ASCP-MLT ASCP MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your ASCP ASCP-MLT MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
The red portion of the NFPA diamond represents fire hazards. The fire classification system for NFPA is as follows:
0 - Will not burn
1 - Must be preheated for ignition; flashpoint above 200°F (93°C)
2 - Must be moderately heated for ignition, flashpoint above 100°F (38°C)
3 - Ignition may occur under most ambient conditions, flashpoint below 100°F (38°C)
4 - Extremely flammable and will readily disperse through air under standard conditions, flashpoint below 73°F (23°C)
A laboratory labels its secondary containers of hazardous chemicals using a color-coded system, with a different color representing each different type of hazard. The coding system follows the color-coding used by the National Fire Protection Agency's "fire diamond." What hazard would be represented by the red section on the hazard label?
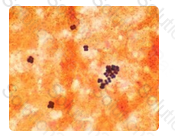
n reporting out Gram stains, one should not go beyond what objective observation will allow. In this case, bacterial cells are observed, which are spherical and gram-positive. Their arrangement in tetrads and clusters might be helpful to the physician, suggesting staphylococci. However, one should stop short of naming staphylococci in an official report, as the large gram-positive cocci in tetrads is also suggestive of Micrococcus species, for which human infections have not been reported.
A Gram stain of the serous exudate is shown in the image. The appropriate report would read:
The intended response is Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies. Each of these conditions lead to a megaloblastic production of the red blood cells in the bone marrow. Since vitamin B12 and folate are needed in order to produce a synchronous development of the nucleus with the cytoplasm in hematologic cells, oval-macrocytosis often occurs if these nutrients are not in adequate supply within the body. This can also affect neutrophils, allowing for the characteristic hypersegmented nucleus.
The photographic field contains several oval-macrocytes and a hypersegmented neutrophil with greater than 5 nuclear segments. Oval macrocytes are most commonly associated with pernicious anemia and malabsorption syndromes leading to vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiencies.
Clinical information relating to chronic infection, aplastic anemia, and other hematologic maligancies provide the context for the presence of the oval macrocyte.
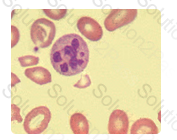
Macrocytic erythrocytes and hypersegmented neutrophils are not present in thalassemias or in Pelger-Huet anomaly (hyposegmented neutrophils).
Conditions suggested by the macrocytes and the neutrophil in the photograph to the right include which of the following?
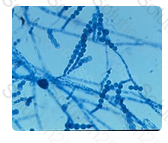
The microscopic features shown here represent Scopulariopsis species. In most instances, particularly if a patient does not have underlying immunologic or hematologic disease, Scopulariopsis species should be considered a contaminant when recovered from a sputum specimen. However, if there is clinical or X-ray evidence of mycotic pulmonary infection, additional daily induced sputum specimens should be obtained.
If Scopulariopsis species or any other hyaline mold is recovered from two or more successive specimens, its potential as a pathogenic agent should be considered. Scopulariopsis species have been reported as the agents of pulmonary fungus ball infections in patients with preexistent cavities and as a cause of pneumonia in patients with leukemia.
Invasive pulmonary disease by this agent has not been reported.
The fungus illustrated in this photomicrograph was recovered from an induced sputum specimen from a 74 year old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This isolate is most likely:
Protein in urine can be confirmed using sulfosalicylic acid (SSA) precipitation. The SSA reagent is added to a small volume of urine. Acidification causes precipitation of protein in the sample, which is subjectively graded as trace, 1+, 2+, 3+ or 4+. SSA reaction will detect albumin, globulins, and Bence-Jones proteins.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate method to confirm a positive protein from a urine dipstick:
IgE levels are often increased in patients with allergic disease. IgE binds to the membranes of mast cells and basophils, and if specific antigen is present to react with the IgE molecule, degranulation of these cells occurs, releasing histamines, and other substances into the blood or tissues.
Which of the following immunoglobulin classes is chiefly responsible for the degranulation of mast cells and basophils:
Joint pain is a common early symptom of HH. Cirrhosis of the liver, cardiomyopathy, and diabetes are late symptoms of HH.
What is a common early symptom of hereditary hemochromatosis (HH)?
