201 F5 TMOS Administration Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your F5 201 TMOS Administration certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
A BIG-IP Administrator is receiving intermittent reports from users that SSL connections to the BIG-IP device are failing. Upon checking the log files, the BIG-IP Administrator notices the following error message:
ere tmm
After reviewing statistics, the BIG-IP Administrator notices there are a maximum of 1200 client-side SSL
TPS and a maximum of 800 server-side SSL TPS.
What is the minimum SSL license limit capacity the BIG-IP Administrator should upgrade to handle this
peak?
Which statement is true regarding failover?
A BIG-IP Administrator reviews the log files to determine the cause of a recent problem and finds the
following entry.
Mar 27.07.58.48 local/BIG-IP notice mcpd {5140} 010707275 Pool member 172.16.20.1.10029 monitor
status down.
What is the cause of this log message?
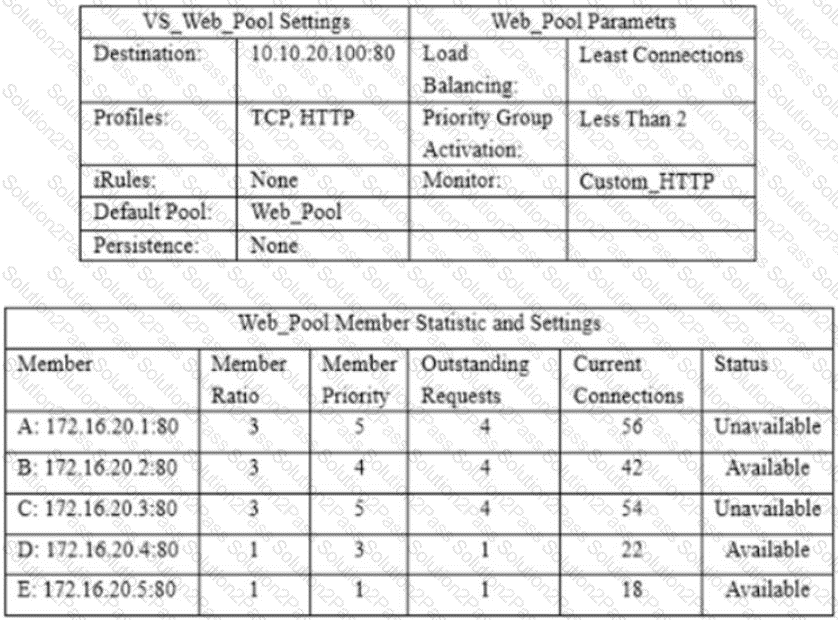
A virtual server is defined per the charts. The last five client connections were to members C, D, A, B, B. Given the conditions shown in the above graphic, if a client with IP address 205.12.45.52 opens a connection to the virtual server, which member will be used for the connection.
The BIG-IP appliance fails to boot. The BIG-IP Administrator needs to run the End User Diagnostics (EUD)
utility to collect data to send to F5 Support.
Where can the BIG-IP Administrator access this utility?
Assume the bigd daemon fails on the active system. Which three are possible results? (Choose three.)
Assume a client's traffic is being processed only by a NAT; no SNAT or virtual server processing takes place. Also assume that the NAT definition specifies a NAT address and an origin address while all other settings are
left at their defaults. If the origin server were to initiate traffic via the BIG-IP, what changes, if any, would take place when the BIG-IP processes such packets?
A BIG-IP device is configured with both an internal external and two Corporate VLANs. The virtual server
has SNAT enabled and is set to listen on all VLANs Auto Last Hop is disabled. The Corporate users are on
10.0.0.0./24 and 172.16.0.0/12. The BIG-IP has a Self-IP on the 1.0.0.0.0./24 subnet.
Internet users are able to access the virtual server. Only some of the Corporate users are able to connect
to the virtual server A BIG-IP Administrator performs a tcpdump on the BIG-IP and verifies that traffic is
arriving from users in 10.0.0.0/24.
What should the BIG-IP Administrator do to correct this behaviour?
Refer to the exhibit.
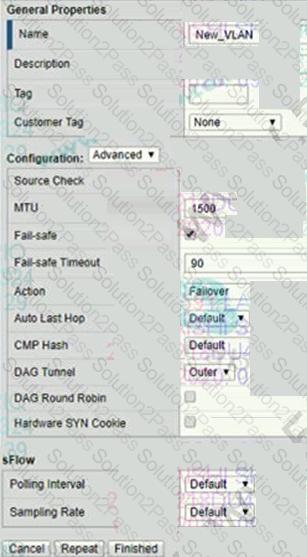
A BIG-IP Administrator configures a now VLAN on an HA pair of devices that does NOT yet have any
traffic. This action causes the assigned traffic group to fail over to the standby device.
Which VLAN setting should be changed to prevent this issue?
A 8IG-IP Administrator configures a Virtual Server to load balance traffic between 50 webservers for an
ecommerce website Traffic is being load balanced using the Least Connections (node) method.
The webserver administrators report that customers are losing the contents from their shopping carts
and are unable to complete their orders.
What should the BIG-IP Administrator do to resolve the issue?
A site needs to terminate client HTTPS traffic at the BIG-IP and forward that traffic unencrypted. Which two are profile types that must be associated with such a virtual server? (Choose two.)
Administrative user accounts have been defined on the remote LDAP server and are unable to log in to
the BIG-IP device.
Which log file should the BIG-IP Administrator check to find the related messages?
In the BIG-IP Configuration Utility, a user requests a single screen view to determine the status of all Virtual Servers and associated pool members, as well as any iRules in use. Where should the BIG-IP Administrator instruct the user to find this view?
Refer to the exhibit.
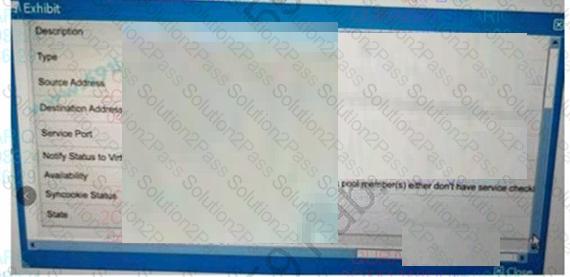
A BIG-IP Administrator configures the Virtual Server to pass HTTP traffic. Users report that they are
unable to access the application
What should the administrator do to resolve this issue?
A BIG-IP Administrator is unable to connect to the management interface via HTTPS. What is a possible reason for this issue?
You have created a custom profile named TEST2. The parent profile of TEST2 is named TEST1. If additional changes are made to TEST1, what is the effect on TEST2?
How is MAC masquerading configured?
A local user account (Users) on the BIG-IP device is assigned the User Manager role. Userl attempts to
modify the properties of another account (User2), but the action fails. The BIG-IP Administrator can
successfully modify the User2 account.
Assuming the principle of least privilege, what is the correct way to allow User 1 to modify User2
properties?
A BIG-IP Administrator discovers malicious brute-force attempts to access the BIG-IP device on the management interface via SSH. The BIG-IP Administrator needs to restrict SSH access to the
management interface.
Where should this be accomplished?
A 816-IP Administrator recently deployed an application Users are experiencing slow performance with
the application on some remote networks.
Which two modifications can the BIG-IP Administrator make to address this issue? (Choose two)
