P1 CIMA Management Accounting Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA P1 Management Accounting certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
How would the cost of recycling scrap be classified in an environmental costing system?
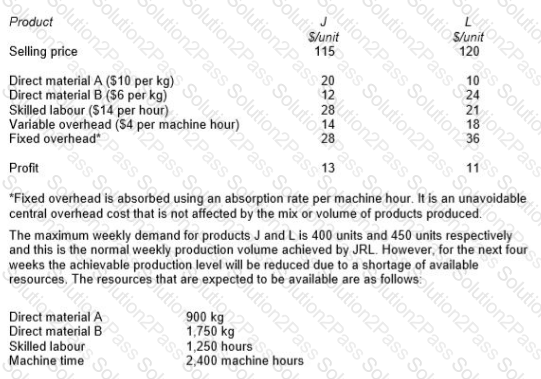
JRL manufactures two products from different combinations of the same resources. Unit selling prices and unit cost details for each product are as follows:
* Refer to your answer in the previous question.
The optimal solution to the previous question shows that the shadow prices of skilled labour and direct material A are as follows:
Skilled labour $ Nil Direct Material A $11.70
Explain the relevance of these values to the management of JRL.
Select ALL the true statements.
You are a trainee management accountant working for a prestigious manufacturing firm. One day you go to a business meeting a business meeting and the managing director is there. They stand up and say that the
company is losing too much money through wastage and losses and so they have decided to implement a total quality management system. They go on to say this system will:
1:Allow the company to improve on a consistent and continual basis
2:Allow the company to identify and allocate quality accountability to certain departments
3:Help the company detect error and fraud
Are ALL of these statements correct?
Which one of the following would NOT be included in a decision to close a division of an organization?
A company has only 10,100 hours of skilled labour available next period.
Data for its three products for next period are as follows.
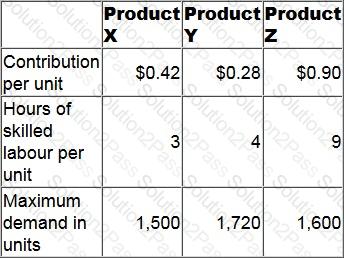
At least 500 units of each product must be sold each period.
No inventories are held.
How many units of Product X should be manufactured next period in order to maximise profit?
Which THREE of the following statements relating to fixed overhead variances are correct?
A snowboard manufacturer is considering investing in technology that will give a good indication of how heavy snowfall will be in the future. The predictions tend to be reasonably accurate.
The current budgeted profit for the year is £2,560,000 but if they invest in this technology and it works, the expected profit will be £2,640,000. The manufacturer is willing to invest a maximum of £40,000 into the venture.
What is the expected profit if the investment is NOT made?
TDM edits, prints and publishes three magazines, Mag A, Mag B and Mag C. The company operates an activity-based costing system.
The following information has been obtained.
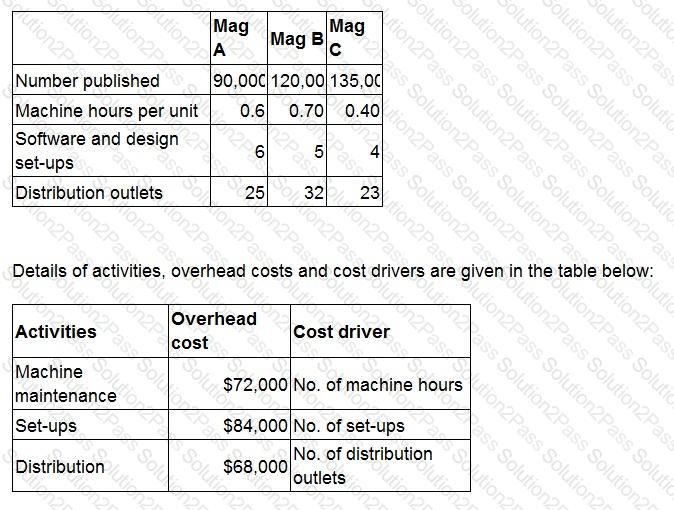
What is the overhead cost attributable for each Mag A publication?
Give your answer to the nearest whole cent.
A bakery manager is deciding how many batches of birthday cakes to decorate each day.
Demand for the birthday cakes varies from 12 to 15 batches per day. Each batch decorated and sold earns a contribution of $40 but each batch unsold leads to loss of contribution of $15.
The payoff table below shows the total $ contribution from each of the possibilities:
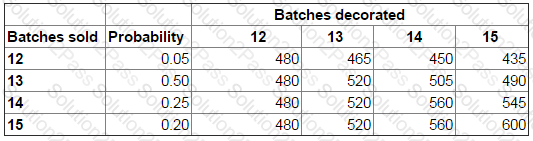
Based on expected values, the number of batches of birthday cakes the bakery manager should decorate each day is:
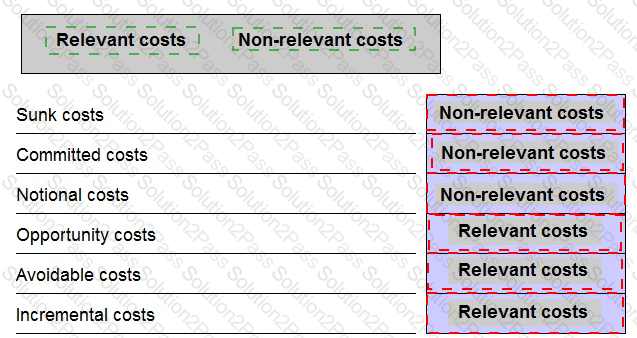
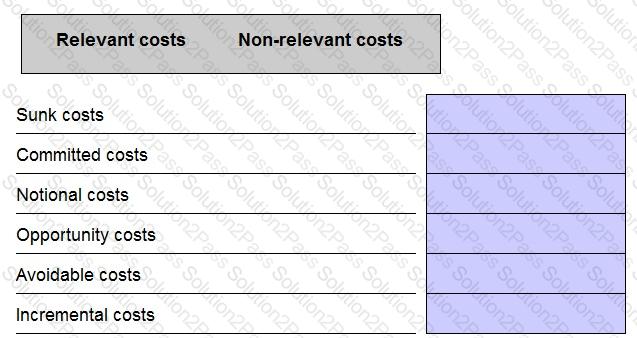
When preparing data for a short term decision, which THREE of the following are relevant costs?
State whether the following costs are relevant or non-relevant in the context of short-term decision making scenarios.
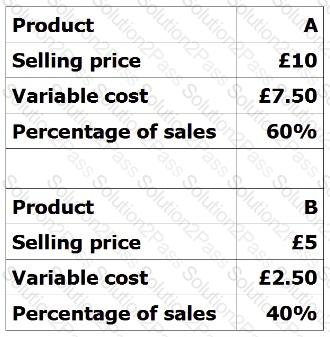
Find the weighted average contribution per unit using the following information:
A company sells and services photocopying machines. Its sales department sells the machines and consumables, including ink and paper, and its service department provides an after sales service to its customers. The after sales service includes planned maintenance of the machine and repairs in the event of a machine breakdown. Service department customers are charged an amount per copy that differs depending on the size of the machine.
The company’s existing costing system uses a single overhead rate, based on total sales revenue from copy charges, to charge the cost of the Service Department’s support activities to each size of machine. The Service Manager has suggested that the copy charge should more accurately reflect the costs involved. The company’s accountant has decided to implement an activity-based costing system and has obtained the following information about the support activities of the service department:
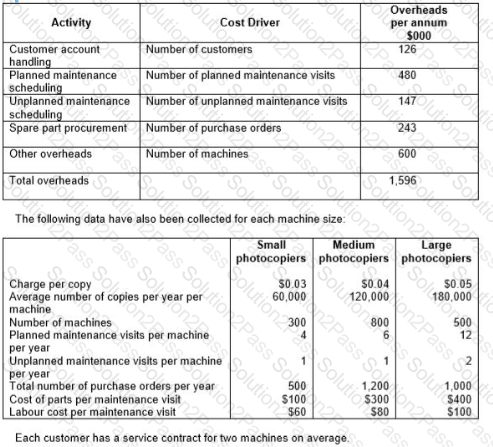
Calculate the annual profit per machine for each of the three sizes of machine, using the current basis for charging the costs of support activities to machines.
What type of budget is prepared on an annual basis taking current year operating results and adjusting them for expected growth and inflation?
A company reports planning and operational variances to its managers. The following data are available concerning the price of direct material M in the last period. Material M is the only material used by the company. The company operates a just-in-time (JIT) purchasing system.
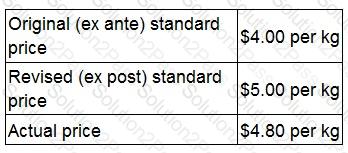
Which TWO of the following statements about last period are definitely correct based on this information?
The direct material price operational variance was adverse.
Which of the following explain why standard costing is less appropriate in the contemporary business environment?
1. In a continuous improvement environment standard costing can restrict the impetus to remain as cost competitive as rivals.
2. Fixed overhead variances are less relevant as fixed costs represent a decreasing proportion of total manufacturing cost.
3. In a just-in-time environment there are fewer costs to control.
A manager is deciding which one of four services to provide next period.
The contribution earned by each service will depend on the weather conditions as follows.
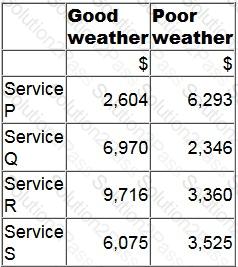
Using the maximin criterion, which service will the manager provide?
Explain the advantages of management participation in budget setting and the potential problems that may arise in the use of the resulting budget as a control mechanism.
Select all the correct answers.
Each finished unit of product G contains 2 litres of ingredient L. Losses during production are 10% of input of ingredient L. Budgeted data for next period are as follows:
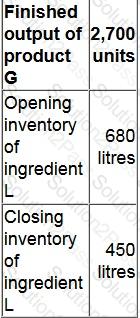
The budgeted purchases of ingredient L for next period are:
A company’s management is considering investing in a project with an expected life of 4 years. It has a positive net present value of $180,000 when cash flows are discounted at 8% per annum. The project’s cash flows include a cash outflow of $100,000 for each of the four years. No tax is payable on projects of this type.
The percentage increase in the annual cash outflow that would cause the company’s management to reject the project from a financial perspective is, to the nearest 0.1%: