ASCP-MLT ASCP MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your ASCP ASCP-MLT MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
The end of the initial phase of HH treatment is considered when the serum ferritin decreases to between 20 and 50 ng/mL.
What is a typical finding for determining the endpoint for the initial or iron-depletion phase of treatment for hereditary hemochromatosis (HH)?
Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of DNA, usually left from the nucleus, that appears as a round, dark-staining inclusion in the cytoplasm of red blood cells. Howell-Jolly bodies can be found in various conditions including splenectomy and anemia.
Remnants of erythrocyte nuclei, nuclear fragments, or aggregates of chromosomes are called:
A patient with tuberculosis would be placed in:
The concentration of circulating ferritin is proportional to the size of iron stores.
Which of the following will give the best overall picture of a patient's iron stores:
Convert the following temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius
102 degrees F
The type of isolation category that always requires a HEPA mask or respirator to be worn is:
The best course of action when entering an isolation room is:
A blood culture to evaluate septicemia is performed in:
Estriol levels in conjunction with hCG and AFP can be obtained during pregnancy to:
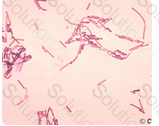
The organisms in this image are demonstrating a gram-variable phenomenon. For the most part, the organisms are staining primarily gram-negative, however, on the tips of some of the rods, there is a gram-positive staining morphology. This can be defined as gram-variable.
Which of the following best describes the organisms seen in this illustration:
Normocytic- G6PD deficiency, Malaria
Microcytic- Iron deficiency, Thalassemia
Macrocytic- Chronic Liver Disease, Vitamin B12 deficiency
Hematology
Match the disease conditions with appropriate red cell size classification
1. G6PD deficiency, Malaria
2. Iron deficiency, Thalassemia
3. Chronic Liver Disease, Vitamin B12 deficiency
What additional fraction would be seen if plasma rather than serum was subjected to electrophoresis:
The MCV is indicative of microcytosis with MCV=<80fL. The RDW is within normal limits and indicative of a homogenous cell population.
If the MCV was >100 fL, this would be indicative of macrocytosis. An RDW that was outside of normal limits would be indicative of a heterogenous cell population.
An 18 year old female has a CBC as part of a routine physical exam. The following results were obtained and the physician determines she is anemic. After reviewing her CBC results shown below, which of the following would be an appropriate description of the anemia?
White blood cells (WBC): 5.6 x 10^9/L (RR:4.0-10.0 x 10^9/L)
Red blood cells (RBC): 3.7 x 10^12/L (RR: 4.2-5.9 x 10^12/L)
Hemoglobin: 9.9 g/dL (RR:12-16 g/dL)
Hematocrit: 28% (RR: 37-48%)
MCV: 75 fL (80-100 fL)
RDW-CV: 14% (RR: 11.0-15.0%)
Though automated extraction machines have many benefits over manual methods the costs are high and generally require a high throughput of samples in order to justify the costs.
Automated extraction has many benefits over the traditional manual methods. The most important benefit is that the nucleic acid isolated is constantly consistent. There is a reduced amount of manipulation with dramatically decreases the chance of cross contamination. Also, automated extraction machines are considered moderate complexity and can be performed by a wider variety of laboratory professionals.
All of the following are considered benefits of automated isolation and extraction equipment EXCEPT:
This type of laboratory professional is responsible for the technical aspects of managing the operation of the laboratory and is most likely an MLS with additional education in administration:
Valine substitutes for glutamic acid in the Beta 6 position to produce HbS.
To produce hemoglobin S, glutamic acid that is normally present in the sixth position on the beta globin chain is substituted with which of the following?
Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of DNA and appear as small round ball-like inclusions inside the red cells. Usually only one Howell-Jolly body will be present in each red cell.
Single erythrocyte inclusions which are large, round, smooth and purplish-blue staining are most likely:
Hemoglobin F has a high affinity for oxygen. When Hb F is elevated, cells containing Hb S are more oxygenated and do not sickle as readily as they would if Hb F were not present or present in small quantities.
Which hemoglobin, when elevated, acts as a protection against sickling in patients with HbS?
Provide the equivalent measurement for one gallon.
Question options:
Immunoassay is the most common technique that is used by clinical laboratories for therapeutic drug monitoring.
Most of the drugs commonly assessed with TDM can be measured on analytical platforms which utilize antibodies (in some form) for detection. Antibodies can be developed that recognize drugs. Although most drugs are much too small to evoke an immune response, scientists can conjugate drugs to immunogenic proteins to produce antibodies that recognize drug-specific epitopes.
Which of the following is the most common technique that is used by clinical laboratories for therapeutic drug monitoring?
Alkaline over acid, or K/A, in TSI reactions is associated with the fermatation of glucose alone and the utilization of peptone.
Which of the following sugars has been fermented by a gram-negative rod that has produced an alkaline slant and an acid butt on triple sugar iron agar (TSI).?
Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions are most commonly due to ABO-incompatible blood being transfused to a recipient with naturally occurring ABO alloantibodies (anti-A, anti-B, anti A,B).
Acute intravascular hemolysis as the result of a blood transfusion is most often associated with which of the following causes?
Neutrophils are typically increased in urinary bacterial infections.
What type of white blood cell is seen MOST frequently in urine sediment with infections of the urinary system?
All the following characteristics are accurate for the influence of Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) except
The tube of choice for trace metal analysis is:
Donor and recipient blood samples (samples utilized for pre-transfusion compatibility testing) must be kept for at least 7 days after transfusion. Blood samples must be available to investigate a transfusion reaction, if necessary.
Donor and recipient blood samples must be kept for at least how long after transfusion?
To prevent blood from clotting the specimen must be:
During primary hypothyroidism, where a defect in the thryoid gland is producing low levels of T3 and T4, the TSH level is increased. TSH is released in elevated quantities in an attempt to stimulate the thryoid to produce more T3 and T4 as part of a feedback mechanism.
Serum TSH levels five-times the upper limit of normal in the presence of a low T4 and low T3 uptake could mean which of the following:
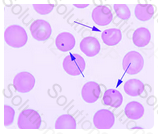
This patient is most likely suffering from sickle cell anemia. This cell, which is sickle-shaped, is indicative of the presence of hemoglobin S. Polychromasia is also commonly observed in sickle cell anemia.
After experiencing crippling pain in her chest, Elizabeth's mother rushes her to the Emergency Room. After a complete blood count and differential are ordered, the hematology technologist views many peripheral cells similar in appearance to those found in the image below. Which condition is most likely present?
The most common specimen analyzed in the hematology section is:
