ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor PECB QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam Free Practice Exam Questions (2025 Updated)
Prepare effectively for your PECB ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam certification with our extensive collection of free, high-quality practice questions. Each question is designed to mirror the actual exam format and objectives, complete with comprehensive answers and detailed explanations. Our materials are regularly updated for 2025, ensuring you have the most current resources to build confidence and succeed on your first attempt.
Scenario 5: Mechanical-Electro (ME) Audit Stages
Mechanical-Electro, better known as ME, is an American company that provides mechanical and electrical services in China. Their services range from air-conditioning systems, ventilation systems, plumbing, to installation of electrical equipment in automobile plants, electronic manufacturing facilities, and food processing plants.
Due to the fierce competition from local Chinese companies and failing to meet customer requirements, ME's revenue dropped significantly. In addition, customers' trust and confidence in the company decreased, and the reputation of the company was damaged.
In light of these developments, the top management of ME decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After having an effective QMS in place for over a year, they applied for a certification audit.
A team of four auditors was appointed for the audit, including Li Na as the audit team leader. Initially, the audit team conducted a general review of ME's documents, including the quality policy, operational procedures, inventory lists, QMS scope, process documentation, training records, and previous audit reports.
Li Na stated that this would allow the team to maintain a systematic and structured approach to gathering documents for all audit stages. While reviewing the documented information, the team observed some minor issues but did not identify any major nonconformities. Therefore, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to prepare a report or conduct a meeting with ME's representatives at that stage of the audit. She stated that all areas of concern would be discussed in the next phase of the audit.
Following the on-site activities and the opening meeting with ME's top management, the audit team structured an audit test plan to verify whether ME’s QMS conformed to Clause 8.2.1 (Customer Communication) of ISO 9001.
To do so, they gathered information through group interviews and sampling. Li Na conducted interviews with departmental managers in the first group and then with top management. In addition, she chose a sampling method that sufficiently represented customer complaints from both areas of ME's operations.
The team members were responsible for the sampling procedure. They selected a sample size of 4 out of 45 customer complaints received weekly for electrical services and 2 out of 10 complaints for mechanical services.
Afterward, the audit team evaluated the evidence against the audit criteria and generated the audit findings.
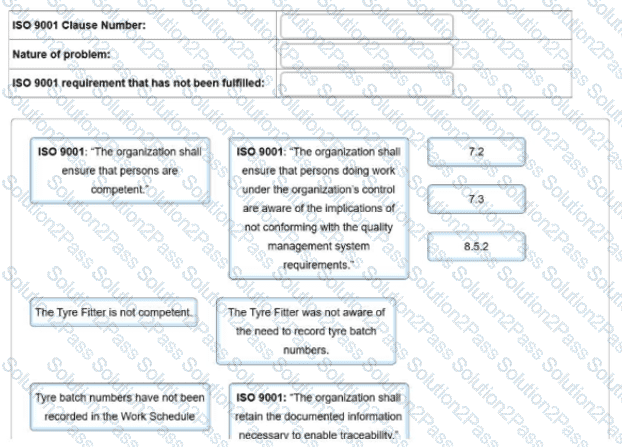
According to general principles of sampling procedure, did the audit team select a valid sample for electrical services?
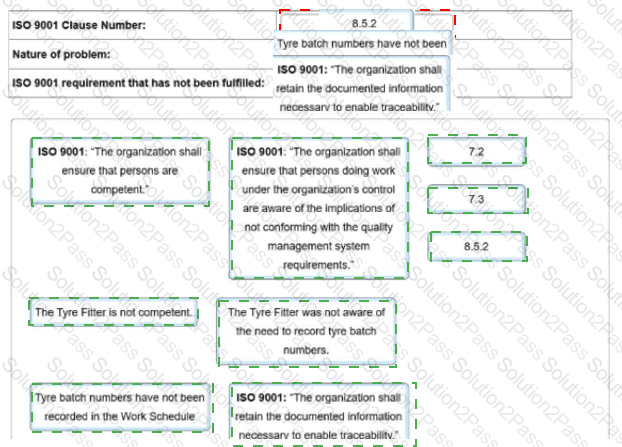
To complete the non-conformity report, click on the blank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the applicable text from the options below. Alternatively, drag and drop the options to the appropriate blank section.
Scenario 3:
Fin-Pro is a financial institution in Austria offering commercial banking, wealth management, and investment services. The company faced a significant loss of customers due to failing to improve service quality as they expanded.
To regain customer confidence, top management implemented a QMS based on ISO 9001. After a year, they contacted ACB, a local certification body, to pursue ISO 9001 certification.
The audit team was led by Emilia, an experienced lead auditor, and included three auditors. After an agreement was reached, ACB sent the audit objectives to the audit team.
The audit team began by gathering information about Fin-Pro’s understanding of ISO 9001 requirements. While reviewing documented information, they noticed missing records of training and awareness sessions. They conducted employee interviews to verify attendance.
The team also reviewed the organizational chart and job descriptions to confirm employee competence. They observed the company’s working environment (social, psychological, and physical conditions).
The audit team analyzed the evidence and prepared an audit report with findings and conclusions.
Based on the last paragraph of scenario 3, which audit principle did the audit team follow?
During a third-party audit of a pharmaceutical organisation (CD9000) site of seven COVID-19 testing laboratories in various terminals at
a major international airport, you interview the CD 9000's General Manager (GM), who was accompanied by Jack, the legal compliance
expert. Jack is acting as the guide in the absence of the Technical Manager due to him contracting COVID-19.
You: "What external and internal issues have been identified that could affect CD9000 and its quality management system?"
GM: "Jack guided us on this. We identified issues like probable competition of another laboratory organisation in the airport, legal
requirements on COVID-19 continuously changing, the shortage of competent laboratory analysists, the epidemic declining soon,
shortage of chemicals for the analysis. It was quite a good experience."
You: "Did you document these issues?"
GM: "No. Jack said that ISO 9001 does not require us to document these issues."
You: "How did you determine the risks associated with the issues and did you plan actions to address them?"
GM: "I am not sure. The Technical Manager is responsible for this process. Jack may be able to answer this question in his absence."
Select two options for how you would respond to the General Manager's suggestion:
Which two of the following are the key expected results of a quality management system that conforms to the requirements of ISO 9001:2015?
An audit team of three people is conducting a Stage 2 audit to ISO 9001 of an engineering organisation which manufactures sacrificial anodes for the
oil and gas industry in marine environments. These are aluminium products designed to prevent corrosion of submerged steel structures. As one of
the auditors, you find that the organisation has shipped anodes for Project DK in the Gulf of Mexico before the galvanic efficiency test results for the
anodes have been fully analysed and reported as required by the customer. The Quality Manager explains that the Managing Director authorised the
release of the anodes to avoid late delivery as penalties would be imposed. The customer was not informed since the tests rarely fall below the
required efficiency. You raise a nonconformity against clause 8.6 of ISO 9001.
During the audit team meeting in preparation for the Closing meeting, the second auditor disagreed with the clause of ISO 9001 selected for the
above nonconformity. He thinks it should be clause 9.1.1.
Choose three options for how the audit team leader should best respond to the situation:
Scenario 5: Mechanical-Electro (ME) Audit Stages
Mechanical-Electro, better known as ME, is an American company that provides mechanical and electrical services in China. Their services range from air-conditioning systems, ventilation systems, plumbing, to installation of electrical equipment in automobile plants, electronic manufacturing facilities, and food processing plants.
Due to the fierce competition from local Chinese companies and failing to meet customer requirements, ME's revenue dropped significantly. In addition, customers' trust and confidence in the company decreased, and the reputation of the company was damaged.
In light of these developments, the top management of ME decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After having an effective QMS in place for over a year, they applied for a certification audit.
A team of four auditors was appointed for the audit, including Li Na as the audit team leader. Initially, the audit team conducted a general review of ME's documents, including the quality policy, operational procedures, inventory lists, QMS scope, process documentation, training records, and previous audit reports.
Li Na stated that this would allow the team to maintain a systematic and structured approach to gathering documents for all audit stages. While reviewing the documented information, the team observed some minor issues but did not identify any major nonconformities. Therefore, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to prepare a report or conduct a meeting with ME's representatives at that stage of the audit. She stated that all areas of concern would be discussed in the next phase of the audit.
Following the on-site activities and the opening meeting with ME's top management, the audit team structured an audit test plan to verify whether ME’s QMS conformed to Clause 8.2.1 (Customer Communication) of ISO 9001.
To do so, they gathered information through group interviews and sampling. Li Na conducted interviews with departmental managers in the first group and then with top management. In addition, she chose a sampling method that sufficiently represented customer complaints from both areas of ME's operations.
