ASCP-MLT ASCP MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your ASCP ASCP-MLT MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
The thrombin time (TT) involves the addition thrombin to platelet poor plasma to stimulate the clotting process. It reflects ability of the patient to convert fibrinogen to fibrin but is also sensitive to the presence of inhibitors that may be present in the plasma, like heparin. Therefore, it can be used to measure the effects of heparin on a coagulation sample.
This assay would be used to help rule-out heparin contamination in a coagulation sample:
Vitamin K dependent factors are those that require Vitamin K for their synthesis in the liver. Vitamin K is an important factor to gamma-glutamyl carboxylase which adds a carboxyl group to glutamic acid residues on factors II, VII, IX and X, as well as Protein S, Protein C. In adding the gamma-carboxyl group to glutamate residues on the immature clotting factors Vitamin K is itself oxidized. Deficiency of Vitamin K due to malabsorption, liver disease, etc. may contribute to bleeding disorders because clotting factor maturation depends on Vitamin K.
Which of these coagulation factors are referred to as "vitamin-K dependent?"
Which immune elements are involved in a POSITIVE TB skin test?
Report the isolate as coagulase negative Staphylococcus is the correct answer because this is an isolate from a urine specimen with a coagulase negative Staphylococcus susceptible to novobiocin. Staphylococcus saprophyticus is resistant to novobiocin. Further testing is required to speciate coagulase negative Staphylococci but only if the specimen is from a sterile body site, not urine.
Gram positive cocci isolated from a catheterized urine culture on a 76-year-old male gave the following reactions:
Blood agar- creamy, white, opaque colonies
Catalase- positive
Slide coagulase- negative
Tube coagulase- negative
Novobiocin- susceptible
The next action the MLS should take is:
Provide the equivalent measurement for 1 decimeter.
Once substance H is developed, the addition of the sugar N-acetylgalactosamine to the terminal position of the chain gives the molecule "A" antigenic activity.
Which specific terminal sugar causes a red cell to have A antigenic activity?
Blood bank
Which of the following is the most common subgroup of A?
A patient is admitted to the hospital with acute chest pain, but which of the following enzymes will be elevated FIRST if the patient had an MI?
"Universal donor", (a misnomer) is usually applied to group O, Rh negative blood. Although it may be necessary to use group O, Rh negative blood in an extreme emergency, it is preferable to use type specific blood for emergencies.
In an extreme emergency , if the ABO and Rh type are unknown which of the following should be given to the patient?
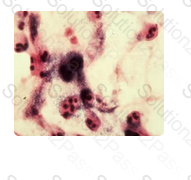
This Gram stain is under-decolorized
This microscopic field is representative of other fields that were observed on a Gram-stained smear. Which of the following describes the quality of the smear?
The Western Blot Assay is used as a confirmatory test for which of the following:
When making a platelet concentrate, the proper procedure is to start with a low centrifugation of the whole blood bag. After the plasma is removed, it is centrifuged again at a higher speed to separate the platelet portion from the plasma portion.
Blood bank
The following steps must be followed in preparation of a platelet concentrate:
This patient is most likely suffering from an immediate-acting coagulation inhibitor; most commonly, lupus anticoagulant. Notice that the addition of normal pooled plasma does not correct upon initial or incubated mix, which means that the inhibitor is not time or temperature-dependent.
Factor VIII is not the correct answer as a factor deficiency would have corrected upon the addition of normal pooled plasma. Factor VII is not the correct answer, as the aPTT assay does not account for factor VII activity or concentration.
The laboratorian completed the mixing study ordered for John Doe. The results are as follows:
Initial aPTT result: 167 seconds
Initial 1:1 Mix with Normal Pooled Plasma: 158 seconds
Incubated 1:1 Mix with Normal Pooled Plasma: 150 seconds
Which of the choices below would most likely explain the results for this patient?
