BA2 CIMA Fundamentals of management accounting Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA BA2 Fundamentals of management accounting certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
A company wishes to compare the variability of its monthly sales revenue in country A with that of country B. The two countries use different currencies.
The monthly sales revenue for the last 48 months in country A (which is measured in $) has been analysed as follows.
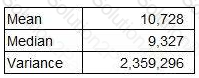
What is the coefficient of variation of this data?
Give your answer as a percentage to one decimal place.
A sales manager has analysed a sample of 350 sales transactions from the latest period. The manager wishes to investigate:
how many customers made their purchase online using the internet and how many purchased by telephone.
how many were new customers and how many were placing repeat orders.
The following table shows the results of the analysis.
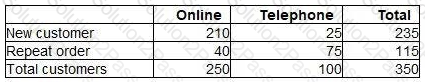
If the pattern of sales occurs next period, the probability of a particular sale being a repeat order placed online is closest to:
Data for the latest period for a company which makes and sells a single product are as follows:
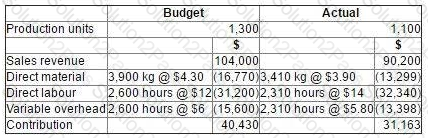
There were no budgeted or actual changes in inventories during the period.
The sales volume contribution variance for the period was:
A confectionery manufacturer is considering adding a new product to the current range. Forecast data for the product are as follows.
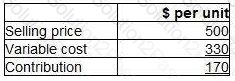
Incremental fixed costs attributable to the new product are forecast to be $24,000 each period.
The forecast sales volume of 180 units is insufficient to achieve the target profit of $10,000 each period.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A project is about to be launched. Two of the three possible outcomes and their associated probabilities are as follows:
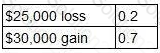
The remaining possible outcome is a $70,000 gain.
What is the correct calculation of the expected value of the project?
The following data are available for a company that produces and sells a single product.
The company’s opening finished goods inventory was 2,500 units.
The fixed overhead absorption rate is $8.00 per unit.
The profit calculated using marginal costing is $16,000.
The profit calculated using absorption costing and valuing its inventory at standard cost is $22,400.
The company’s closing finished goods inventory is:
A company which manufactures and sells one product has fixed costs of $80,000 per period. The selling price per unit of $25 generates a contribution/sales ratio of 40%.
How many units would need to be sold in a period to earn a profit of $10,000?
In responsibility accounting, costs and revenues are grouped according to:
The records of a manufacturing company show the following relationship between total cost and output.
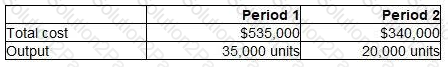
The budgeted output for Period 3 is 27,000 units. Assume that previous cost behaviour patterns will continue.
What is the total budgeted cost for Period 3?
Give your answer in the nearest whole number.
Which of the following would NOT require taking into account the time value of money?
In order for the information in a management accounting report to be authoritative its contents must be:
Which of the following statements regarding variances is valid?
Which of the following would NOT be an appropriate performance measure for a profit centre manager?
Which of the following is NOT a valid purpose of budgeting?
A company makes and sells a range of products. The standard details per unit for one of these products, product X, are as follows.
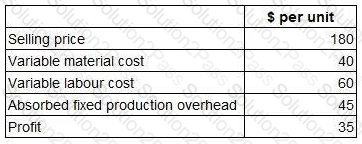
To meet sales demand, the company must obtain 2,000 units of product X next month. There is sufficient labour capacity to produce 1,500 of these units in-house during normal time. However, any production above this level would require overtime working which would be paid at a premium of 50%.
The company can buy as many units of product X as it wishes next month from an external supplier at a price of $120 per unit.
What is the total financial benefit to the company of purchasing the appropriate number of units from the external supplier rather than producing them in-house?
The possible returns and associated probabilities of two independent projects are as follows:
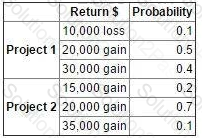
It has been decided that both projects are to be launched.
Which TWO of the following statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Data for the latest period for a company which makes and sells a single product are as follows:
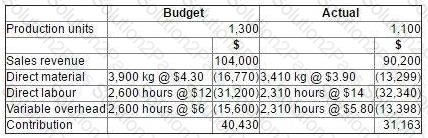
There were no budgeted or actual changes in inventories during the period.
The variable overhead expenditure variance for the period was:
A company has two production departments and two service departments (Maintenance and Stores). The overhead costs of each of the departments are as follows.

The following equations represent the reapportionment of each of the service department overheads to the other.
M = 4,700 + 0.1S
S = 5,800 + 0.2M
Where M = total Maintenance overhead after reapportionment from Stores
S = total Stores overhead after reapportionment from Maintenance
60% of the total Maintenance overhead and 50% of the total Stores overhead are to be apportioned to Production Department 1.
The total production overhead for Production Department 1 after reapportionment of the service departments’ overhead costs is closest to:
Which type of budget would be the most suitable for a cash budget?
The management accountant has completed the appraisal of an investment in new office equipment.
It has now been discovered that the cost of capital used in the appraisal should have been higher.
What will be the effect on the calculated net present value (NPV) and the payback period?