The team members were responsible for the sampling procedure. They selected a sample size of 4 out of 45 customer complaints received weekly for electrical services and 2 out of 10 complaints for mechanical services.
Afterward, the audit team evaluated the evidence against the audit criteria and generated the audit findings.
After reviewing the documented information, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to report the minor nonconformities that were identified; instead, they would be discussed in the next audit phase. Is this acceptable?
Scenario 6: Davis Clinic (DC) is an American medical center focused on integrated health care. Since its establishment DC was committed to providing qualitative services for its clients, which is the reason why the company decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After a year of having an active QMS in place, DC applied for a certification audit.
A team of five auditors, from a well-known certification body, was selected to conduct the audit. Eva was appointed as the audit team leader. After three days of auditing, the team gathered to review and examine their findings. They also discussed the audit findings with DC's top management and then drafted the audit conclusions.
In the closing meeting, which was held between the audit team and the top management of DC. Eva presented two nonconformities that were detected during the audit. Eva stated that the company did not retain documented information regarding its outsourced services for an analysis laboratory and regarding the conducted management reviews. During the closing meeting, the audit team required from DCs top management to come up with corrective action plans within two weeks. Although the top management did not agree with the audit findings, the audit team insisted that the auditee must submit corrective actions within the given time frame in order for the audit activities to continue.
Once the action plans were evaluated, the audit team began preparing the audit report. Eva required from the team to provide accurate descriptions of the audit findings and the audit conclusions. The report was then distributed to all the interested parties involved in the audit, including the certification body Based on the report, the certification body together with Eva, as the audit team leader, made the certification decision.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
The audit team delayed audit activities until DC’s top management submitted their action plans. Is this acceptable?
'XYZ' has already sent to you a list with all documented procedures and work instructions related to the services provided to 'ABC' (a quality manual is not included in the list).
To complete the audit planning which additional information would you ask to XYZ to submit? Select four.
The ISO 9001 clause 5.1.1 states top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to the quality management system.
In the context of the ISO 9001 management system certification, select the one correct description of top management's responsibilities.
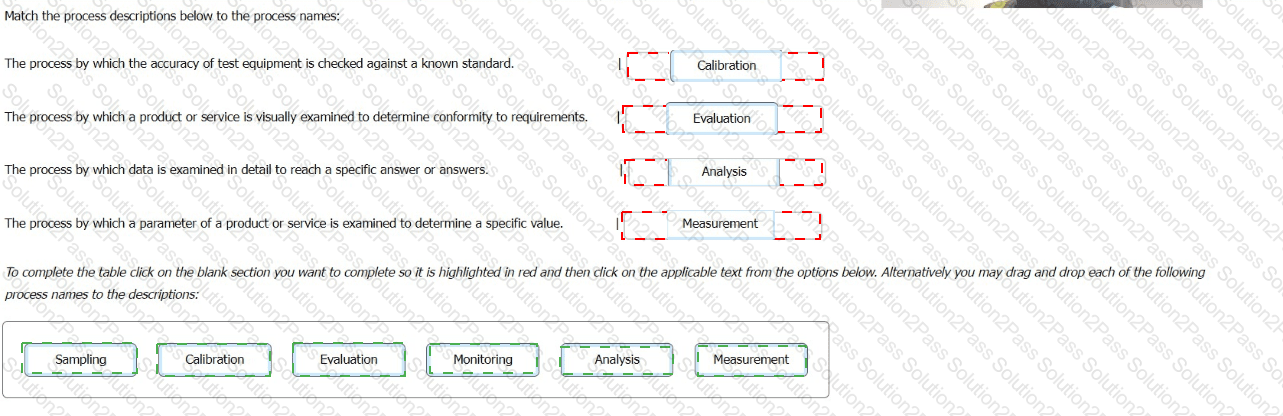
Match the process descriptions below to the process names:

You are conducting a third-party audit to ISO 9001 and the next item on your audit plan is 'internal auditing'.
When reviewing a sample of audit records up to 5 years previously, you find that many contain non-conformance reports and no actions have been taken. You interview the Quality Manager.
You: "I have noted that many of the older files contain non-conformances that have not had any corrective action taken."
Quality Manager: "Because the business is always changing, the departmental managers tell me that the non-conformances are no longer applicable. I made a decision that any non-conformance over 3 years old is automatically closed"
You: "Do you obtain any confirmation beforehand from the appropriate departments that the non-conformances are no longer applicable."
Quality Manager: " No, because they are so old I consider that they are no longer appropriate. Please remember that we take a risk-based approach which means we audit where and when it is considered important to do so.
Select one course of action you would now take from the options.
You are carrying out an audit at an organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organisation offers health and safety training to customers. Training courses are offered either as open courses, delivered at a public venue, or online, or as courses that are tailored to meet specific requirements. The business operates from a single office and those who deliver the training are either full-time employees or subcontractors.
You are interviewing the Training Manager (TM).
You: "What quality objectives apply to the training process?"
TM: "One of the quality objectives we aim for is a 90% minimum exam pass rate for all open training courses."
You: "How do you measure this objective?"
The Training Manager shows you a record on her computer and you see the following:
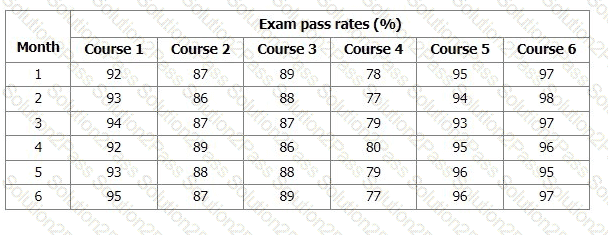
Which two of the following statements are true?
Scenario 2:
Bell is a Canadian food manufacturing company that operates globally. Their main products include nuts, dried fruits, and confections. Bell has always prioritized product quality and has maintained a good reputation for many years. However, the company's production error rate increased significantly, leading to more customer complaints.
To increase efficiency and customer satisfaction, Bell implemented a Quality Management System (QMS) based on ISO 9001. The top management established a QMS implementation team comprising five middle managers from various departments, including Leslie, the quality manager.
Leslie was responsible for assigning responsibilities and authorities for QMS-related roles. He also suggested including a top management representative in the QMS team, but top management declined due to other priorities.
The team defined the QMS scope as:
"The scope of the QMS includes all activities related to food processing."
Leslie established a quality policy and presented it to the team for review before top management approval. Top management also proposed a new strategy for handling customer complaints, requiring biweekly customer surveys to monitor customer perceptions.
Which situation presented in scenario 2 is NOT compliant with ISO 9001?
You are conducting a Stage 1 audit at an organisation that services refrigeration equipment for a large customer base.
The scope of certification is "Provision of refrigeration equipment maintenance and repair services". You are interviewing
the Managing Director to learn more about the organisation and to explore how the requirements for policy, objectives,
and risks and opportunities in ISO 9001 are addressed.
The Managing Director explains that they only use sub-contract refrigeration engineers and do not have any full-time
refrigeration engineers, which helps to optimise overhead costs. The full-time staff employed are essentially a small team
of office staff who process customer enquiries, schedule jobs and process invoices.
The Managing Director adds that the ISO 9001 requirements for competence of personnel extends to both sub-contract
and full-time staff. He also states that the full-time staff are aware of the Quality Policy, objectives and plans to address
risk and opportunities.
You ask if the sub-contract engineers have been informed of the Quality Policy, objectives and plans to address risks and
opportunities, to which the Managing Director replies that this is not applicable as they only use sub-contractors who
operate ISO 9001 certificated quality management systems. The documented information provided to the auditor
confirms this.
Which clause in ISO 9001 is most likely not to have been fulfilled in this instance?
Who would be defined as a witness during a witness audit?
Choose two of the following options:
Scenario 2:
Bell is a Canadian food manufacturing company that operates globally. Their main products include nuts, dried fruits, and confections. Bell has always prioritized product quality and has maintained a good reputation for many years. However, the company's production error rate increased significantly, leading to more customer complaints.
To increase efficiency and customer satisfaction, Bell implemented a Quality Management System (QMS) based on ISO 9001. The top management established a QMS implementation team comprising five middle managers from various departments, including Leslie, the quality manager.
Leslie was responsible for assigning responsibilities and authorities for QMS-related roles. He also suggested including a top management representative in the QMS team, but top management declined due to other priorities.
The team defined the QMS scope as:
"The scope of the QMS includes all activities related to food processing."
Leslie established a quality policy and presented it to the team for review before top management approval. Top management also proposed a new strategy for handling customer complaints, requiring biweekly customer surveys to monitor customer perceptions.
The quality policy was established by Leslie and approved by top management. Is this acceptable? Please refer to scenario 2.
Whistlekleen is a national dry cleaning and laundry company with 50 shops. You are conducting a surveillance audit of the Head Office and are sampling customer complaints. You find that 80% of complaints originate from five shops in the same region. Most of these complaints relate to damage to customer laundry. The Quality Manager tells you that these are the oldest shops in the company. The cleaning equipment needs replacing but the company cannot afford it at the moment. You learn
that the shop managers were told to dismiss most of the claims on the basis of the poor quality of the laundered materials.
On raising the matter with senior management, you are told that there are plans to replace the equipment in these shops over the next five years.
When reviewing the customer complaint file, you find that the organisation is facing a legal dispute with a customer over damage to an expensive cashmere coat.
Select the best option for how this should be handled by the Quality Management System.
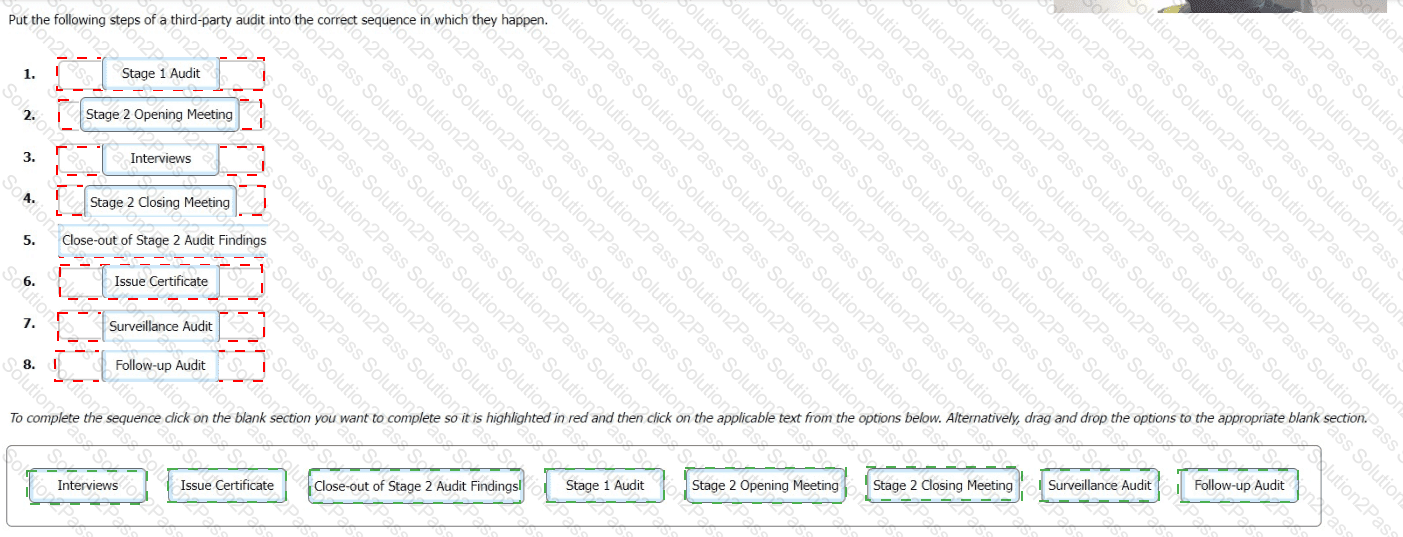
Put the following steps of a third-party audit into the correct sequence in which they happen.
You are carrying out an annual audit at an organisation that has been certificated to ISO 9001 for two years. The organisation offers home security
services. The scope of the quality management system covers alarm installation, alarm servicing, alarm monitoring and response. The business
operates from a single office and employs subcontract installers and service technicians across the country.
You have just completed the opening meeting. You are interviewing the Managing Director (MD).
You: "I would like to gain an understanding of how the quality management system has been supporting your business and its strategic direction."
MD: "We are continuing to face difficult times. The market is extremely competitive, and customers typically look for the least expensive option when
choosing home security services. We have not yet seen any business benefit from our quality management system."
You: "Tell me how you determine external and internal issues."
MD: "We use SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)."
You: "How have the outputs from your SWOT been used?"
Select two of the following audit trails would you take to explore the extent to which the SWOT analysis and the outputs from this
have been used to enable the business to achieve the intended results(s) of its quality management system according to ISO 9001.
 A white background with black text Description automatically generated
A white background with black text Description automatically generated