ARA-R01 Snowflake SnowPro Advanced: Architect Recertification Exam Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your Snowflake ARA-R01 SnowPro Advanced: Architect Recertification Exam certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
A user has the appropriate privilege to see unmasked data in a column.
If the user loads this column data into another column that does not have a masking policy, what will occur?
Which SQL alter command will MAXIMIZE memory and compute resources for a Snowpark stored procedure when executed on the snowpark_opt_wh warehouse?
A)
B) 
C) 
D) 
An Architect is using SnowCD to investigate a connectivity issue.
Which system function will provide a list of endpoints that the network must be able to access to use a specific Snowflake account, leveraging private connectivity?
A company is storing large numbers of small JSON files (ranging from 1-4 bytes) that are received from IoT devices and sent to a cloud provider. In any given hour, 100,000 files are added to the cloud provider.
What is the MOST cost-effective way to bring this data into a Snowflake table?
Which columns can be included in an external table schema? (Select THREE).
What are purposes for creating a storage integration? (Choose three.)
A company has built a data pipeline using Snowpipe to ingest files from an Amazon S3 bucket. Snowpipe is configured to load data into staging database tables. Then a task runs to load the data from the staging database tables into the reporting database tables.
The company is satisfied with the availability of the data in the reporting database tables, but the reporting tables are not pruning effectively. Currently, a size 4X-Large virtual warehouse is being used to query all of the tables in the reporting database.
What step can be taken to improve the pruning of the reporting tables?
An Architect for a multi-national transportation company has a system that is used to check the weather conditions along vehicle routes. The data is provided to drivers.
The weather information is delivered regularly by a third-party company and this information is generated as JSON structure. Then the data is loaded into Snowflake in a column with a VARIANT data type. This
table is directly queried to deliver the statistics to the drivers with minimum time lapse.
A single entry includes (but is not limited to):
- Weather condition; cloudy, sunny, rainy, etc.
- Degree
- Longitude and latitude
- Timeframe
- Location address
- Wind
The table holds more than 10 years' worth of data in order to deliver the statistics from different years and locations. The amount of data on the table increases every day.
The drivers report that they are not receiving the weather statistics for their locations in time.
What can the Architect do to deliver the statistics to the drivers faster?
A company is using Snowflake in Azure in the Netherlands. The company analyst team also has data in JSON format that is stored in an Amazon S3 bucket in the AWS Singapore region that the team wants to analyze.
The Architect has been given the following requirements:
1. Provide access to frequently changing data
2. Keep egress costs to a minimum
3. Maintain low latency
How can these requirements be met with the LEAST amount of operational overhead?
A Snowflake Architect is designing a multiple-account design strategy.
This strategy will be MOST cost-effective with which scenarios? (Select TWO).
Based on the Snowflake object hierarchy, what securable objects belong directly to a Snowflake account? (Select THREE).
A new table and streams are created with the following commands:
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE LETTERS (ID INT, LETTER STRING) ;
CREATE OR REPLACE STREAM STREAM_1 ON TABLE LETTERS;
CREATE OR REPLACE STREAM STREAM_2 ON TABLE LETTERS APPEND_ONLY = TRUE;
The following operations are processed on the newly created table:
INSERT INTO LETTERS VALUES (1, 'A');
INSERT INTO LETTERS VALUES (2, 'B');
INSERT INTO LETTERS VALUES (3, 'C');
TRUNCATE TABLE LETTERS;
INSERT INTO LETTERS VALUES (4, 'D');
INSERT INTO LETTERS VALUES (5, 'E');
INSERT INTO LETTERS VALUES (6, 'F');
DELETE FROM LETTERS WHERE ID = 6;
What would be the output of the following SQL commands, in order?
SELECT COUNT (*) FROM STREAM_1;
SELECT COUNT (*) FROM STREAM_2;
A company is designing its serving layer for data that is in cloud storage. Multiple terabytes of the data will be used for reporting. Some data does not have a clear use case but could be useful for experimental analysis. This experimentation data changes frequently and is sometimes wiped out and replaced completely in a few days.
The company wants to centralize access control, provide a single point of connection for the end-users, and maintain data governance.
What solution meets these requirements while MINIMIZING costs, administrative effort, and development overhead?
A table, EMP_ TBL has three records as shown:

The following variables are set for the session:

Which SELECT statements will retrieve all three records? (Select TWO).
The IT Security team has identified that there is an ongoing credential stuffing attack on many of their organization’s system.
What is the BEST way to find recent and ongoing login attempts to Snowflake?
What is a key consideration when setting up search optimization service for a table?
An Architect needs to improve the performance of reports that pull data from multiple Snowflake tables, join, and then aggregate the data. Users access the reports using several dashboards. There are performance issues on Monday mornings between 9:00am-11:00am when many users check the sales reports.
The size of the group has increased from 4 to 8 users. Waiting times to refresh the dashboards has increased significantly. Currently this workload is being served by a virtual warehouse with the following parameters:
AUTO-RESUME = TRUE AUTO_SUSPEND = 60 SIZE = Medium
What is the MOST cost-effective way to increase the availability of the reports?
A Snowflake Architect Is working with Data Modelers and Table Designers to draft an ELT framework specifically for data loading using Snowpipe. The Table Designers will add a timestamp column that Inserts the current tlmestamp as the default value as records are loaded into a table. The Intent is to capture the time when each record gets loaded into the table; however, when tested the timestamps are earlier than the loae_take column values returned by the copy_history function or the Copy_HISTORY view (Account Usage).
Why Is this occurring?
An Architect has chosen to separate their Snowflake Production and QA environments using two separate Snowflake accounts.
The QA account is intended to run and test changes on data and database objects before pushing those changes to the Production account. It is a requirement that all database objects and data in the QA account need to be an exact copy of the database objects, including privileges and data in the Production account on at least a nightly basis.
Which is the LEAST complex approach to use to populate the QA account with the Production account’s data and database objects on a nightly basis?
The diagram shows the process flow for Snowpipe auto-ingest with Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) with the following steps:
Step 1: Data files are loaded in a stage.
Step 2: An Amazon S3 event notification, published by SNS, informs Snowpipe — by way of Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) - that files are ready to load. Snowpipe copies the files into a queue.
Step 3: A Snowflake-provided virtual warehouse loads data from the queued files into the target table based on parameters defined in the specified pipe.
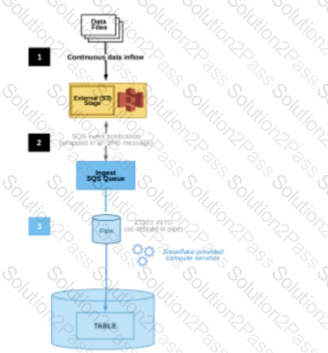
If an AWS Administrator accidentally deletes the SQS subscription to the SNS topic in Step 2, what will happen to the pipe that references the topic to receive event messages from Amazon S3?
