ASCP-MLT ASCP MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your ASCP ASCP-MLT MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Which of the following tubes contains an anticoagulant that does not bind calcium?
Question options:
Lavender stopper tubes can be used for all of the following except:
Which one of the following conditions is NOT associated with hereditary spherocytosis?
Specimens collected from patients in contact isolation should be:
Hemolytic anemia, myelodysplasia, and liver disease may each fit this peripheral blood picture. Each of these conditions can display peripheral blood macrocytosis. It is easy to observe the overall larger size of the red blood cells in this image compared to the normal lymphocyte also present.
When macrocytes are present, they should be examined for their shape (round vs. oval), the hemoglobin content (central pallor), and whether or not there are any inclusions present in the cell.
Iron deficiency would not be the correct answer in this case, since this condition is associated with microcytosis instead.
The complete blood count was obtained from a patient recently admitted to the emergency room. The red blood cell indices obtained revealed an MCV of 115 femtoliters (fL) (normal range 80 - 90 fL). The patient met the criteria for a peripheral blood smear examination. A representative field is shown on the right.
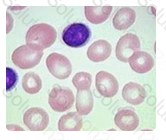
Which of the following conditions may be indicated by the results seen on this peripheral blood smear?
The activities conducted in a laboratory with a certificate of registration include:
Antibodies are differentiated based on their heavy chains; different heavy chains create different isotypes. Humans have five different isotypes of immunoglobulins.
Immunology
The part of the molecule responsible for differences among immunoglobulin classes is:
Creatinine clearance tests are utilized to estimate the glomerular function of the kidney. The creatitine clearance calculation is defined as the volume of plasma that is cleared of creatinine by the kidney per unit of time and uses the following formula:
creatinine clearance = Urine creatinine conc x Volume / Plamsa creatinine conc
Creatinine clearance measurements have a recommended specimen requirement = 24-hour urine collection.
Which of the following tests would be useful in the assessment of glomerular filtration:
This type of laboratory testing provides immediate assessment of the patient and can be performed at their bedside:
A quality control program is to be set up for the following tests:
Phenylalanine deaminase (PAD)
Indole production
Voges-Proskauer (V-P)
Which pair of stock culture organisms would be MOST suitable to verify the performance of these three tests?
Which of the following is a current title for clinical laboratory professionals with a 4 year degree?
First, the RBC indices must be calculated. The MCV ((Hct/RBC) x 10) = 71 fL. Since the reference range for the MCV is 80-100 fL, this anemia would be classified as microcytic. The MCH ((Hgb/RBC) x 10) = 19.3 pg. Since the reference range for the MCH is 27-33 pg, this would be considered hypochromic. Finally, the MCHC ((Hgb/Hct) X 100) = 27%. Since the normal range for the MCHC is 33%-36%, this would indicate hypochromia which correlates with the MCH findings. The correct answer is therefore microcytic, hypochromic anemia.
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with lethargy and pallor. The CBC results are as follows:
RBC = 4.1 x 1012/L
Hemoglobin = 7.9 g/cL
Hematocrit = 29%
How would you classify this anemia?
The term affinity refers to the strength of attraction between a single antigenic determinant and a corresponding antigen binding site. The term avidity refers to the total strength of the attraction between an antibody and a multivalent antigen. The reaction between an IgM molecule (which has 10 antigen binding sites), and a multivalent antigen is therefore much stronger than that of an IgG antibody (which has only 2 antigen binding sites).
Avidity is best described by which of the following statements:
Synovial fluid is actually quite viscous and does not have the same consistency as plasma. The reason for its thicker consistency is to provide cushion and reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement.
Urinalysis & Other Body Fluids
All of the statements below about synovial fluid are true EXCEPT:
No HLA matching is performed for corneal tissue transplants as the cornea occupies a privileged site not usually seen by the immune system. This term has been coined "immune privileged".
Corneal tissue may be transplanted successfully from one patient to another because:
Once substance H is developed, the addition of the sugar N-acetylgalactosamine to the terminal position of the chain gives the molecule "A" antigenic activity.
