8006 PRMIA Exam I: Finance Theory Financial Instruments Financial Markets - 2015 Edition Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PRMIA 8006 Exam I: Finance Theory Financial Instruments Financial Markets - 2015 Edition certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Caps, floors and collars are instruments designed to:
A)
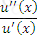
B)
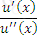
C)
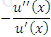
D)
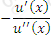
According to the CAPM, the beta of a risky asset depends upon:
Which of the following statements are true:
I. For a delta neutral portfolio, gamma and theta carry opposite signs
II. The sum of the absolute value of gamma for a call and a put for the same option is 1
III. A large positive gamma is desirable in a delta neutral portfolio
IV. A trader needs at least two separate tradeable options to simultaneously make a portfolio both gamma and vega neutral
The cheapest to deliver bond for a treasury bond futures contract is the one with the :
For a pair of correlated assets, the achievable portfolio standard deviation will be the lowest when the correlation ρ is:
What would be the most profitable strategy for an investor who expects interest rates to rise:
How are foreign exchange futures quoted against the US dollar?
When hedging an equity portfolio with index futures that carry no basis risk, the number of futures contracts to hold is determined by:
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
Which of the following describes a 'quanto' instrument:
A floating rate note pays daily overnight LIBOR. It matures in exactly one year. What is the duration of the note?
If the quoted discount rate of a 3 month treasury bill futures contract is 10%, what is the price of a 3-month treasury bill with a principal at maturity of $100?
What is the notional value of one equity index futures contract where the value of the index is 1500 and the contract multiplier is $50:
A stock sells for $100, and a call on the same stock for one year hence at a strike price of $100 goes for $35. What is the price of the put on the stock with the same exercise and strike as the call? Assume the stock pays dividends at 1% per year at the end of the year and interest rates are 5% annually.
What can the buyer of a 6 x 12 FRA expect to receive (or pay) if the contracted rate is 10% and the settlement rate is 12%? Assume contract notional is $100m.
The theta of a delta neutral options position is large and positive. What can we say about the gamma of the position?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. The swap rate, also called the swap spread, is initially calculated so that the value of the swap at inception is zero.
II. The value of a swap at initiation is different from zero and is equal to the difference between the NPV of the cash flows of the two legs of the swap
III. OTC swaps are standardized and limited to a defined set of standard contracts
IV. Interest rate and commodity swaps are the types of swaps that are most traded
What would be the expected return on a stock with a beta of 1.2, when the risk free rate is 3% and the broad market index is expected to earn 8%?
Given identical prices, a bond trader prefers dealing with Bank A over Bank B. Given a choice between Bank B and Bank C, he prefers Bank B. Yet, when given a choice between Bank A and Bank C, he prefers dealing with Bank C. What axiom underlying the utility theory is he violating?
A bond with a 5% coupon trades at 95. An increase in interest rates by 10 bps causes its price to decline to $94.50. A decrease in interest rates by 10 bps causes its price to increase to $95.60. Estimate the convexity of the bond.
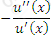 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.a.png is the coefficient of risk aversion at x. Its inverse, ie
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.a.png is the coefficient of risk aversion at x. Its inverse, ie 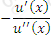 https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.b.png , is called the coefficient of risk tolerance.
https://riskprep.com/images/stories/questions/102.07.b.png , is called the coefficient of risk tolerance.