Blood Bank
What other component(s) can be shipped together with Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)?
L/S ratio <2.0 indicates an increased risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) at delivery. L/S ratio <1.5 indicates a very high risk of developing RDS.
Which of the following statements regarding the L/S ratio is TRUE?
The correct answer is highlighted below
A ratio of 2:1 or greater usually indicates adequate pulmonary surfactant to prevent respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
A ratio of 1.5:1 indicates fetal lung maturity in pregnancies associated with diabetes mellitus.
Sphingomyelin levels increase during the 3rd trimester causing the L/S ratio to fall slightly during the last two weeks of gestation.
A phosphatidylglycerol (PG) spot indicates the presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid
Lecithin is in direct ratio with sphingomyelin
Heparin contamination is characterized by an elevation in the aPTT test and can also cause an increased PT test as well. Reptilase time tests are used to elimate the effects of heparin contamination as the reagents and method are resistant to the effects of antithrombin III, unlike the PT and aPTT tests. Therefore, it would be expected that a patient sample containing pre-analytical heparin contamination will show an increased aPTT (and sometimes PT as well) while showing a normal reptilase time.
A specimen drawn from an indwelling catheter that was contaminated by heparin would be indicated by:
The correct answer which best fits the characteristics in this question is Mycobacterium kansasii.
The remaining Mycobacterium strains can be elimated as:
Mycobacterium marinum is considered a fast-grower.
Mycobacterium scrofulaceum produce deep-yellow to orange pigmented colonies when grown in the either the light or dark.
Mycobacterium avium grows colonies which are nonpigmented in the light and dark which do not intensify after light exposure.
What is the MOST likely identification of an acid-fast bacillus that demonstrates the following characteristics?
slow growth
cream to tan colored colonies when grown in the dark
development of yellow pigment upon exposure to light
Only non-self antigens can be immunogenic. Self antigens are normally recognized by the immune system as part of the host, so an immune response does not normally occur. Non-self antigens are immunogenic since they have the potential to cause an immune response.
For a substance to be immunogenic it must be:
Although any one of the answers might be considered correct, a report of gram-positive cocci in chains provides sufficient information without going beyond what the observation might allow. In off-the record conversation with the physician, a technologist might divulge that the picture is consistent with Streptococcus; however, enterococci may have a similar Gram stain appearance, potentially leading to the wrong choice of empiric antibiotic agents.
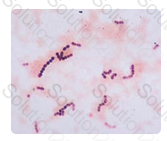
The image shows the Gram stain prepared from the positive blood culture. What is the MOST appropriate report?
Which of these advancements in the clinical laboratory has led to concerns about patient privacy
Insulin is the hormone that is mainly responsible for the entry of glucose into the cell for energy production
Glucagon and epinephrine promote glycogenolysis, conversion of glycogen to glucose, which increases plasma glucose. Cortisol, along with glucagon, increases gluconeogenesis, formation of glucose from noncarbohydrates, which also raises plasma glucose concentration.
Chemistry
Which of the following hormones is mainly responsible for the entry of glucose into the cell for energy production?
The cell shown in this image is a myelocyte. Myelocytes typically have an eccentric nucleus with cytoplasm similar to a mature neutrophils with a slightly bluer tint due to the cell's immaturity.
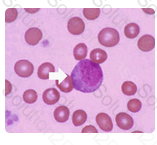
Myelocytes have both primary and secondary granules present in the cytoplasm. The nucleus is less mature and therefore has a loose chromatin clumping pattern.
Identify the cell in this illustration indicated by the arrow:
Phase of reactivity is primarily at immediate spin (4+) and reactions get weaker at AHG (w+). There is no specific pattern of reactivity and the auto control is negative which rules out an autoantibody. This is a strong cold antibody which is still slightly present after incubation and washing.
Activation and binding of the antibody takes place at room temperature or colder. Eliminating this phase will prevent the antibody from binding. Cold antibodies usually are more of a nuisance to blood bankers and are not clinically significant.
When performing an antibody screen, both the screen cells are 4+ at immediate spin and W+ at AHG. The antibody panel shows 4+ reactions at immediate spin and W+ reactions at AHG and there is no specific match to the reaction pattern. The auto control is negative. What would be a logical next step?
Overcentrifugation may cause either a false negative result (if too much agitation is required for resuspension), or a false positive, (if centrifuged clumps cannot be completely dispersed). High concentration of IgG paraprotein, and failure to adequately wash cells can leave unbound IgG which will neutralize antiglobulin reagent. Delay of addition of antiglobulin reagent may allow previously bound IgG antibody to dissociate from red cells.
Blood bank
Which of the following might cause a false positive indirect antiglobulin test:
Osteoblasts are generally seen in clusters while plasma cells are often more diffusely distributed. Osteoblasts have delicate cytoplasm, whereas plasma cells have dense basophilic cytoplasm with a perinuclear halo.
Hematology
The large cell shown in the illustration to the right is occasionally seen in the bone marrow and can be mistaken for a plasma cell - what is this cell called:
Type B blood is found in higher frequency in:
Which EBV markers would be MOST likely positive for an individual who had infectious mononucleosis 9 years ago?
A combination of (nonselective) 5% sheep blood and (selective) MacConkey agars is sufficient for the recovery of the pathogenic microorganisms that are most commonly encountered in urinary tract infections (UTIs). MacConkey is the selective culture medium that is most commonly used to inhibit growth of gram-positive organisms (most UTIs are caused by gram-negative organisms).
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) is a selective agar that also inhibits the growth of gram-positive organisms. Therefore, using only a combination of MacConkey and EMB would prevent the detection of a gram-positive organism, if this were the cause of the infection.
Chocolate agar or other enriched media may be needed in addition to blood and MacConkey if a more fastidious organism is suspected.
Thayer-Martin would be used specifically for recovery of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Thayer-Martin (or Modified Thayer-Martin) inhibits other microorganisms and allows the selective recovery of both N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis.
Microbiology
Which culture agar combinations below will usually be sufficient for MOST routine urine culture investigations?
Match each of the following:
1. Ratio of cellular area to total area in the bone marrow section.
2. Number of myeloid cells compared to nucleated erythroid cells.
3. Use low power to estimate their quantity and appearance.
4. Use Perls' Prussian blue stain.
Which of the following tubes produces a serum sample?
Question options:
Public health guidelines recommend that manipulation of samples for influenza testing be done inside a safety cabinet. Safety goggles could be worn if the specimen or procedure may be prone to splashes or sprays of infectious material. Utility gloves are not necessary.
Public health guidelines recommend that laboratory specimens for influenza testing must be manipulated using which of the following safety precautions?
Some elderly individuals can have poor dietary habits which can lead to decreased nutrient absorption, including zinc.
A zinc deficiency in the elderly is often caused by:
The deposition of plaques containing cholesterol and lipids on the innermost layer of the walls of large and medium-sized arteries is the defintion of atherosclerosis.
Arteriosclerosis is a more general term that describes a thickening and loss of elasticity of the walls of the arteries (hardening of the arteries). Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis but is not synonymous with it.
Atherosclerosis is not the most common outcome for risk marker studies because it can be hard to measure. Infarcts, cardiac procedures, death, and 'events' are more common. Most humans have visible or measureable atherosclerosis by early middle age.
Chemistry
Which of the following is true concerning atherosclerosis?
Yellow stopper tubes are used for all of the following except:
Question options:
Bacitracin susceptibility is a presumptive test for the identification of Lancefield group A Streptococcus.
Which of the following is a presumptive test for the identification of Lancefield group A Streptococcus:
The patient's BUN is within normal range (5-20 mg/dL) while the creatinine is about five times the upper normal range (0.6-1.2 mg/dL). Gross elevations in creatinine are almost always accompanied by elevations in BUN when there is kidney impairment. Either the BUN or creatinine value in this case is incorrect. Both tests should be repeated.
A patient's BUN value is 15 mg/dl and his creatinine is 5 mg/dl. If this patient is not undergoing dialysis, what conclusion would you draw from these results?
Secondary granules, also known as specific granules first appear in the myelocyte stage next to the nucleus. In neutrophils this is termed the "dawn of neutrophilia".
What is one of the main characteristics of secondary granules in the neutrophilic granulocyte cytoplasm?