Rapid vascular constriction, not dilation, immediately occurs when there is vascular injury in order to constrict the amount of blood that escapes the vessels; ultimately preventing massive loss of blood.
Primary hemostatic processes resulting from vascular damage include all of the following EXCEPT:
Identify the following cell types by matching them with their respective image.
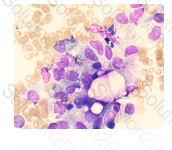
FAB M5 is acute monoblastic leukemia
FAB M1 is acute myeloblastic leukemia without maturation
FAB M3 is acute promyelocytic leukemia
FAB M4 is acute myelomonocytic leukemia
Which FAB designation is called the "true" monocytic leukemia and is characterized by monoblasts, promonocytes, and monocytes?
Troponin is a very specific biomarker that is released during cardiac injury or stress. CK is found not only in cardiac tissue, but also in muscle and brain tissue. LD levels can be elevated in cardiac events, tissue breakdown, and hemolysis. Myoglobin is elevated when muscle tissue is damaged and is not specific for the heart muscle.
Chemistry
Which one of the following is the MOST specific biochemical marker of myocardial infarction?
What has happened in a titer, if tubes #5-7 show a stronger reaction than tubes #1-4?
High triglycerides may be caused by disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypothyroidism, Cushing's sydnrome, liver disease, uremia, dysglobulinemia, nephrotic syndrome, and alcoholism can cause hypertriglyceridemia.
A 46-year old known alcoholic with liver damage is brought in the ER unconscious. One would expect his lipid values to be affected in what way?
The production of long, tapered phialides is one of the key identifying features of Trichoderma species. In contrast, Penicillium species, produce phialides with blunt ends.
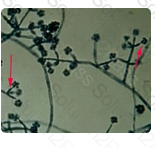
The phialides of Beauveria species are geniculate, forming a zig-zag pattern.
The arrows in the image on the right point to single, long, tapered phialides that extend laterally from either side of the hyphae. This is an identifying feature of which of the fungi listed below?
The laboratory is under the direction of a:
Platelets do not circulate in inactivated, spiny forms. The spiny, sticky form of the platelet is initiated once the platelets become activated in response to blood vessel damage.
Which of the following is not true in terms of platelet characteristics?
Isotonic or normal saline is a 0.85 % solution of sodium chloride in water.
The concentration of sodium chloride in an isotonic solution is :
What are the certification requirements for clinical laboratory professionals?
Which area of the laboratory is responsible for blood coagulation studies that test for the patient's ability to clot their blood?
VLDL transports endogenous lipids, whereas chylomicrons transport exogenous (dietary) lipids. Cholesterol is transported by HDL and LDL.
The function of the very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) is to transport:
AABB Standards do not require a DAT, autologous control, or a minor crossmatch for pretransfusion testing.
Essential components of compatibility testing include all of the following except :
P. vivax characteristically displays Schuffner's dots and often enlarged RBCs along with brownish granules. P. vivax can also have 12-24 merozoies in each cell, actually filling the entire RBC. This parasite also has very irreglar shapes often referred to as "Ameboid".
P. falciparum and P. malariae do not display Shuffner's dots, therefore could not be the correct choice.
P. ovale does display Shuffner's dots in all stages, but characteristically has about 8-12 merozoites in rosettes or irregular clusters inside the RBC. Also, P. ovale characteristically shows enlarged, ovoid RBCs with fimbriated edges.
Identify the parasite of a patient with suspected malaria who demonstrates the following findings on a blood smear:
- Enlarged RBCs, some with fine brownish granules
- > 15 parasites in some cells
- Ameboid structures
- Schuffner's dots
Normal pH of semen must be a value equal to or greater than which of the following?
Myoglobin release is strongly associated with muscle damage; therfore, it would most closely match a diagnosis of massive muscle trauma in this question.
Myoglobinuria is MOST likely to be noted in urine specimens from patients with which of the following disorders?
