality in data when considering a large number of correlated variables
IV. The smallest absolute eigenvalues and their associated eigenvectors are the most useful for explaining most of the variation
When compared to a medium severity medium frequency risk, the operational risk capital requirement for a high severity very low frequency risk is likely to be:
An asset has a volatility of 10% per year. An investment manager chooses to hedge it with another asset that has a volatility of 9% per year and a correlation of 0.9. Calculate the hedge ratio.
Which of the following is true for the actuarial approach to credit risk modeling (CreditRisk+):
Which of the following was not a policy response introduced by Basel 2.5 in response to the global financial crisis:
Which of the following is additive, ie equal to the sum of its components
Under the standardized approach to calculating operational risk capital, how many business lines are a bank's activities divided into per Basel II?
In the case of historical volatility weighted VaR, a higher current volatility when compared to historical volatility:
The standard error of a Monte Carlo simulation is:
Which of the following statements is true:
I. If the sum of its parameters is less than one, GARCH is a mean reverting model of volatility, while EWMA is never mean reverting
II. Standardized returns under both EWMA and GARCH show less non-normality than non standardized returns
III. Steady state variance under GARCH is affected only by the persistence coefficient
IV. Good risk measures are always sub-additive
There are three bonds in a diversified bond portfolio, whose default probabilities are independent of each other and equal to 1%, 2% and 3% respectively over a 1 year time horizon. Calculate the probability that none of the three bonds will default.
Which of the following is not a limitation of the univariate Gaussian model to capture the codependence structure between risk factros used for VaR calculations?
When building a operational loss distribution by combining a loss frequency distribution and a loss severity distribution, it is assumed that:
I. The severity of losses is conditional upon the number of loss events
II. The frequency of losses is independent from the severity of the losses
III. Both the frequency and severity of loss events are dependent upon the state of internal controls in the bank
Which of the following correctly describes survivorship bias:
For a FX forward contract, what would be the worst time for a counterparty to default (in terms of the maximum likely credit exposure)
What percentage of average annual gross income is to be held as capital for operational risk under the basic indicator approach specified under Basel II?
The VaR of a portfolio at the 99% confidence level is $250,000 when mean return is assumed to be zero. If the assumption of zero returns is changed to an assumption of returns of $10,000, what is the revised VaR?
What would be the correct order of steps to addressing data quality problems in an organization?