F3 CIMA Financial Strategy Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA F3 Financial Strategy certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Company Z has identified four potential acquisition targets: companies A, B. C and D.
Company Z has a current equity market value of S590 million.
The price it would have to pay for the equity of each company is as follows:
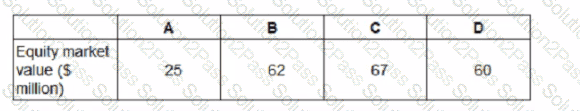
Only one of the target companies can be acquired and the consideration will be paid in cash.
The following estimations of the new combined value of Company Z have been prepared for each acquisition before deduction of the cash consideration:
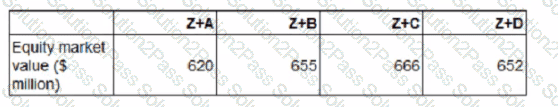
Ignoring any premium paid on acquisition, which acquisition should the directors pursue?
XYZ has a variable rate loan of $200 million on which it is paying interest of Liber ‘3%.
XYZ entered into a swap with AG bank to convert this to a fixed rate 8% loan. AB bank charges an annual commission of 0.4% for making this arrangement
Calculate the net payment from KYZ to AB bank at the end of the first year if Libor was 2% throughout the year.
Give your answer in $ million, to one decimal place.

The competition authorities are investigating the takeover of Company Z by a larger company, Company Y.
Both companies are food retailers.
The takeover terms involve using a part cash, part share exchange means of payment.
Company Z is resisting the bid, arguing that it undervalues its business, while lobbying extensively among politicians to sway public opinion against the bidder.
Which of the following actions by Company Y is most likely to persuade the competition authorities to approve the acquisition?
Modigliani and Miller are the main proponents of the view that the dividend policy is irrelevant to the value of a company's shares.
They argue that a company that continually reinvests its entire earnings would generate the same shareholder wealth if it engaged in a policy of high dividends and financed its expansion with funds obtained from rights issues.
Which THREE of the following statements are assumptions that are required in order to support this proposition?
A company is reporting under IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures for the first time and the directors are concerned about whether this will lead to the disclosure of information that could affect the company's share price.
The company is based in a country that uses the A$ but 40% of revenue relates to export sales to the USA and priced in US$.
When the company reports under IFRS 7 for the first time, the share price is most likely to:
A company is owned by its five directors who want to sell the business.
Current profit after tax is $750,000.
The directors are currently paid minimal salaries, taking most of their incomes as dividends.
After the company is sold, directors' salaries will need to be increased by $50,000 each year in total.
A suitable Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio is 7, and the rate of corporate tax is 20%.
What is the value of the company using a P/E valuation?
On 1 January:
• Company ABB has a value of $55 million
• Company BBA has a value of $25 million
• Both companies are wholly equity financed
Company ABB plans to take over Company BBA by means of a share exchange Following the acquisition the post-tax cashflow of Company ABB for the foreseeable future is estimated to be $10 million each year The post-acquisition cost of equity is expected to be 10%
What is the best estimate of the value of the synergy that would arise from the acquisition?
Company Z has identified four potential acquisition targets: companies A, B, C and D.
Company Z has a current equity market value of $580 million.
The price it would have to pay for the equity of each company is as follows:
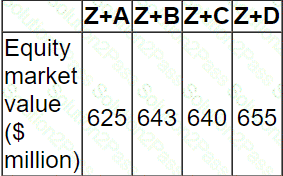
Only one of the target companies can be acquired and the consideration will be paid in cash.
The following estimations of the new combined value of Company Z have been prepared for each acquisition before deduction of the cash consideration:
Ignoring any premium paid on acquisition, which acquisition should the directors pursue?
A company's Board of Directors is assessing the likely impact of financing future new projects using either equity or debt.
The directors are uncertain of the effects on key variables.
Which THREE of the following statements are true?
Company A is planning to acquire Company B. Both companies are listed and are of similar size based on market capitalisation No approach has yet been made to Company B's shareholders as the directors of Company A are undecided about the most suitable method of financing the offer Two methods are under consideration a share exchange or a cash offer financed by debt.
Company A currently has a gearing ratio (debt to debt plus equity) of 30% based on market values. The average gearing ratio (debt to debt plus equity) for the industry is 50% Although no formal offer has been made there have been market rumours of the proposed bid. which is seen as favorable to Company A. As a consequence. Company As share price has risen over the past few weeks while Company B's share price has fallen.
Which THREE of the following statements are most likely to be correct?
Company HJK is planning to bid for listed company BNM
Financial data for BNM for the financial year ended 31 December 20X1:
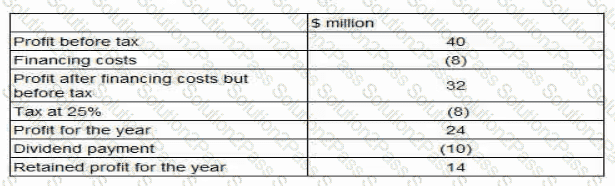
HJK is not forecasting any growth in these figures for the foreseeable future
Profit and cost data above should be assumed to be equivalent to cash flow data when answenng this question
Which THREE of the following approaches would be most appropriate for HJK to use to value the equity of BNM?
A company plans to raise finance for a new project.
It is considering either the issue of a redeemable cumulative preference share or a Eurobond.
Advise the directors which of the following statements would justify the issue of preference shares over a bond?
Company AEE has a 10 year 6% corporate bond in issue which has a nominal value of $400 million, which is currently trading at 95%. The bond is secured on the company's property
The Board of Directors has calculated the equity value of Company AEE as follows;

Which THREE of the following are errors in the valuation?
The directors of the following four entities have been discussing dividend policy:
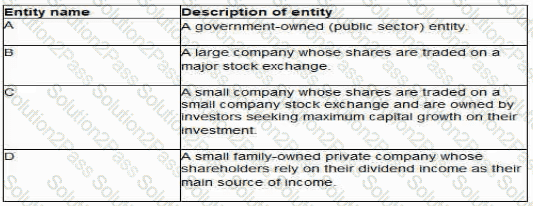
Which of these four entities is most likely to have a residual dividend policy?
Company A has agreed to buy all the share capital of Company B.
The Board of Directors of Company A believes that the post-acquisition value of the expanded business can be computed using the "boot-strapping" concept.
Which of the following most accurately describes "boot-strapping" in this context?
On 31 October 20X3:
• A company expected to agree a foreign currency transaction in January 20X4 for settlement on 31 March 20X4.
• The company hedged the currency risk using a forward contract at nil cost for settlement on 31 March 20X4.
• The transaction was correctly treated as a cash flow hedge in accordance with IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement.
On 31 December 20X3, the financial year end, the fair value of the forward contract was $10,000 (asset).
How should the increase in the fair value of the forward contract be treated within the financial statements for the year ended 31 December 20X3?
An all-equity financed company currently generates total revenue of $50 million.
Its current profit before interest and taxation (PBIT) is $10 million.
Due to difficult trading conditions, the company expects its total revenue to be constant next year, although some margins will reduce.
It forecasts next year's PBIT will fall to 18% on 40% of its revenue, but that the PBIT on the other 60% of its revenue will be unaffected.
The rate of corporate tax is 20%.
What is the forecast percentage reduction in next year's Earnings?
A company based in Country A with the A$ as its functional currency requires A$500 million 20-year debt finance to finance a long-term investment The company has a high credit rating, but has not previously issued corporate bonds which are listed on the stock exchange Which THREE of the following are advantages of issuing 20 year bonds compared with simply borrowing for a 20 year period?
A company is considering either directly exporting its product to customers in a foreign country or setting up a subsidiary in the foreign country to manufacture and supply customers in that country.
Details of each alternative method of supplying the foreign market are as follows:
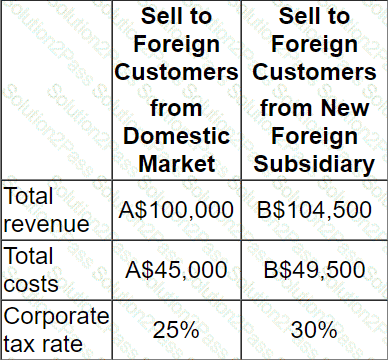
There is an import tax on product entering the foreign country of 10% of sales value.
This import duty is a tax-allowable deduction in the company's domestic country.
The exchange rate is A$1.00 = B$1.10
Which alternative yields the highest total profit after taxation?
It is now 1 January 20X0.
Company V, a private equity company, is considering the acquisition of 40% of the equity of Company A for a total amount of $15 million.
Company A has been established to develop a new type of engine which will be launched at the end of 20X1. Company A is forecasting that the new engine will result in free cash flows to equity of $2m in its first year of operation and that this will rise by 8% per year for the foreseeable future.
The new engine is the only commercial activity that Company A is involved in.
Company V intends to sell its stake in Company A when the new engine is launched.
Company A has a cost of equity of 12%.
Assuming that Company V receives an amount that reflects the present value of their shares in company A. what is the estimated annual rate of return to Company V from this investment? (To the nearest %)
