CWM_LEVEL_2 AAFM Chartered Wealth Manager (CWM) Certification Level II Examination Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your AAFM CWM_LEVEL_2 Chartered Wealth Manager (CWM) Certification Level II Examination certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Section A (1 Mark)
____________ is defined as a dollar per thousand dollars of assessed value of property and is used to calculate a property owner's tax bill.
Section A (1 Mark)
If a portfolio manager consistently obtains a high Sharpe measure, the manager's forecasting ability __________.
Section A (1 Mark)
Mr. Sharma invested Rs. 2,00,000 in an investment that gives Rs 40,000/- for the first 4 years, and Rs. 60,000/- for next 3 years. If the discount rate is 12 %, calculate the Present Value of these cash flows?
Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the following is true regarding the resistance level?
Section C (4 Mark)
Dyder System is a full-service truck leasing, maintenance, and rental firm. The following are selected numbers from the financial statements for 1992 and 1993 (in millions).
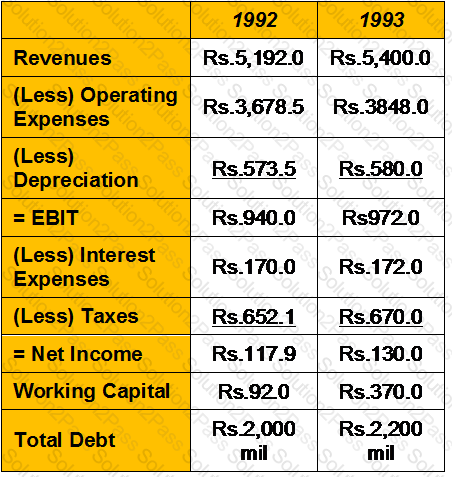
The firm had capital expenditures of Rs800 million in 1992 and Rs850 million in 1993. The working capital in 1991 was Rs34.8 million, and the total debt outstanding in 1991 was Rs1.75 billion. There were 77 million shares outstanding, trading at Rs29 per share.
Estimate the cash flows to the firm in 1992 and 1993(in Rs Millions)
Section C (4 Mark)
Suppose Nifty is at 4450 on 27th April. An investor, Mr. A, enters into a short straddle by selling a May Rs 4500 Nifty Put for Rs. 85 and a May Rs. 4500 Nifty Call for Rs. 122.
What would be the Net Payoff of the Strategy?
• If Nifty closes at 4293
• If Nifty closes at 5158
Section C (4 Mark)
Dinex Ltd, a leader in the development and manufacture of electronic devices, reported earnings per share of Rs 2.02 in 2003, and paid no dividends. These earnings are expected to grow 14% a year for five years (2004 to 2008) and 7% a year after that. The firm reported depreciation of Rs 2 million in 2003 and capital spending of Rs 4.20 million, and had 7 million shares outstanding. The working capital is expected to remain at 50% of revenues, which were Rs 106 million in 2003, and are expected to grow 6% a year from 2004 to 2008 and 4% a year after that. The firm is expected to finance 10% of its capital expenditures and working capital needs with debt. Dinex Ltd had a beta of 1.20 in 2003, and this beta is expected to drop to 1.10 after 2008. The current risk free rate is 7%.
Estimate the value per share today, based upon the FCFE model.
Section A (1 Mark)
You buy a investment plan by investing Rs. 5000/- per month for first 12years and Rs. 10000/- per month for next 12 years. If the rate of interest is 15% per annum compounded monthly . How much amount would you have after 24 years?
Section A (1 Mark)
Deduction under section 80C shall be allowed:
Section C (4 Mark)
Harish Rawat has approached you on 26th Nov 2010, a Chartered Wealth Manager, for preparing a comprehensive Wealth plan to accomplish his financial goals. From your initial meeting, you have gathered the following information:
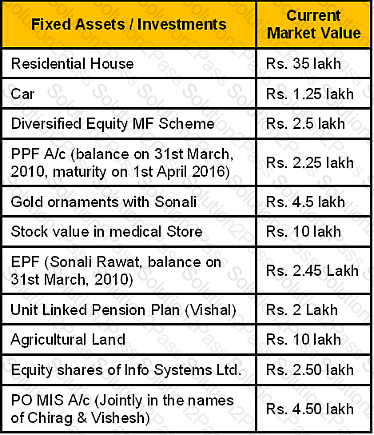
Harish Rawat, aged 44 years with life expectancy 70 years, is self-employed in Dehradun. Harish’s wife Sonali, aged 41 years with life expectancy 72 years, is working as a Assistant Manager in a Telecom
Company and is having a post-tax income of Rs. 4 lakh p.a. She is expected to retire at the age of 55 years. The couple has two children Chirag, aged 16 years and Vishesh, aged 10 years. Chirag is studying in 10th standard while Vishesh is studying in 4th standard. Harish’s net annual Income from retail medical store is Rs. 8 Lakh and their monthly household/living expenses, excluding housing loan EMI, are Rs. 32,500.
