ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor PECB QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam Free Practice Exam Questions (2026 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PECB ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2026, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
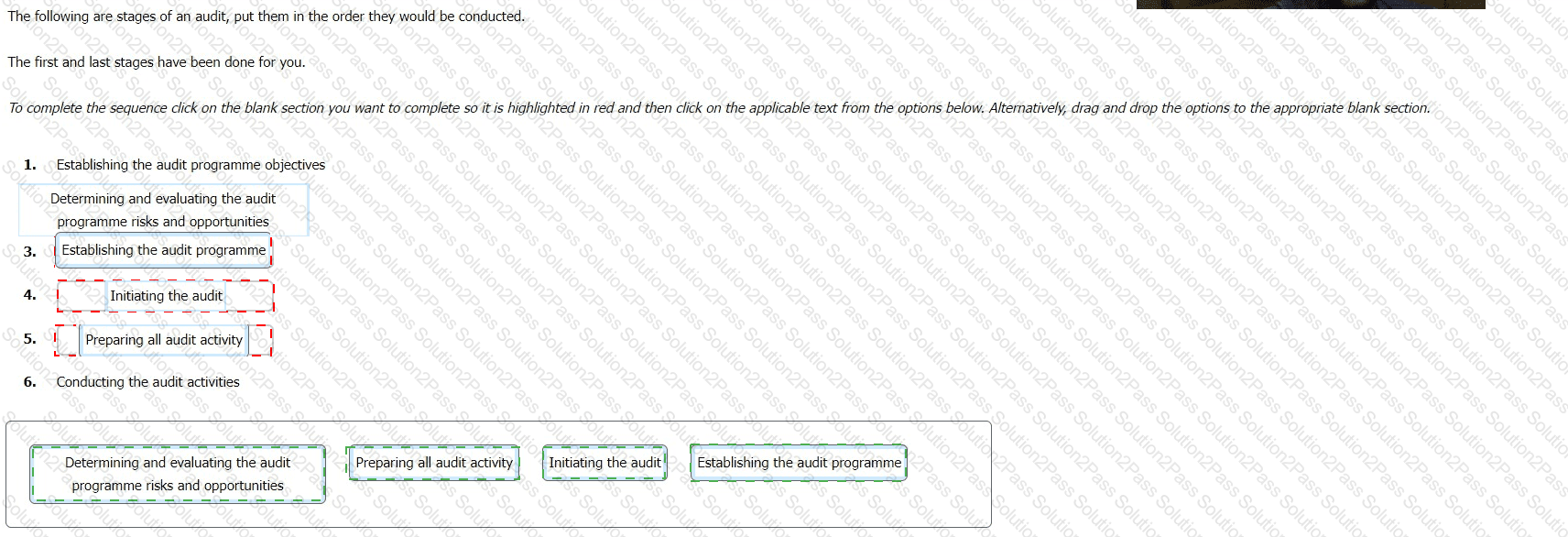
The following are stages of an audit, put them in the order they would be conducted.
You are carrying out an audit at an organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organisation offers health and safety training to
customers.
You are interviewing the Quality Systems Manager (QSM).
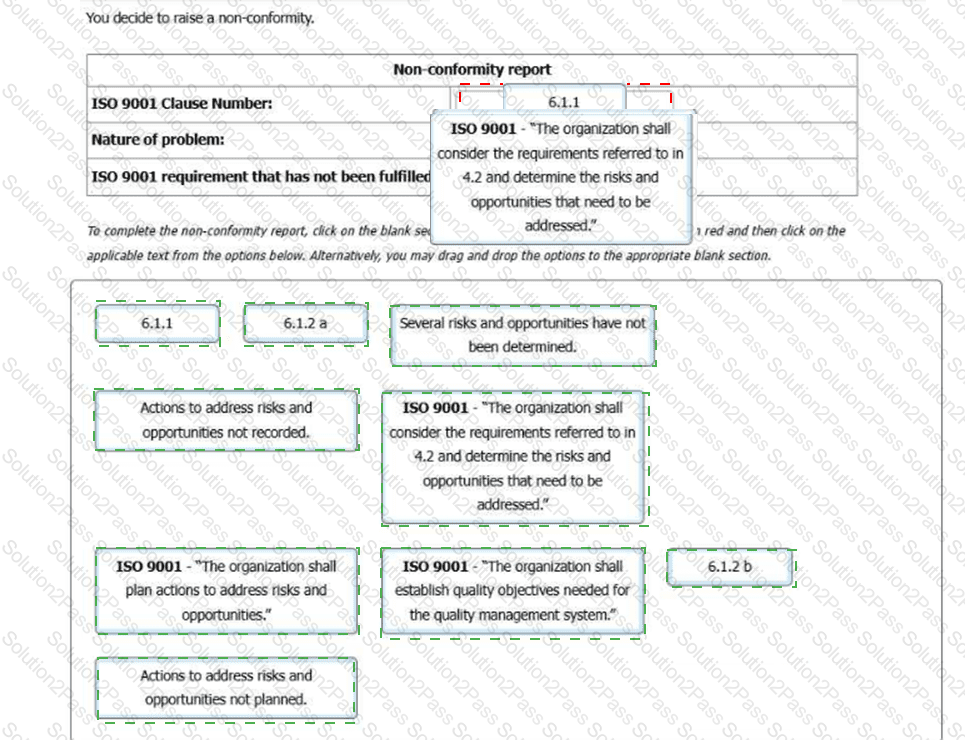
You: "What risks and opportunities have the business identified?"
QSM: "I'1l show you. This was discussed with the Managing Director at the latest management review."
Narrative: The QSM shows you the latest management review record and points to the following table:

You: "How is the business planning to address these risks and opportunities?"
QSM: "The MD said that they already knew about them so it was not necessary."
Which statement below indicates that an organization has developed its communication strategy by taking into account the principle of appropriateness?
During an internal audit, it was discovered that the calibration of a spectrometer used daily for production had expired, causing a nonconformance under Clause 7.1.5.2 of ISO 9001:2015. The root cause was the organization not considering the risk of the calibration provider leaving the country.
Which corrective action is the best one?
(From the following, select six tasks you would expect to be completed during the audit team meeting of a second-party audit in preparation for the closing meeting of a four-day audit being performed by organisation ABC to an external provider.)
How much time is usually spent on the Stage 1 audit?
Consultancy ABC, which is a subsidiary of a certification body called ABC-CERT, provided consultancy services regarding the implementation of a QMS based on ISO 9001 to an organization. Considering this, can ABC-CERT provide certification services to the organization which obtained consultancy services from Consultancy ABC?
You are an auditor from a construction organisation who is conducting a second party audit to ISO 9001 at a steel rolling mill producing
structural steelwork. When auditing the rolling process, you find that the operator who is unloading the furnace does not use the
adjacent infrared pyrometer to measure the appropriate product temperature in readiness for the next production stage.
You: "How do you tell when the billet is ready for the rolling stage?"
Operator: "I've done this job for 20 years. I can tell by the bright red colour."
You: "What happens if the colour is wrong?"
Operator: "The billet goes back into the furnace."
You: "Is the pyrometer ever used?"
Operator: "Only in borderline cases."
You continue to interview the operator and find that around 25% of the billets are sent back to the furnace. This includes 80% of the borderline cases.
Select three options that would provide evidence of conformance with clause 9.1.1 of ISO 9001.
Scenario 4:
TD Advertising is a print management company based in Chicago. The company offers design services, digital printing, storage, and distribution. As TD expanded, its management recognized that success depended on adopting new technologies and improving quality.
To ensure customer satisfaction and quality improvement, the company decided to pursue ISO 9001 certification.
After implementing the QMS, TD hired a well-known certification body for an audit. Anne Key was appointed as the audit team leader. She received a document listing the audit team members, audit scope, criteria, duration, and audit engagement limits.
Anne reviewed the document and approved the audit mandate. The certification body and TD’s top management signed the certification agreement.
Before contacting TD, Anne reviewed the audit scope and noticed that TD made changes to it due to the adoption of new printing equipment. However, Anne disagreed with the changes, stating they would affect the audit timeline. She considered withdrawing from the audit.
How do you assess the situation presented in the last paragraph of scenario 4?
You are the supervisor in Production of a medium size manufacturing organisation. You are qualified as an internal auditor. The Quality Manager asks you to lead the next internal audit of Production and Logistics Dispatch. The audit team includes two other internal auditors.

Confidence in the audit process and its ability to achieve its objectives depends on the competence of those involved in performing audits:
According to ISO 19011, select the two participants who need to be competent in performing audits.
What is the responsibility of the audit committee during an internal audit?
Scenario 5: Mechanical-Electro (ME) Audit Stages
Mechanical-Electro, better known as ME, is an American company that provides mechanical and electrical services in China. Their services range from air-conditioning systems, ventilation systems, plumbing, to installation of electrical equipment in automobile plants, electronic manufacturing facilities, and food processing plants.
Due to the fierce competition from local Chinese companies and failing to meet customer requirements, ME's revenue dropped significantly. In addition, customers' trust and confidence in the company decreased, and the reputation of the company was damaged.
In light of these developments, the top management of ME decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After having an effective QMS in place for over a year, they applied for a certification audit.
A team of four auditors was appointed for the audit, including Li Na as the audit team leader. Initially, the audit team conducted a general review of ME's documents, including the quality policy, operational procedures, inventory lists, QMS scope, process documentation, training records, and previous audit reports.
Li Na stated that this would allow the team to maintain a systematic and structured approach to gathering documents for all audit stages. While reviewing the documented information, the team observed some minor issues but did not identify any major nonconformities. Therefore, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to prepare a report or conduct a meeting with ME's representatives at that stage of the audit. She stated that all areas of concern would be discussed in the next phase of the audit.
Following the on-site activities and the opening meeting with ME's top management, the audit team structured an audit test plan to verify whether ME’s QMS conformed to Clause 8.2.1 (Customer Communication) of ISO 9001.
To do so, they gathered information through group interviews and sampling. Li Na conducted interviews with departmental managers in the first group and then with top management. In addition, she chose a sampling method that sufficiently represented customer complaints from both areas of ME's operations.
The team members were responsible for the sampling procedure. They selected a sample size of 4 out of 45 customer complaints received weekly for electrical services and 2 out of 10 complaints for mechanical services.
Afterward, the audit team evaluated the evidence against the audit criteria and generated the audit findings.
After reviewing the documented information, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to report the minor nonconformities that were identified; instead, they would be discussed in the next audit phase. Is this acceptable?
(As the audit team leader, you are planning an audit at an organisation that is seeking certification to ISO 9001. You have confirmed and agreed on the audit scope and audit date with the auditee. The audit team comprises of you and one other auditor. The auditee has two sites and one of these sites is the Head Office where the top management team are based.
The other site is referred to as Site 1, which is located in another country. Apart from that, each site is essentially similar in terms of customer service provision. The other auditor has been selected to audit Site 1 as she lives nearby.
Select four issues you need to finalise before documenting the audit plan.)
The Closing meeting of a second-party audit was planned for 6 pm with the general manager and the quality manager.
At 6 pm, when the audit team enters the meeting room, only the Quality Manager is present and walting for them.
The dialogue among them is as follows:
Auditor team leader: "Good evening, could you please inform the general manager that we are ready to start with the closing meeting?"
Quality manager: "Good evening. I am sorry to inform you that the general manager will not be able to attend the meeting. He will try to
participate virtually to make some closing remarks."
Auditor team leader: "OK. We identified seven nonconformities - these are the reports. Could you please review them and sign them?"
Quality manager: "OK. As you know, I reviewed them after yesterday's meeting and accept of all them, where shall I sign?"
General manager (from speakers in the room and addressing the quality manager): "Hold on! Do not sign the two nonconformities related to ABC
Bank! I have just checked, and we did not provide any services to ABC Bank during September! You can sign the remaining five nonconformities."
How would you proceed with the audit? Select one.
You are carrying out an audit at a single-site organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organization manufactures cosmetics for major retailers and the name of the retailer supplied appears on the product packaging. Sales turnover has increased significantly over the past five years.
You are interviewing the new Product Development Manager. You note that a software application called SWIFT is used to help control the product development process.
You have gathered audit evidence as outlined in the table. Match the ISO 9001 clause 8.3 extracts to the audit evidence.

Which action indicates that an organization is meeting the requirements of ISO 9001 regarding nonconforming outputs?
During an internal audit, a manufacturer of polystyrene packaging products for the electronics industry found that six per cent of finished products being ejected from the moulding machines fell onto the factory floor instead of into collection baskets. The factory floor was wet and dirty in places, so a lot of products were rejected at inspection. Auditors raised a non-conformity to the Maintenance Manager.
Select three options for the corrective action to be taken by the Maintenance Manager that could be needed to prevent rejects from recurring.
When should the certification body accept the audit?
Whistlekleen is a national dry cleaning and laundry company with 50 shops. You are conducting a surveillance audit of the Head Office and are sampling customer complaints. 80% of complaints originate from five shops in the same region. Most of these complaints
relate to customer laundry not being cleaned as customers require. The Quality Manager tells you that these are the oldest shops in the company. The cleaning equipment needs replacing but the company cannot afford it now. You learn that the shop managers were
told to dismiss most of the complaints because of the poor quality of the laundered materials.
On raising the matter with senior management, you are told that there are plans to replace the equipment in these shops over the next five years.
You raised a nonconformity against clause 8.5.1 of ISO 9001.
Based on the scenario, select the three options which best describe the evidence for raising such a nonconformity.