ASCP-MLT ASCP MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your ASCP ASCP-MLT MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN - MLT(ASCP) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
A phlebotomist has just performed a venipuncture on a patient. How would the phlebotomist dispose of the used needle?
HCG levels rise rapidly during the first trimester, then the levels start to decline around week 16. The hCG levels slowly decrease and can level off during the remainder of the pregnancy.
The following BEST describes serum hCG levels during pregnancy:
Granulocytes are the most granular population; they have the most side scatter of the cell populations that are listed.
Which of these white blood cell populations would have the MOST side scatter when analyzed using flow cytometry?
UA & Body Fluids
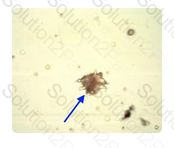
What is the identification of this crystal seen in a urine with an alkaline pH?
A key laboratory characteristic by which Mycobacterium bovis can be separated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis is:
Antibodies in the Rh system typically exhibit which one of the following characteristics?
Microcontainer collection order of draw differs from regular peripheral blood collection order of draw. When performing a capillary draw, the lavender top container is obtained first. This decreases the possibility of clots in the container which would invalidate the results of the complete blood count test.
After the lavender is drawn, other containers with anticoagulants would be collected, and containers without anticoagulants would be collected last.
A phlebotomist must perform a skin puncture to obtain capillary specimens for a complete blood count (CBC), a plasma-based chemistry test, and a serum-based immunology test. The microcollection containers that will be used are lavender top containing EDTA anticoagulant, green top containing heparin anticoagulant, and gold top containing no anticoagulant. Which microcollection container should be collected first?
Certain recipients have increased risk for developing TA-GVHD. They are:
Neonates less than 4 months of age
Fetuses
Recipients with a congenital or acquired immunodeficiency, such as bone marrow or stem cell recipients, and patients receiving chemotherapy
recipients of donor units from a blood relative
Which of the following patients are at risk for transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD) and require irradiated cellular blood products? (Choose all that apply)
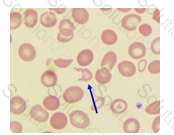
What is the cell that is indicated by the arrow in this field?
Which of the procedures listed below will increase the platelet concentration in the preparation of Platelets?
Twelve weeks after onset of the disease, patients with uncomplicated acute hepatitis B usually will demonstrate which of the following in their serum?
Infection early in the pregnancy is the most dangerous time period for the manifestation of anomalies due to rubella. In fact, defects are rare when infection occurs after 20 weeks gestation.
Immunology
The greatest risk for the manifestation of anomalies in maternal rubella infection during gestation is the:
Atherosclerosis is a hardening of an artery specifically due to the build up of plaque. The risk to patients with significant atherosclerosis is that eventually a narrowing of the artery (stenosis) can cause a reduction in oxygen delivery to tissues and plaque rupture can lead to an acute coronary event.
Atherosclerosis is a hardening of an artery specifically due to which of the following?
The presence of a clot is acceptable in:
Basophilic stippling is the term used to describe red blood cells that contain tiny particles of RNA within their cytoplasm. Basophilic stippling is associated with many conditions, but is strongly associated with lead poisoning.
Multiple small, dark blue particles scattered throughout the cytoplasm of erythrocytes is/are called:
Ammonium biurate crystalsare typically round, irregularly spiked and yellow-brown in color.
A microscopic examination of a normal urine pH 8.0 shows 2+ yellow-brown thorny spheres which are MOST probably:
Beta-thalassemia major, also known as Cooley's anemia, has inherited two genes for beta thalassemia without a normal beta-chain gene. This disease is assoicated with a marked deficiency in beta chain production and in the production of normal Hb A. These patients exhibit increased amounts of iron due to the mutliple transfusions that keep them alive. There is also a striking increase in hemoglobin F and an elevation in hemoglobin A2.
Hematology
A 5-year-old African American child with hepato-splenomegaly and skeletal abnormalities has the following lab results:
WBC = 4,800/cu.mm
20 NRBC/100 WBC
RBC = 2.70 X 106
HGB = 6.2 g/dL
Many target cells
Marked hypochromasia, anisocytosis & poikilocytosis
Serum Iron = 200 µg/dL (elevated)
Sickle Solubility = negative
Hemoglobin F = elevated
What is the PROBABLE cause of these findings?