Harish is a Graduate. He earlier served in a pharmaceutical company as a medical representative for approx. 10 years. After separation from the company, he started his own wholesale business of medicines but could not sustain for long due to lack of working capital. He shut down his operations after 3.5 years. Thereafter he got a contract for retail medical shop in the premises of a nursing home. The terms of the contact are profit sharing in the ratio 50:50. Investment in stock and handling all activities of medical store are of Harish and no rent is charged by the owner of nursing home.
Harish had taken a housing loan of Rs. 15 Lakh disbursed on 1st April 2005. They are presently paying an EMI of Rs. 17,285 at the end of every month beginning from the month of disbursement. The loan is at fixed rate of interest of 11.25% p.a. (reducing monthly balance basis) with tenure of 15 years. Harish has taken a money back insurance plan of 20 year term with sum assured of Rs. 6 Lakh, the annual premium being Rs. 26,250. He has paid 14 annual premiums till date regularly. The policy provides for 20% of the basic sum assured to the insured as survival benefit after 4th, 8th, 12th, 16th years from the start of the policy. He has also taken a Mediclaim family floater policy which covers his spouse and two sons to the extent of Rs. 5 Lakh. He has also paid four regular annual premiums of Rs. 36,000 in a unit linked pension plan and next premium is due on 1st Dec 2010.
Harish’s parents are senior citizens and live in their own house in Haldwani District. Their only source of income is by way of interest received from their joint Senior Citizen Savings Scheme account. Harish’s younger brother, who is also self-employed, is living with his parents.
Harish had invested Rs. 1 lakh to buy 200 shares of a listed company, Mobizox, in the year 2001-02. The Company had issued Bonus shares in the ratio 1:1 in the year 2005-06.Harish also subscribed to the Company’s Rights issue of one share for every four shares held at a price of Rs. 250 per share in Feb 2010. Harish also invested Rs. 4 lakh in an Agriculture land at his native village in Haldwani in 2000-01.
Goals and aspirations
1.To make provision for their children’s higher education expenses at their respective age of 21 years.
2.Such expenses are Rs. 5 lakh for each child at current prices.
3.To make provision for children’s marriage expected at the end of 10 years and 15years from now; presently valued at Rs. 5 lakh each.
4.Build a corpus for his retirement at the age of 58 years
5.To go on vacation with family in January, 2011
Assumptions
1.Inflation is currently 6% p.a. and is likely to remain the same.
2.Risk free interest rate is at 7% p.a.
3.Return on equity MF is 12% p.a.
4.Return on debt MF is 8% p.a.
5.Cost Inflation index is 281 for 1995-96, is 406 for 2000-01, is 463 for 2003-04, is 551for 2007-08, is 582 for 2008-09 and is 632 for 2009-10.
Section A (1 Mark)
A(n) _____________ is related to the credit option and is usually aimed at lenders able to handle comparatively limited declines in value but wants insurance against serious losses.
Section B (2 Mark)
Regular collateralized debt obligations (CDO) have been surpassed by:
Section B (2 Mark)
A fixed-rate mortgage for Rs210 000 with monthly payments is amortized over 20 years. The interest rate is 4.85% compounded semi-annually for a 7-year term. How much of the mortgage principal has been repaid by the end of the 7-year term?
Section B (2 Mark)
A hired a bicycle from B. The written contract contained a clause which read “Nothing in this agreement shall render the owner liable for any personal injuries to the rider of the machine hired”. Owing to a defect in the brakes of the cycle, A met with an accident and got injured. Can A recover Damages?
Section A (1 Mark)
A(n)____________________________________________ is where the customer can use the difference between some percentage of the appraised value of their home and the mortgage remaining to secure a loan. This loan can be used to fund a college education, pay for a vacation or pay for home improvements.
Section B (2 Mark)
Mr. Subhash Bansal, a marketing manager is employed with IMFB limited. He took an advance of Rs. 1,20,000 against the salary of Rs. 30,000 per month in the month of March 2007. The gross salary of Mr Bansal for the assessment year 2007-08 shall be:
Section C (4 Mark)
Amit an industrialist wants to buy a flat in a housing society presently costing Rs. 35,00,000/- after 6 years. The cost of the house is expected to increase by 15% p.a for the first 3 years and by 10% in the remaining years. Amit wants to start a SIP with monthly contributions in Birla Front Line Equity Mutual Fund to pay for the down payment of the house which would be 25% of the house value at that time. You as a CWM expect that the fund would give ROI of 14% p.a. compounded monthly in the next 10 years. Please advise Amit the monthly SIP amount starting at the beginning of every month for the next 6 years to fulfill his goal of buying the Flat he desires.
Section A (1 Mark)
You buy a investment plan by investing Rs. 5000/- per month for first 12years if the investment pays Rs. 5000 for the next 12 years and the rate of interest is 15% per annum compounded monthly. How much amount would you have after 24 years?
Section C (4 Mark)
Suppose you have a two-security portfolio containing Bonds A and B. The market value of Bond A is Rs. 6,000, and the market value of Bond B is Rs4,000. The duration of Bond A is 8.5, and the duration of Bond B is 4.0. Calculate the duration of the portfolio.
Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the following types of income is received by individuals without deduction of basic rate tax?
Section A (1 Mark)
We divide phenomena into different departments and try to optimize each department rather than the whole. Which of the following is most likely consistent with this bias?
Section B (2 Mark)
Mr Dixit is considering purchasing an office building for Rs. 2,500,000. He expects the potential gross income (PGI) in the first year to be Rs. 450,000; vacancy and collection losses to be 9 percent of PGI; and operating expenses to be 42 percent of effective gross income (EGI). What is the (effective) gross income multiplier?
Section C (4 Mark)
Read the senario and answer to the question.
Which types(s) of investment(s), would be consistent with their retirement goal?

Section A (1 Mark)
A loan where the borrower pays interest each period, and repays some or all of the principal of the loan over time is called a(n) _________ loan.
Section A (1 Mark)
A ____________________ tax system takes the same percentage of each person's income, regardless of whether the income is high, medium, or low.
Section B (2 Mark)
A bank is about to make a Rs50 million project loan to develop a new oil field and is worried that the petroleum engineer's estimates of the yield on the field are incorrect. The bank wants to protect itself in case the developer cannot repay the loan. Which type of credit derivative contract would you most recommend for this situation?
Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the following is NOT a dimension of service quality?
Section C (4 Mark)
Personal Data
Financial Data
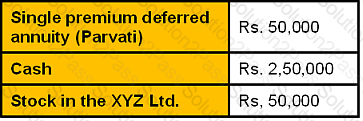
Shanker and Parvati Pandey have the following assets at fair market value (FMV):
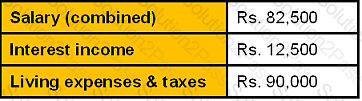
Their simplified income statement is presented as follows:
They have no liabilities and no company-sponsored retirement plans.
They have no wills and they live in a non-community property state.
Shankers’ parents can meet all current expenses from current cash flow but have very limited reserve funds
Other Relevant Data
●They are inexperienced investors, but they are willing to take reasonable and normal investment risk if appropriate, but they do not wish to invest aggressively.
●Both Shanker and Parvati have purchased term life insurance policies with Rs. 250,000 death benefit on each; they own their own policies, and Ganesh is the contingent beneficiary on both policies.
●Shanker is the primary beneficiary of Parvati’s single premium deferred annuity; Ganesh is the contingent beneficiary.
●You have found their disability insurance inadequate. The Pandey have indicated they could fit your proposed Rs. 3500 annual premium for an adequate policy into their living expenses.
●You have reviewed their auto, homeowner’s, liability, and life insurance and found their policies adequate. Shanker and Parvati are responsible for their medical expenses.
●Ganesh is an intelligent high school student who earns scholarship of Rs. 2,000 annually and has a Rs. 500 in savings account.
●The “cash” is invested in a variety of money market funds and insured savings accounts.
●They do not plan additional children and they have no other dependents.
●The Pandey currently can save Rs. 5,000 per year out of current salary and can continue to do so (in inflation-adjusted Rupees) until they retire in 20 years. This savings rate assumes that all planned asset acquisition and replacements are paid out of income before savings (except the three goals as per below.
Goals (in order of priority)
1.College education for Ganesh. They expect to spend a total of Rs. 5,00,000 (Present value) for his entire education.
2.Retirement in 20 years which maximizes their standard of living at retirement.
3.Parvati and Shanker plan to take 6 months off from work (“sabbatical”) in 4 years for travel and research and to spend Rs. 1,50,000.
Economic Environment
The economy has been in a period of modest economic growth for about 2 years. Inflation, as measured by the CPI, was at a 4.9% annual rate over the last year. Ninety-day T-bill rates are currently 6%, while the yield to maturity on 20-year government bonds is 7.5%. Most forecasts call for little change in these conditions over the short and long term.
Assumptions provided by Wealth Manager
Section C (4 Mark)
Vinod has a investment portfolio of Rs. 100000, a floor of Rs. 75000, and a multiplier of 2. So the initial portfolio mix is 50000 in stocks and 50000 in bonds. If stock market falls by 20%, what should Vinod do assuming he is following a CPPI policy?
Section C (4 Mark)
The Meryl Corporation's common stock is currently selling at Rs100 per share, which represents a P/E ratio of 10. If the firm has 100 shares of common stock outstanding, a return on equity of 20 percent, and a debt ratio of 60 percent, what is its return on total assets (ROA)?
Section A (1 Mark)
An investor will take as large a position as possible when an equilibrium price relationship is violated. This is an example of _________.
Section A (1 Mark)
___________ is a measure of the ratio between the net income produced by an assets (usually real estate) and its capital cost.
Section A (1 Mark)
With the______________, the buyer gets no protection from encumbrances. This deed type has very specialized uses.
Section B (2 Mark)
The feature of the APT that offers the greatest potential advantage over the CAPM is the ______________.
Section A (1 Mark)
The following is capital receipt:
Section B (2 Mark)
Mr. Kishan owns a factory producing some small spare parts.Under which policy he can get cover against the claim for paying damages and legal costs arising from any bodily injury or damage in the premises of his property ?
Section A (1 Mark)
Single men trade far more often than women. This is due to greater ________ among men.
Section A (1 Mark)
During “Financial Independence” life stage, typical asset allocation should be
Section A (1 Mark)
Which part of the wealth management planning deals with efficient and optimum use of credit for the business.?
Section A (1 Mark)
The following is exempt income:
Section A (1 Mark)
The following is not a capital receipt
Section A (1 Mark)
For claiming exemption u/s 54G, the assessed shall acquire the new asset within:
Section A (1 Mark)
Which ONE of the following in not the requirement for managing customer?
Section A (1 Mark)
Land plus anything permanently fixed on it, including building, sheds and other items attached to the structure refers to _____.
Section A (1 Mark)
Which of the following is NOT the general purpose of CRM?
Section C (4 Mark)
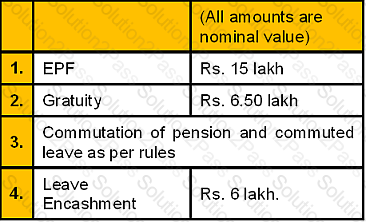 Mr. Vinay, aged 36 years is working in a company, at a managerial level, and has an income of Rs. 40,000 p.m. comprising of Basic salary and DA as on 31/03/2008. His other allowances amount to Rs. 18,000 p.m. He would retire at the age of 60 years. His wife Reena, aged 32 years, is working in a High School and has a post-tax income of Rs. 2,76,000 per annum. Mr. and Mrs. Vinay have two daughter Deepika, aged 10 years and Rekha, aged 5 years.
Mr. Vinay, aged 36 years is working in a company, at a managerial level, and has an income of Rs. 40,000 p.m. comprising of Basic salary and DA as on 31/03/2008. His other allowances amount to Rs. 18,000 p.m. He would retire at the age of 60 years. His wife Reena, aged 32 years, is working in a High School and has a post-tax income of Rs. 2,76,000 per annum. Mr. and Mrs. Vinay have two daughter Deepika, aged 10 years and Rekha, aged 5 years.
Mr. Vinay’s father died of heart attack, 5 months back, at the age of 72 years, leaving a house (Value as on date Rs. 30 lakh) in which Vinay is staying at present and other assets worth Rs. 20 lakh (shares of large cap companies worth Rs. 10 lakh, Fixed deposit in post office of Rs. 5 lakh and Bank FD of Rs. 5 lakh) in Vinay’s mother’s name. His mother 63 years old is disabled and fully dependent on Vinay, he being the only child of his parents. Vinay has to keep an attendant for his mother, round the clock.
