CWM_LEVEL_2 AAFM Chartered Wealth Manager (CWM) Certification Level II Examination Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your AAFM CWM_LEVEL_2 Chartered Wealth Manager (CWM) Certification Level II Examination certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Section B (2 Mark)
In 2011-12, an individual receives a net dividend of £648. The equivalent gross income is:
Section A (1 Mark)
An example of ________ is that a person may reject an investment when it is posed in terms of risk surrounding potential gains but may accept the same investment if it is posed in terms of risk surrounding potential losses.
Section C (4 Mark)
Azhar deposits Rs. 12,500 in an account that pays a ROI of 20% p.a compounded annually on 5th. Of March 2010. Calculate the date on which the balance in his account would be Rs.35,338/-
Section A (1 Mark)
Select the CORRECT statement regarding basis risk associated with futures.
Section A (1 Mark)
Surender is a driver who causes injuries to a pedestrian by his rash driving. The injured victim had to spend Rs.1000 in treating his injuries. Surender ‘s act has created liabilities under:
Section A (1 Mark)
Mr. Sharma is aged 50 years at present. He has invested some amount in an annuity which will pay him after 10 years Rs. 25,000/- p.a. at the beginning of every year for 10 years. Rate of interest is 6% p.a. Calculate how much amount he has invested now?
Section C (4 Mark)
To create a common size income statement ____________ all items on the income statement by ____________.
Section C (4 Mark)
As a CWM you are required to calculate the tax liability of an individual whose Taxable income is:
• $ 178650 in US dollars and he is a US citizen (single individual)
• $ 85300 in SGD and he is a citizen of Singapore
Section A (1 Mark)
An activity is presumed to be a profit-making activity rather than a hobby if the
Section C (4 Mark)
A Portfolio manager is holding the following portfolio:

The risk free rate of return is 6% and the portfolio’s required rate of return is 12.5%. The manager would like to sell all of his holdings in stock A and use the proceeds to purchase more shares of stock D. What would be the portfolio’s required rate of return following this change?
Section B (2 Mark)
Ramesh has invested Rs 3,000/- in Reliance Growth Fund two years ago and its worth is now 4,000/-. Ram has received dividend Rs.300 at the end of two years. Calculate Compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of Ram’s investment.
Section B (2 Mark)
On 1st January 2011, Mr. Dutt took a personal loan of Rs.1,00,000/- for a period of 3 years at an 21% rate of interest. The loan is to be on monthly EMI on monthly reducing balance method.
What about be interest and principal amount to be paid in October 2013?
Section A (1 Mark)
Holistic advisory services which cater to specific client segments such as entrepreneurs, professionals are known as____________________.
Section C (4 Mark)
Mr. XYZ sells a Nifty Put option with a strike price of Rs. 4000 at a premium of Rs. 21.45 and buys a further OTM Nifty Put option with a strike price Rs. 3800 at a premium of Rs. 3.00 when the current Nifty is at 4191.10, with both options expiring on 31st July.
What would be the Net Payoff of the Strategy?
• If Nifty closes at 3980.55
• If Nifty closes at 4800
Section B (2 Mark)
A disadvantage of using swaps to control interest rate risk is that
Section C (4 Mark)
Mr. Amit Jain has bought a house today which cost him Rs. 50 lacs by taking a loan of 30lacs for 15 years at 11% per annum compounded monthly. He currently has 10 lacs of financial assets and plans to save Rs. 3.25 lacs every year at the beginning of the year for the next 5 years. All his investments are expected to grow at a ROI of 15%per annum compounded quarterly. What will be the net worth of Mr. Amit after 5 years if the value of the house after 5 years is expected to be 75 lacs.
Section B (2 Mark)
If JVM Industries pays dividend of Rs.6 per share which is growing at a 8 percent rate per year and is expected to grow at the same rate in future. Its required rate of return is 16%. Determine its share price.
Section B (2 Mark)
Calculate the treynor measure, Sharpe measure and Jensen measure from the following data:
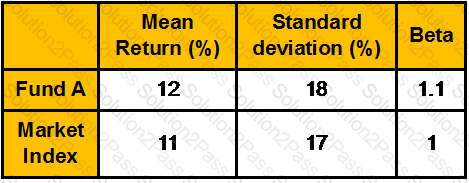
The mean risk free rate was 6 percent.
Section C (4 Mark)
Paridhi has an investment portfolio of Rs.2,00,000; the initial portfolio mix is Rs.1,00,000 in stocks, Rs.60000 bonds and Rs.40000 in bank.
If market goes up by 10% and the value of bonds decreases by 10%, what should Paridhi do under the constant mix policy?
Section B (2 Mark)
In UK, which of the following types of income is not specifically exempt from income tax?
Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the following factors have proven most important in credit scoring models?
Section B (2 Mark)
What is the outstanding balance at the 23rd payment interval of a 16-year loan for Rs11 234 with semi-annual payments and an interest rate of 7.95% compounded quarterly?
Section A (1 Mark)
A cognitive heuristic in which a decision-maker relies upon knowledge that is readily available rather than examining other alternatives or procedures. Which of the following is most likely consistent with this bias?
Section B (2 Mark)
Assume that you purchased 100 shares of ABC in a self directed account and paid a commission on the transaction. Shortly following the purchase, you realize that you momentarily overlooked another 100 shares of ABC that you already owned in another account. Now, the redundant holdings are causing an imbalance in your overall portfolio.
What is your reaction to this situation, in case of Endowment Bias?

Section B (2 Mark)
____________ are good examples of the limits to arbitrage because they show that the law of one price is violated.

Section A (1 Mark)
In US, how many states do not have a corporate income tax?
Section B (2 Mark)
Manav wishes to have a retirement corpus of Rs. 2,50,000/- in 30 years’ time. Assuming that he can earn a ROI of 12 % per annum, what amount he should invest yearly into a fund to reach his goal?
Section A (1 Mark)
Wealth Erosion can happen due to _______
Section C (4 Mark)
The assumptions concerning the shape of utility functions of investors differ between conventional theory and prospect theory. Conventional theory assumes that utility functions are __________ whereas prospect theory assumes that utility functions are __________.
Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the followings are the important features of Real estate Investment?
Section A (1 Mark)
Ratio of loading charge over the gross rate is called _________
Section B (2 Mark)
Mr. Aggarwal is working in a reputed company and earning Rs. 4,50,000/- p.a. and is now 55 years old. He has invested Rs. 2,00,000/- in an annuity which will pay him after 5 years a certain amount p.a. at the beginning of every year for 10 years. Rate of interest is 8% p.a. Calculate how much he will receive at the beginning of every year after 5 years?
Section B (2 Mark)
How much total principal is repaid between the 1st and 17th payment interval of a 4.5-year loan for Rs 4567 at an interest rate of 7.44% compounded monthly. The payments are also monthly.
Section B (2 Mark)
The Net Worth Required for an Individual is _________________ for a Partnership Firm is ____________________ and Body Corporate is______________ to fulfil the Capital Adequacy requirements under the SEBI Investment Advisor Regulations 2013.
Section B (2 Mark)
An investor is considering the purchase of a small office building and, as part of his analysis, form the following given data calculate the Net Operating Income (NOI).
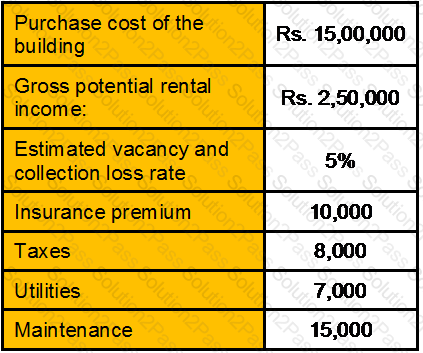
Section A (1 Mark)
Retiring early will need
Section B (2 Mark)
One unit of trading for Guar Seed futures is 10 MT and delivery unit is 10 MT. A trader sells 1 unit of Guar Seed at Rs.2500/Quintal on the futures market. A week later Guar Seed futures trade at Rs.2550/Quintal. How much profit/loss has he made on his position?
Section A (1 Mark)
Hedge funds often seek to take advantage of market inefficiencies such as:
Section B (2 Mark)
There are two parties to Power of Attorney, namely, Donor and Donee.

Section A (1 Mark)
These people are so well balanced, they cannot be placed in any specific quadrant, so they fall near the center.
Section A (1 Mark)
The concept of designing marketing communication programs that coordinate all promotional activities to provide a consistent message across all audiences is called
Section B (2 Mark)
In the calculation of rates of return on common stock, dividends are _______ and capital gains are _____.
Section C (4 Mark)
Read the senario and answer to the question.
Mahesh’s company has made plans for the next year. It is estimated that the company will employ total assets of Rs. 1000 lakh: 50% of the assets being financed by borrowed capital at an interest cost of 8% per year. The direct costs are estimated at Rs. 500 lakh. All other operating expenses are estimated at Rs. 76 lakh. The good will be sold to customer at 140% of the direct costs. Income tax rate is assumed to be 30%. Calculate net profit margin and return on owners’ equity.
Section A (1 Mark)
Mr. Roy is now 45 years old. He has invested Rs. 1,75,000/- in an annuity which will pay him after 10 years a certain amount p.a. at the end of every year for 10 years. Rate of interest is 7% p.a. compounded annually Calculate how much he will receive at the end of every year after 10 years?
Section A (1 Mark)
As per Hindu succession Act 1956 following person is not considered as a class I heir of the person who dies intestate
Section B (2 Mark)
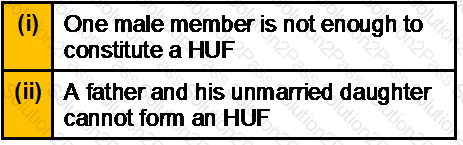
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Section B (2 Mark)
What is the projected sale price of an apartment building that produces an annual net cash flow Rs. 120,000, if we set a projected capitalization rate at 7%?
Section A (1 Mark)
AUM stands for
Section B (2 Mark)
Ram born in 1950 has a life expectancy at birth of 65 years. Sita his wife born in 1955 has a life expectancy at birth of 70 years. Assuming that the life expectancies have not changed. Ram is planning to buy an annuity to be paid to him or his wife till anyone of them is alive. Assuming Ram will retire on attaining age 58 i.e. in 2008, what should be the time period of the annuity?
Section B (2 Mark)
Which of the following investment options would most likely be part of the portfolio of a Moderate investor?

Section B (2 Mark)
Which of the Following are the Negative Effects of Sample-Size neglect for investors

Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the following services are related to the field of Real Estate?
Section B (2 Mark)
If an investor strongly believes that the stock market is going to have a sharp decline shortly, he or she could maximize profit by
Section B (2 Mark)
Mahesh wants to sell a property for Rs. 30 lakhs. He is earning rent from tenant Rs. 3,60,000. He is spending following amounts annually on that property.
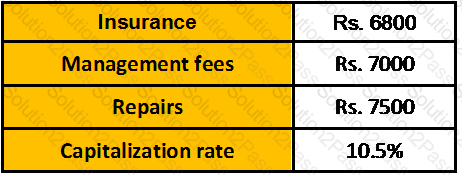
Based on the above information what should be the value of the property would be:
Section B (2 Mark)
Narayan expects to receive Rs 25000 in net receipts each year for five year and to sell the property for Rs 350,000 at the end of the five-year period, if Narayan expects a 15% return, what would be the value of the property?
Section B (2 Mark)
As per Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement, the Royalties in UK is charged at:
Section B (2 Mark)
All of the following are assumptions made by technical analysts except:
Section A (1 Mark)
__________ is the most important investment decision because it determines the risk-return characteristics of the portfolio.
Section B (2 Mark)
Which of the following are the two skills associated with being a good listener?
Section A (1 Mark)
If the deceased has two widows, four sons and two daughters then what is the share of each widow