The personal protective equipment (PPE) that is used in the laboratory to protect the personnel when performing tests on patient blood samples is which of the following:
Patients who develop severe sepsis or septic shock commonly have increased plasma lactic acid values.
Patients who develop severe sepsis or septic shock commonly have __________ plasma lactic acid values.
Listeria are non-capsulated, non-acid-fast, ß-hemolytic, gram-positive bacilli that have a characteristic tumbling motility. They are found primarily in the environment and in the human GI tract. Since L. monocytogenes multiplies intracellularly, control of listeriosis requires cell-mediated immunity; thus, immunocompromised patients (such as newborns) are at high risk.
Which bacterial species is a common agent of neonatal bacteremia?
Match each of the descriptions with the appropriate magnification:
1. Color, Rouleau, Overall Slide Quality, Cell Distribution
2. Platelet estimates RBC-platelet-WBC morphology WBC differential RBC inclusions
3. Select area to examine, WBC estimate
The Fc portion of immunoglobulin can activate the classical complement pathway, where the heavy chains, light chains, hinge regions and Fab portions cannot.
Which part of the immunoglobulin molecule is responsible for activating complement?
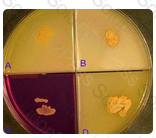
One of the key characteristics to the identification of Nocardia asteroides is its inability to hydrolyze casein, tyrosine or xanthine, as shown in this photograph. Nitrates are reduced to nitrites. Both Nocardia brasiliensis and Actinomadura madurae hydrolyze both casein and tyrosine; Streptomyces griseus hydrolyzes all three of the substrates.
Illustrated in this photograph is an agar quadrant plate containing casein (A), tyrosine (B), nitrate (C) and xanthine (D). None of the substrates have been hydrolyzed and nitrate has been reduced. The most likely identification is:
Gamma globulin (anti-D) is given to Rh-negative mothers to prevent any D antibody production, which could cause harmful effects in future pregnancies with an Rh-positive fetus. The administered anti-D will bind fetal Rh-positive cells that may come from the fetus in vivo; therefore the mother will not produce anti-D herself, preventing sensitization.
A solution of gamma globulins containing anti-Rh (D) is given to an Rh (D) negative mother to:
Spirochetes such as Borrelia and Treponemes are best visualized using darkfield microscopy. Borrelia, which causes Relapsing fever, can be visualized under darkfield microscopy of wet preps of peripheral blood. Treponema can be visualized by darkfield microscopy of early primary lesions, and aspirates of affected lymph nodes.
Which of the following organisms is best visualized by use of a darkfield microscope:
The term that is used to describe the color in these tubes of CSF is "xanthochromia." Xanthochromia is an abnormal color, usually yellow, orange, or pink, in the supernatant of the CSF sample. It may indicate that a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has occurred.

Jaundice and icterus both describe a yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, and eyes. Blood plasma/serum that is deep yellow is also described as icteric.
What term is used to describe the color in these tubes of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
As magnification DECREASES, the opening of the iris diaphragm will...
DAT ( Direct Antiglobulin Test ).
When AHG or Coombs serum is used to demonstrate that red cells are antibody coated in vivo, the procedure is termed:
The image shown in this question is depicting a rosette formation. Here the red blood cells are surrounding and adhering to the outside of the white blood cell.
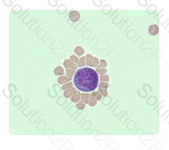
What is the best description of the phenomenon seen in this illustration?
The Bethesda assay is used to measure the titer and activity of the antibody present in a patient's sample. Prothrombin time is an initial screening procedure for bleeding disorders and a test used for monitoring anticoagulant therapy. A thrombin time is used to detect heparin interference in an aPTT mixing study. A mixing study is performed to detect the presence of a factor deficiency or coagulation inhibitor, but does not quantify the result.
Hematology
Which of the following tests is used to quantify a coagulation inhibitor?