The Assets of the Couple are:
1.Cash in HandRs. 18,000
2.Bank balanceRs. 40,000 (Vinay) Rs. 25,000 (Reena)
3.JewelleryRs. 400000 (Reena)
4.Money Market Mutual FundRs. 3,00,000 (Vinay)
5.Shares
?ICICI Bank 200 shares bought at Rs. 1000 per share,
?Infosys 150 shares bought at Rs. 1700 per share
?Reliance Communication 350 shares bought at Rs. 350 share.
6.Debt oriented mutual FundsRs. 2,00,000
7.PPFRs. 5,00,000 (Vinay), Rs. 4,00,000 (Reena)
8.House in the joint name of Vinay and Reena with 50% ownership of each. This house has two floors and is let out for Rs. 9,000 pm for each of the floors. Present value of this house is Rs. 60,00,000.
Vinay and Reena had taken a housing loan of Rs. 15,00,000 each. Of this Rs. 10,00,000 is pending on each name. They are presently paying an EMI of Rs. 20,000 each, Rate of interest being 10.75% p.a.
The Retirement Benefits of Vinay after 15 years hence, are expected to be as follows:
Vinay has taken a term insurance of Rs. 30 lakh for 20 years, which is expiring 5 years from now. He has no other insurance. Vinay’s monthly household/ living expenses are Rs. 50,000. This excludes EMI on loans but includes all other expenses including expenses on his mother’s care.
Vinay expects Deepika to get married 12 years hence for which likely expenditures in today’s term is 15 lakh.
Vinay’s salary is likely to grow at 7% pa and Reena’s salary is likely to grow at 6% p.a. Risk free rate of interest is 8% pa and inflation is 6% p.a. Long term growth on Equity/Equity based MF is taken as 15% p.a.
Section A (1 Mark)
_________________makes us throw more good money after money already gone bad.
Section C (4 Mark)
As a CWM you are required to calculate the tax liability of an individual whose taxable income is:
• $92120 in SGD and he is a Singapore citizen
• £ 57482p.a (only Savings Income) and he is a UK citizen
Section B (2 Mark)
In _____________ first the cost incurred by the supplier of property is determined. An appropriate cost plus mark-up is then added to the cost so as to arrive at an appropriate profit in the light of the functions performed and market conditions.
Section B (2 Mark)
Which of the following is closest to the forward price of a share price if

Dividend expected is 6%?
Section C (4 Mark)
Mr. XYZ is bearish about Nifty and expects it to fall. He sells a Call option with a strike price of Rs. 2600 at a premium of Rs. 154, when the current Nifty is at 2694. If the Nifty stays at 2600 or below, the Call option will not be exercised by the buyer of the Call and Mr. XYZ can retain the entire premium of Rs.154.
What would be the Net Payoff of the Strategy?
• If Nifty closes at 2900
• If Nifty closes at 2400
Section C (4 Mark)
Read the senario and answer to the question.
Assume the following additional facts:
The Shankers have purchased a homeowner’s policy (comprehensive) covering 100% of the replacement cost of their residence. This policy has a Rs. 500 deductible. Also, they have purchased a disability income policy with a 30-day elimination period and an any-occupation definition of disability.
What actions should the Shankers consider in order to improve the quality of the insurance program described above?

Section A (1 Mark)
In hedge funds the risk of no standard platform for measurement and no standard format for reporting is called __________________
Section A (1 Mark)
Investments that are difficult to convert to cash are said to have _________
Section A (1 Mark)
Premium under endowment plans equals
Section B (2 Mark)
Rajiv's company was just surprised by a new competitor in their field. Rajiv wants to plan a way for his business to retake the lead. For this purpose, Rajiv offered a plan to compete in the market. Which one of the following parts of the strategic landscape has been described?
Section B (2 Mark)
A taxpayer has taxable income for 2011-12 (after deducting the personal allowance) of £75,200. None of the income is derived from savings or dividends. The income tax liability for the year is:
Section B (2 Mark)
In US which form tells your employer all they need to know about your tax-related allowance information?
Section C (4 Mark)
In 2011-12, Lily (who is resident and ordinarily resident in the UK for the year) earns a gross salary from her UK employment of £45,000. PAYE (Pay as you Earn)of £7,600 is deducted from this income.
She owns a holiday home in France and receives rents of £2,250 for the year. This is the net figure after withholding tax of 25% has been deducted.
Her income tax payable for the year is:
Section C (4 Mark)
Arvind Ltd. currently EPS is Rs.5. Its return on equity (ROE) is 25% and it retains 60% of its earning. Stocks of similar risk are priced to return 18%. What is the intrinsic value of Arvind Ltd’s Stock?
