Associate-Android-Developer Google Developers Certification - Associate Android Developer (Kotlin and Java Exam) Free Practice Exam Questions (2025 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your Google Associate-Android-Developer Google Developers Certification - Associate Android Developer (Kotlin and Java Exam) certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2025, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Total 128 questions
LiveData.postValue() and LiveData.setValue() methods have some differences. So if you have a following code executed in the main thread:
liveData.postValue("a"); liveData.setValue("b");
What will be the correct statement?
Android uses adapters (from the Adapter class) to connect data with View items in a list. There are many different kinds of adapters available, and you can also write custom adapters. To connect data with View items, the adapter needs to know about the View items. From what is extended the entity that is usually used in an adapter and describes a View item and its position within the RecyclerView?
If constant LENGTH_INDEFINITE is used as a parameter for the setDuration method in Snackbar, what will happen?
As an example. In an Activity we have our TimerViewModel object (extended ViewModel), named mTimerViewModel. mTimerViewModel.getTimer() method returns a LiveData
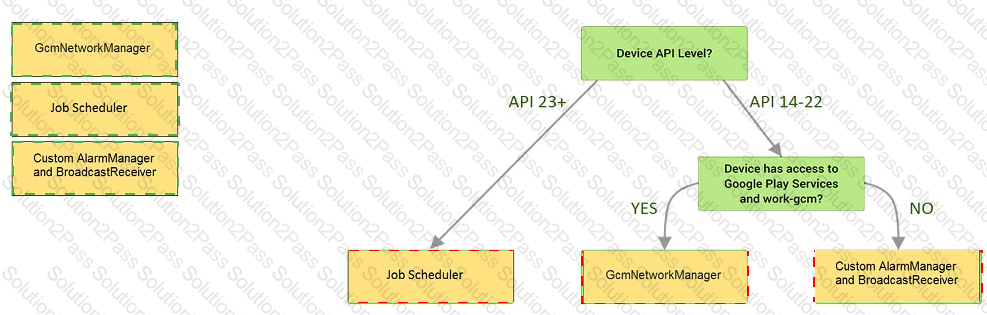
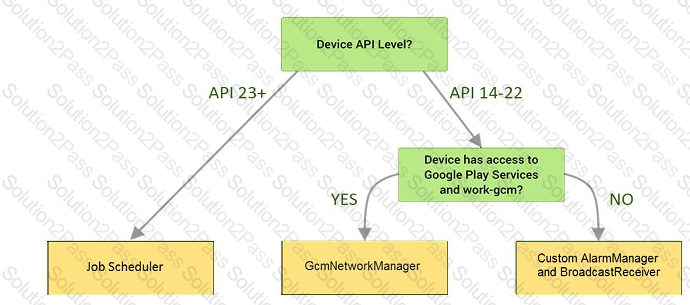
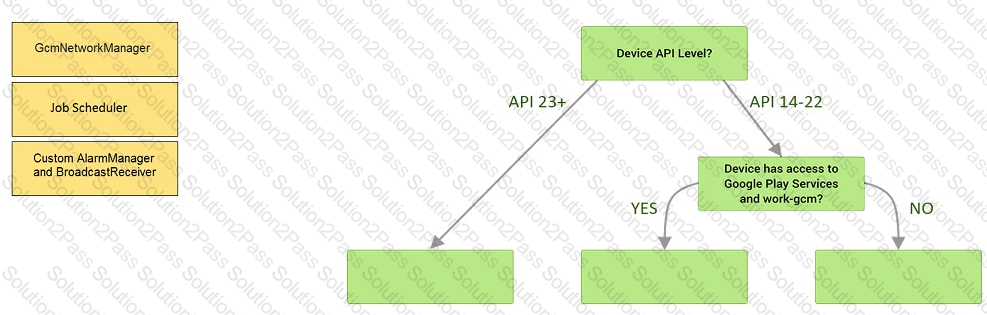
Under the hood WorkManager uses an underlying job dispatching service based on the following criteria. You need to move services to the correct places.
Select a correct statement about PagedList.
When scheduling unique work, you must tell WorkManager what action to take when there is a conflict. You do this by passing an enum when enquing the work. For one-time work, you provide an ExistingWorkPolicy, which supports some options for handling the conflict. (Choose four.)
What method should we use with Notification.Builder to supply a PendingIntent to be sent when the notification is clicked?
Choose the most correct statement.
What public methods are there in android.widget.Toast.Callback? (Choose two.)
Select correct statements about Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL). (Choose two.)
Custom duration in milliseconds as a parameter for the setDuration method is available when you are working with:
Assume that an app includes a default set of graphics and two other sets of graphics, each optimized for a different device setup:
res/drawable/
Contains default graphics. res/drawable-small-land-stylus/
Contains graphics optimized for use with a device that expects input from a stylus and has a QVGA low- density screen in landscape orientation.
res/drawable-ja/
Contains graphics optimized for use with Japanese.
What happens if the app runs on a device that is configured to use Japanese and, at the same time, the device happens to be one that expects input from a stylus and has a QVGA low-density screen in landscape orientation?
Which build options in the Build menu to choose to delete all intermediate/cached build files.
In application theme style, flag windowNoTitle (
What happens when you create a DAO method and annotate it with @Insert?
Example:
@Dao
public interface MyDao {
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
public void insertUsers(User... users);
}
For example, we have a BufferedReader reader, associated with the json file through
InputStreamReader. To get a file data we can do this:
Total 128 questions