P2 CIMA Advanced Management Accounting Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your CIMA P2 Advanced Management Accounting certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
The cash flows from a project are detailed in the table below.
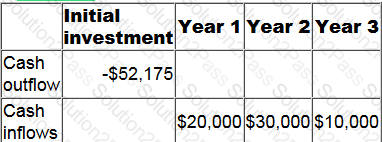
To the nearest 1%, what is the project's internal rate of return?
An 80% learning curve will apply to the production of a new product. The first unit will require 120 labor hours. The labor rate is $11 per hour.
To the nearest $1, the expected total labor cost for the first 4 units is:
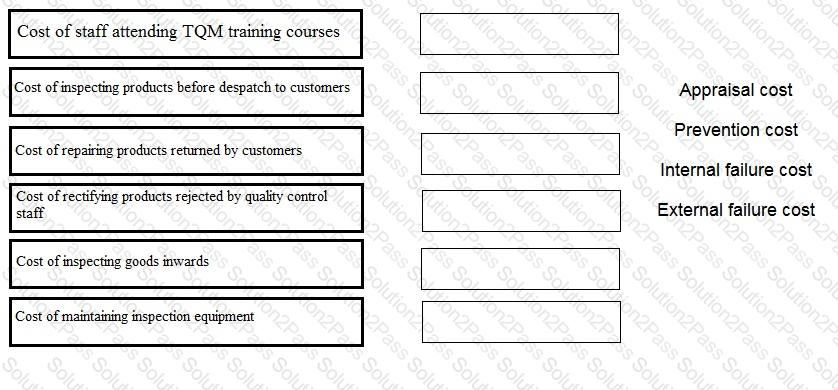
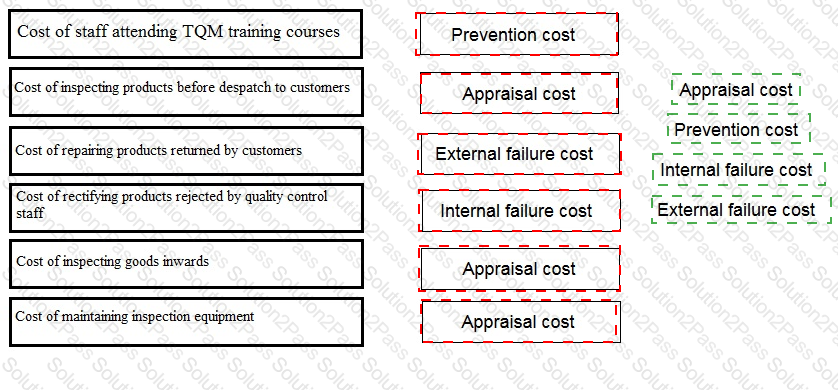
A company is classifying its quality costs to prepare a quality cost report. Which of the following are conformance costs?
Select ALL that apply.
Under the absorption costing system, which simply allocates our entire amount of production overheads based on machine hours, we have found that out of our 4 products, 2 are profitable, 1 breaks even and 1 is
making a loss.
Model D the most recent addition to the range is making a large loss after the price of a major component rose dramatically. Model A is only just breaking now too as costs have risen. The only two products making profit
are Models B and C. These two require the least about of machine hours so this makes sense.
However, the management have a few reservations. They cannot understand how B is so profitable. It requires several more stages of production than the other models and a whole day longer to be customised by an
expert.
Select the correct answer from the list below that can help to explain this situation.
A not-for-profit organization measures performance using the three Es. If the organization has made optimum utilization of available resources then it should be described as:
A product requires one each of three different components.
Faulty components are identified only at the end of the manufacturing process.
The following average fault rates have been identified:
Component A – 1 in 100
Component B – 1 in 20
Component C – 1 in 10
The probability that a unit of finished product contains no faulty components is:
A public sector service organization is considering whether to use a balanced scorecard or a value for money approach based on the three Es to assess its performance.
Which of the following are correct comparisons of the balanced scorecard and value for money based on the three Es as performance measurement frameworks?
Select ALL that apply.
A project with a 6 year life generates a positive net present value of $1,100. The discount rate is 8%.
To the nearest $, the equivalent annual benefit is:
A company is comprised of two divisions, each of which manufactures a single product. Division A manufactures a product which can be sold in a perfect external market or transferred as an intermediate product to division B. Division B finishes the intermediate product and sells this in a perfect external market.
Due to company policy, internal transfers are recorded at the external market price. At this transfer price both divisions make a profit from their activities.
Which of the following will NOT be achieved by the company's transfer pricing policy?
Which TWO of the following are reasons why cost-based approaches to transfer pricing are often used in practice?
A company comprises several divisions.
One of these divisions was originally expected to earn an operating profit next year of $800,000 on net assets of $4 million.
However, the divisional manager is considering investing in a project that would generate a project return on investment (ROI) of 38% on additional net assets of $500,000.
What would be the divisional ROI next year if the project was implemented?
Give your answer to the nearest percentage.
Performance measures that monitor the extent to which a not-for-profit organization's objectives have been achieved are measures of:
Division A is an investment centre with assets of $7.3 million. The following is an extract from the annual budget for division A:
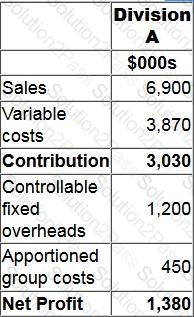
The cost of capital is 14%.
Calculate the residual income for division A.
A senior manager is concerned about the dysfunctional consequences of a company's current approach to budget preparation. The senior manager has discovered that budget holders are carrying budgetary slack forward from one period to the next without this being identified or challenged.
Which of the following approaches to budget preparation is the company using?
A small company currently uses an information system that was implemented several years ago and is based entirely on internal data. The company is considering replacing it with a more up to date system. It has been suggested that the new system should include the use of big data.
Which TWO of the following statements are correct?
Oliver owns a computer repair company. He is looking to close of of his departments as the demand for computer cleaning has dropped dramatically in the last 2 years and is no longer profitable.
The contribution margin of the department is £12,000, and the overheads are £23,000 (out of which £4,000 cannot be eliminated).
How would closing this department impact operating income?
Which basis of transfer pricing retains the full autonomy of divisional managers?
A company makes three products, E, F and G. Total overheads for the year are expected to be $1.2 million, with the following split between cost pools:
Cost driver information has been estimated as follows:
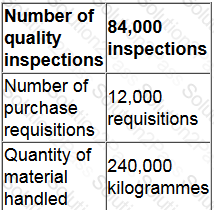
The company plans to make 10,000 units of product E in the year, with an expected direct cost of $0.60 per unit. This annual production of product E is expected to require 20 quality inspections, 28 purchase requisitions, and 400 kilogrammes of materials.
What is the overhead cost per unit of product E?
A company has just received the latest in a series of annual payments; this payment was $620. The annual payments are expected to continue for three more years with each payment being increased by the expected rate of inflation. The real cost of capital is 8% per year and the expected rate of inflation is 6% per year.
What is the present value of the future payments the company expects to receive?
Give your answer to the nearest $.
Place the correct quality cost classification against each cost described below.