P2 CIMA Advanced Management Accounting Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA P2 Advanced Management Accounting certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
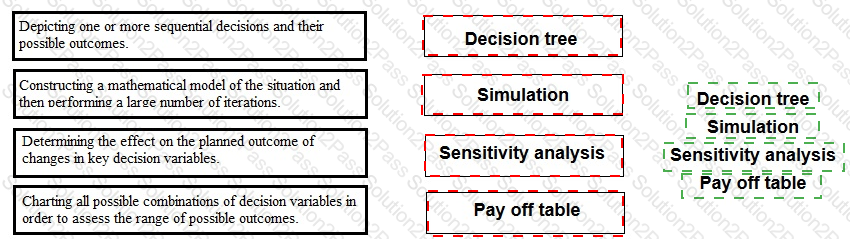
Place each method of analysing risk and uncertainty against the statement that describes it correctly.

A project requires an initial investment of $50,000. It will generate positive cash flows for two years as follows.
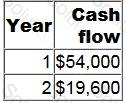
The cost of capital is 12% per year.
What is the equivalent annual net present value of the project?
Give your answer to the nearest $10.
The directors of a company wish to evaluate two mutually exclusive capital investment projects. Both projects have conventional cash flows: an initial outflow followed by a series of annual cash inflows.
The directors are aware of the following three investment appraisal methods: internal rate of return (IRR), net present value (NPV) and accounting rate of return (ARR).
The directors have asked for your advice about which method should be used to evaluate these two projects.
Which of the following is valid advice to give to the directors?
A very large organization is financed by both debt and equity. It evaluates all projects on the basis of their net present value (NPV) using an organization wide weighted average cost of capital as the discount rate.
For a small project, which TWO of the following would affect the project's cash flows AND the discount rate?
Which of the following investment appraisal methods provides an absolute monetary value on which to base decisions?
A company is determining the selling price for its new product.
At a selling price of $16 per unit there will be zero demand but for every $1 reduction in the price, demand will increase by 100 units per period.
Production must be in batches of 100 units. The variable cost per unit will be $8 if 400 units are produced in a period. For each additional batch produced in a period the variable cost per unit will increase by $1 per unit for the additional batch only.
No inventories will be held.
Which of the following sales and production volumes will generate the highest contribution per period?
A company's competitor has just launched a rival product at a selling price of $38 per unit. Until now the company's selling price of $41.60 per unit has achieved a 30% mark-up on the product's unit cost. The company proposes to use a target costing approach to pricing to remain competitive.
Management has decided to match the competitor's selling price and has set a target cost to achieve a 20% return on the target price.
What is the cost gap?
PorkyCo is a leading bread manufacturer in Toyland operating two functional divisions: pulled and roasted. PorkyCo uses IT systems in all of its functions, for example, accounting has one system, manufacturing has its
system, warehousing has another and human resources is the latest to develop a dedicated system to manage training and development
The issue now is that when the CEO, Mr Button, needs information about two or more functions, he has to convene the department heads to get their reports and then study each in turn. As senior management
accountant at PorkyCo, help free up Mr Button's time by suggesting the most efficient way of getting all the information he needs.
An organization's transfer pricing system involves:
• The transferring division receiving $20 per unit; an amount equal to its variable costs.
• The receiving division paying an additional $30,000 every month to the transferring division.
Which transfer pricing system is the organization using?
Which of the following factors would prevent a learning curve being observed for a task?
A risk averse decision maker will:
A company operates a divisional structure. The manager of division D receives a bonus based on the division's annual return on capital employed (ROCE).
A minimum ROCE of 20% must be achieved to receive any bonus and thereafter the bonus increases in line with increases in ROCE.
This year division D achieved a ROCE of 24% and the divisional manager received a large bonus.
The manager is considering an investment in a new machine for next year. The incremental ROCE earned by the machine is expected to be 19% although the ROCE for the division as a whole with the machine is expected to be 22%. Without the machine, ROCE is likely to be stable at 24%.
The cost of capital for the company as a whole is 18% per year.
Which of the following statements is correct?
Company S has two divisions, X and Y. Division X transfers 50,000 component units to Division Y each quarter. The market price of the component is $20. Division X's variable cost is $10 per unit and its fixed cost is $150,000 each quarter.
What price would be credited to Division X for each component that it transfers to Division Y under:
two-part tariff pricing (where the two divisions have agreed that the fixed fee will be $100,000); and dual pricing (based on market price and marginal cost).
Which THREE of the following are advantages of changing from a 'top-down' to a 'bottom-up' (participative) style of budgeting?
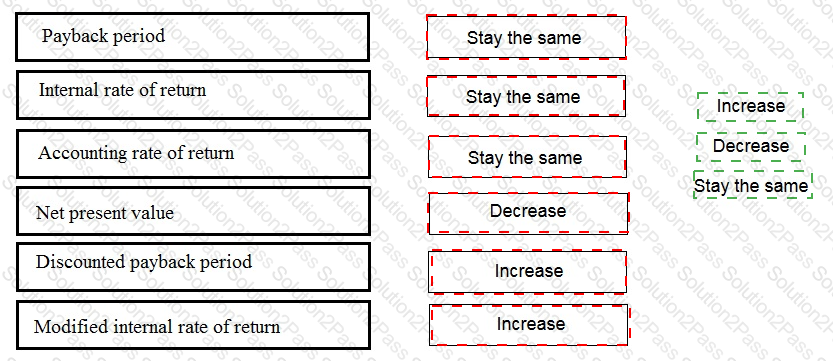
An investment appraisal has identified that a project has a positive net present value when discounted at the company's cost of capital. If the cost of capital is now increased, indicate whether each of the following appraisal measures will increase, decrease or stay the same.

SDF is a newly-established production company that is experiencing high staff turnover in its factory. The production department is studying the manufacturing process and its associated learning curve.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A cost centre manager's performance is monitored based on a comparison of actual and budgeted cost. A summary performance report for the latest period is shown below.
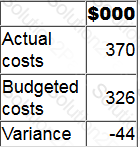
The actual costs include:
*$28,000 for allocated head office costs.
*$18,000 payment for a rental agreement entered into by the cost centre manager two years ago.
*$34,000 for depreciation.
What is the cost centre manager's controllable actual cost for the period?
Give your answer to the nearest $000.
For a pharmaceutical manufacturer, in which perspective of the Balanced Scorecard should the performance measure 'number of patents granted during the year' be included?
Which of the following is a valid objective of a transfer pricing system?
Which TWO of the following expressions are correct?