Which specific terminal sugar causes a red cell to have A antigenic activity?
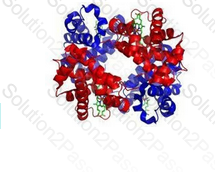
A normal hemoglobin molecule consists of a tetramer, of four heme and four globin chains, with a molecular weight of 64,500 daltons. Each of the four units can bind a molecule of oxygen for transport to the body's tissues. In the image shown below, there are four monomers (2 red globin chains and 2 blue globin chains) which form the entire hemoglobin tetramer structure. The green portions represent the 4 heme groups.
A normal hemoglobin molecule is comprised of the following:
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) is used as an aid in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular disease (CVD). At low levels, it can detect those at risk for cardiac heart disease. At high levels in those with no history of heart disease, it indicates a high risk for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), stroke, or peripheral vascular disease. For patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or stable coronary disease, hs-CRP is used to predict future coronary events.
Ranges of hs-CRP in prediction of risk for CVD are:
<1.0 mg/L Low CVD risk
1.0-3.0 mg/L Average risk for CVD
>3.0 mg/L High risk for future CVD
If results are >10.0 mg/L, the patient should be evaluated for an acute inflammatory condition.
Chemistry
A high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) test result of 5 mg/L (normal = < 1 mg/L) may indicate which of the following?
The area of the federal government that ensures that the laboratory is stocked with gloves for their employees when performing tests on patient blood sample is:
Hybridization is a technique used to determine presence of target DNA or RNA by adding a synthetic strand that binds by complementary base pairing to the target.
Microbiology
In molecular diagnostic testing, hybridization employs complementary base pair binding of a synthetic strand to DNA or RNA.
The liver is the primary target organ for the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). The inflammation caused by HBV can result in permanent liver damage, including cirrhosis, liver failure, and even hepatocellular carcinoma.
What is the primary target of the Hepatitis B virus?
Set of comprehensive safety guidelines designed to protect patients and health care workers
hs-CRP is a more sensitive version of the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, a test that has been used for many years to assess inflammation in settings such as lupus, transplantation, infection, etc.
Which of the following cardiovascular risk markers is a more sensitive version of a test that is used to assess inflammation?
In sickle cell anemia, rapid hemoglobin turnover may be present. HbA1C and other glycated hemoglobin assays are not valid in rapid hemoglobin turnover and in abnormal hemoglobin conditions. Fructosamine measurements can be used because of shorter half life of albumin.
HbA1C measurements are NOT ordinarily used to monitor long-term diabetic control in a diabetic with sickle cell anemia.
PCT usually rises within 3-6 hours of infection. CRP also increases rapidly following infection, but is not as specific for infection as PCT. A rise in CRP could also occur with SIRS. Lactic acid is usually used to detect and monitor impaired circulation and tissue oxygenation in critically ill patients.
Chemistry
Of the three laboratory tests that are listed, which has proven to be most effective for early differentiation of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) from sepsis due to its increase following infection and higher specificity?
Pink or Red stopper tubes can be used for Blood Bank!
Question options:
Failure to deliver glucose drawn in a serum separator tube (SST) to the laboratory within the recommended time will cause:
Question options:
The red blood cell distribution width (RDW) increases as the severity of alpha thalassemia increases because of changing MCV as the bone marrow produces smaller cells. In addition, if Hemoglobin H bodies are present, they result in the formation of schiztocytes (RBC fragments) that can have an effect on the MCV and RDW.
The Red cell Distribution Width (RDW) in alpha thalassemia is
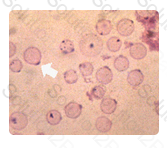
Heinz bodies occur as the result of denaturation and precipitation of hemoglobin, and are often attached to the red cell membrane. They require staining with crystal violet or methyl violet to be visible. They may be seen in thalassemia, with unstable hemoglobins, or during a hemolytic episode in G6PD deficiency.
Hematology
The intracellular precipitates seen in the RBCs in this illustration is termed:
Personal protective equipment (PPE) should be put on in the following order:
