8013 PRMIA PRM Exam 1: Finance Foundations Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PRMIA 8013 PRM Exam 1: Finance Foundations certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Imagine two perpetual bonds, ie bonds that pay a coupon till perpetuity and the issuer does not have an obligation to redeem. If the coupon on Bond A is 5%, and on Bond B is 15%, which of the following statements will be true:
I. The Macaulay duration of Bond A will be 3 times the Macaulay duration of Bond B.
II. Bond A and Bond B will have the same modified duration
III. Bond A will be priced at less than 1/3rd the price of Bond B
IV. Both Bond A and Bond B will have a duration of infinity as they never mature
A US treasury bill with 90 days to maturity and a face value of $100 is priced at $98. What is the annual bond-equivalent yield on this treasury bill?
A stock is selling at $90. An investor writes a covered call on the stock with an exercise price of $100 in return for a premium of $3 per share. What would be the maximum gain or loss per share that the investor could make on this position?
The spot exchange rate between USD and AUD is 0.70. The risk free interest rates in the US and Australia are 2% and 3.5% respectively. What is the forward exchange rate between the two currencies one year hence?
Where futures are being used to hedge a commodities position, which of the following formulae should be used to determine the number of futures contracts to buy (or sell)?
What is the yield to maturity for a 5% annual coupon bond trading at par? The bond matures in 10 years.
An investor holds $1m in a 10 year bond that has a basis point value (or PV01) of 5 cents. She seeks to hedge it using a 30 year bond that has a BPV of 8 cents. How much of the 30 year bond should she buy or sell to hedge against parallel shifts in the yield curve?
An investor expects stock prices to move either sharply up or down. His preferred strategy should be to:
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
A company that uses physical commodities as an input into its manufacturing process wishes to use options to hedge against a rise in its raw material costs. Which of the following options would be the most cost effective to use?
According to the dividend discount model, if d be the dividend per share in perpetuity of a company and g its expected growth rate, what would the share price of the company be. 'r' is the discount rate.
The 'transformation line' expresses the relationship between
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Protective puts are a form of insurance against a fall in prices
II. The maximum loss for an investor holding a protective put is equal to the decline in the value of the underlying
III. The premium paid on the put options held as a protective put is a loss if the value of the underlying goes up
IV. Protective puts can be a useful strategy for an investor holding a long position but with a negative short term view of the markets
What is the coupon on a treasury bill?
When considering an appropriate mix of debt and equity, Chief Financial Officers generally consider:
I. Tax advantage of debt
II. Financial distress costs
III. Agency costs of equity
IV. Retaining financial flexibility
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Caps allow the buyer of the cap protection against rise in interest expense
II. Floors offer investors protection from downward movement in interest rates
III. Collars can be used as hedges
IV. Both caps and collars can be used to hedge against widening credit spreads
A company has a long term loan from a bank at a fixed rate of interest. It expects interest rates to go down. Which of the following instruments can the company use to convert its fixed rate liability to a floating rate liability?
Which of the following portfolios would require rebalancing for delta hedging at a greater frequency in order to maintain delta neutrality?
If the zero coupon spot rate for 3 years is 5% and the same rate for 2 years is 4%, what is the forward rate from year 2 to year 3?
If x represents wealth, and u(x) its utility, then a logarithmic utility function can be represented by:
Which of the following statements is true in relation to the capital markets line (CML):
I. The CML is a transformation line that is tangential to the efficient frontier
II. The CML allows an investor to obtain the highest return for a given level of risk chosen according to the investor's risk attitude
III. The CML is the line passing through the point on the efficient frontier with the highest Sharpe ratio, and a y-intercept equal to the risk free rate
IV. The Sharpe ratio for the points on the CML increase in a linear fashion
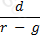 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.a.png
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.a.png 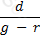 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.c.png
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.c.png 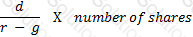 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.d.png
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.d.png 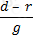 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.b.png
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/123.01.b.png 